Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, enhancing security and reducing transaction fees compared to traditional order book systems that rely on centralized platforms for matching buy and sell orders. Order book systems offer liquidity and price transparency but expose users to counterparty risk and higher fees, especially during periods of high market volatility. Explore the advantages and challenges of atomic swaps and order book trading to optimize your cryptocurrency exchange strategy.
Why it is important
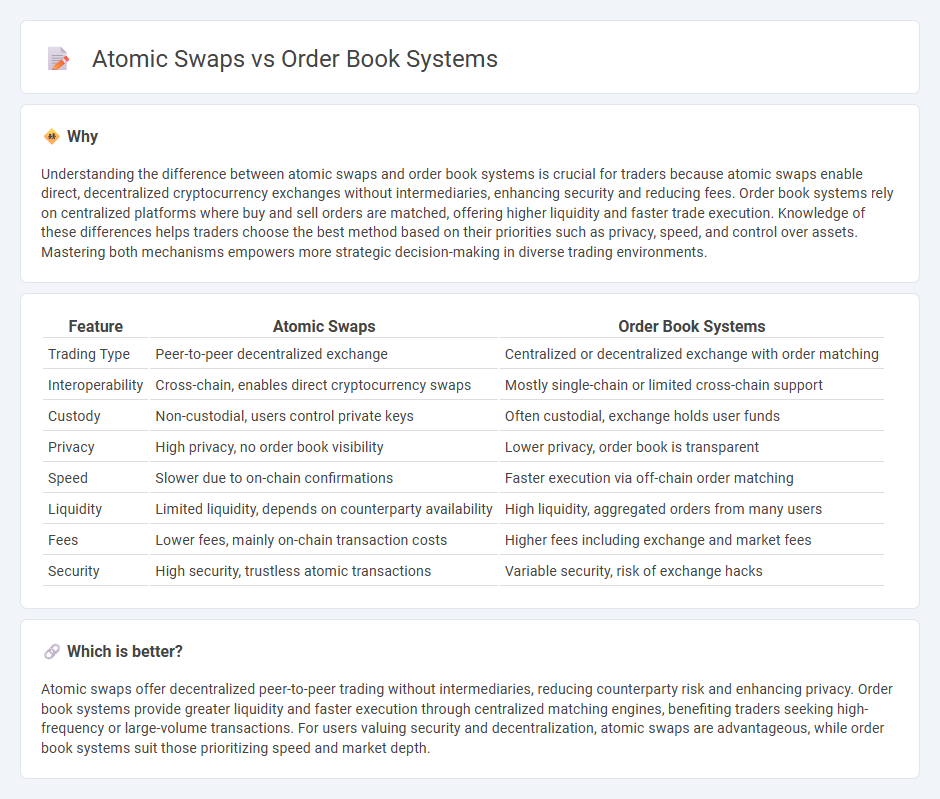
Understanding the difference between atomic swaps and order book systems is crucial for traders because atomic swaps enable direct, decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, enhancing security and reducing fees. Order book systems rely on centralized platforms where buy and sell orders are matched, offering higher liquidity and faster trade execution. Knowledge of these differences helps traders choose the best method based on their priorities such as privacy, speed, and control over assets. Mastering both mechanisms empowers more strategic decision-making in diverse trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Atomic Swaps | Order Book Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Trading Type | Peer-to-peer decentralized exchange | Centralized or decentralized exchange with order matching |
| Interoperability | Cross-chain, enables direct cryptocurrency swaps | Mostly single-chain or limited cross-chain support |
| Custody | Non-custodial, users control private keys | Often custodial, exchange holds user funds |
| Privacy | High privacy, no order book visibility | Lower privacy, order book is transparent |
| Speed | Slower due to on-chain confirmations | Faster execution via off-chain order matching |
| Liquidity | Limited liquidity, depends on counterparty availability | High liquidity, aggregated orders from many users |
| Fees | Lower fees, mainly on-chain transaction costs | Higher fees including exchange and market fees |
| Security | High security, trustless atomic transactions | Variable security, risk of exchange hacks |
Which is better?
Atomic swaps offer decentralized peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries, reducing counterparty risk and enhancing privacy. Order book systems provide greater liquidity and faster execution through centralized matching engines, benefiting traders seeking high-frequency or large-volume transactions. For users valuing security and decentralization, atomic swaps are advantageous, while order book systems suit those prioritizing speed and market depth.
Connection
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, enhancing security and decentralization in trading. Order book systems facilitate the organization and execution of buy and sell orders by matching trades efficiently on centralized and decentralized exchanges. The integration of atomic swaps within order book frameworks allows seamless and trustless cross-chain trading, combining liquidity management with secure asset transfers.
Key Terms
Centralized Exchange
Centralized Exchange (CEX) order book systems rely on a centralized authority to match buy and sell orders, providing high liquidity, fast execution, and a user-friendly interface. Atomic swaps enable trustless peer-to-peer trading across different blockchains without intermediaries but often face challenges like lower speed and limited liquidity in CEX environments. Explore how these mechanisms impact trading efficiency and security in centralized platforms for a deeper understanding.
Decentralization
Order book systems rely on centralized or semi-centralized platforms to match buy and sell orders, which can introduce points of control and potential censorship. Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries, enhancing decentralization and reducing counterparty risk. Explore how these mechanisms impact the future of decentralized finance and cross-chain interoperability.
Settlement
Order book systems centralize settlement by matching buy and sell orders within a single platform, enabling rapid execution and liquidity aggregation. Atomic swaps facilitate decentralized settlement through smart contracts, ensuring trustless cross-chain asset exchanges without intermediaries. Explore the intricacies of each settlement method to understand their impact on trading efficiency and security.
Source and External Links
What is an Order Book, and How Do You Read & Analyze it? - An order book is a system recording all buy and sell orders for an asset, commonly categorized into centralized, decentralized, and limit order books, with centralized ones managed by exchanges like NYSE and Binance, using algorithms to match orders and provide market liquidity and transparency.
What is an Order Book and How Does it Work? - Order books operate as the backbone of financial markets by electronically tallying buy and sell orders arranged by price, using sophisticated algorithms to match orders and ensure trades occur at the best available market prices dynamically.
Order Book Management System for Private Markets - This system provides digital, real-time, and secure order tracking for private investment deals, allowing management of orders, investor indications, and termsheets with features like order limits, approvals, and multi-currency support in a centralized platform.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com