Dark pool activity involves private trading venues where large orders are executed anonymously to minimize market impact, contrasting with market making, which provides liquidity by continuously quoting bid and ask prices on public exchanges. Market makers facilitate smoother price discovery and tighter spreads while dark pools offer institutional investors anonymity and reduced market exposure. Explore the nuances of dark pool trades and market making strategies to enhance your trading insights.
Why it is important
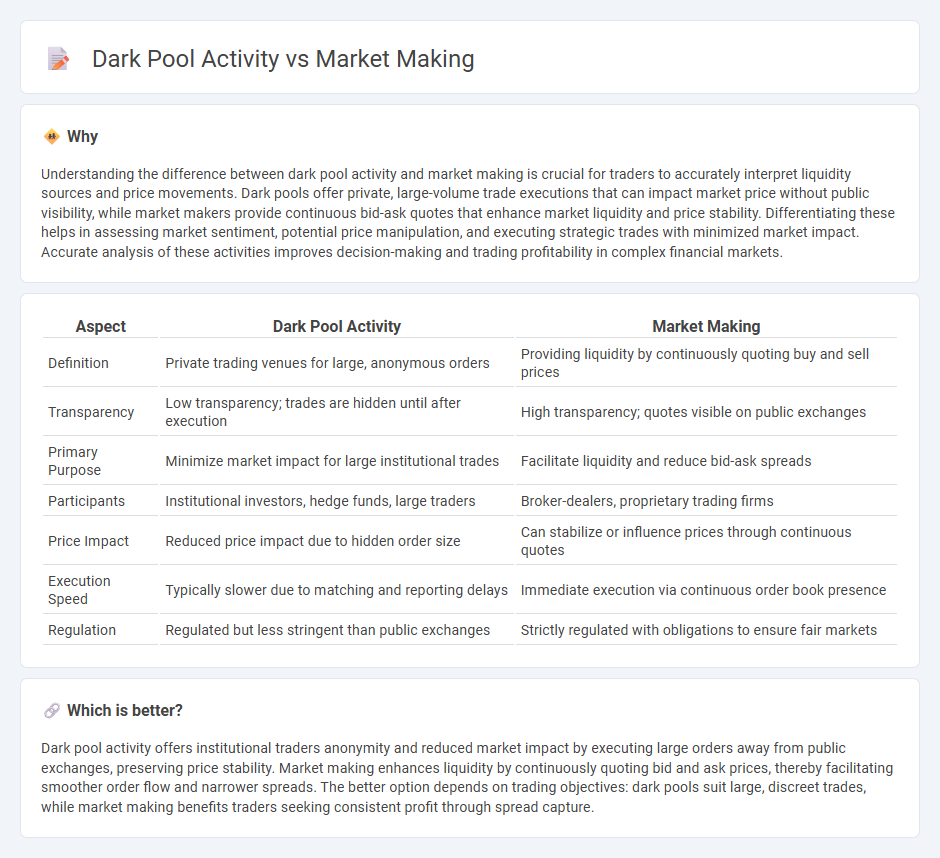
Understanding the difference between dark pool activity and market making is crucial for traders to accurately interpret liquidity sources and price movements. Dark pools offer private, large-volume trade executions that can impact market price without public visibility, while market makers provide continuous bid-ask quotes that enhance market liquidity and price stability. Differentiating these helps in assessing market sentiment, potential price manipulation, and executing strategic trades with minimized market impact. Accurate analysis of these activities improves decision-making and trading profitability in complex financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pool Activity | Market Making |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private trading venues for large, anonymous orders | Providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices |
| Transparency | Low transparency; trades are hidden until after execution | High transparency; quotes visible on public exchanges |
| Primary Purpose | Minimize market impact for large institutional trades | Facilitate liquidity and reduce bid-ask spreads |
| Participants | Institutional investors, hedge funds, large traders | Broker-dealers, proprietary trading firms |
| Price Impact | Reduced price impact due to hidden order size | Can stabilize or influence prices through continuous quotes |
| Execution Speed | Typically slower due to matching and reporting delays | Immediate execution via continuous order book presence |
| Regulation | Regulated but less stringent than public exchanges | Strictly regulated with obligations to ensure fair markets |
Which is better?
Dark pool activity offers institutional traders anonymity and reduced market impact by executing large orders away from public exchanges, preserving price stability. Market making enhances liquidity by continuously quoting bid and ask prices, thereby facilitating smoother order flow and narrower spreads. The better option depends on trading objectives: dark pools suit large, discreet trades, while market making benefits traders seeking consistent profit through spread capture.
Connection
Dark pool activity and market making are interconnected through the provision of liquidity and price discovery in private trading venues. Market makers facilitate trades within dark pools by offering bid and ask prices, enabling large institutional orders to execute with minimal market impact. This interaction helps maintain market efficiency by balancing supply and demand away from public exchanges.
Key Terms
Bid-Ask Spread
Market making involves continuously quoting bid and ask prices to provide liquidity, directly influencing tighter bid-ask spreads and enhancing market efficiency. Dark pool activity, characterized by large, anonymous trades away from public exchanges, typically results in wider bid-ask spreads due to reduced price transparency. Explore how the interaction between market making and dark pool volume shapes liquidity and price discovery in modern trading environments.
Liquidity
Market making significantly enhances liquidity by continuously quoting bid and ask prices, facilitating smoother trade execution and tighter spreads. Dark pool activity, however, provides liquidity without immediate public exposure, minimizing market impact and preserving anonymity for large orders. Explore more on how these mechanisms influence overall market liquidity and trading strategies.
Trade Transparency
Trade transparency significantly impacts market making by providing clearer price signals and reducing information asymmetry, essential for efficient liquidity provision. Dark pool activity, by contrast, limits transparency as trades occur privately, often obscuring market intent and potentially influencing price discovery outside public view. Explore how evolving regulations balance transparency and anonymity in market ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Mastering the Market Maker Trading Strategy | EPAM SolutionsHub - Market makers earn profits primarily through the bid-ask spread by buying at a lower bid price and selling at a higher ask price, while also managing inventory and analyzing order flow to anticipate price movements and maintain liquidity under regulatory constraints.
Market maker: What it is, importance, benefits & examples - StoneX - A market maker is a financial institution that continuously quotes buy (bid) and sell (ask) prices for securities to provide liquidity, profiting from the bid-ask spread and managing risks involved with their inventory.
Market Maker - Definition, Role, How They Work - Market makers are firms or individuals that provide two-sided markets by posting bids and asks, profiting from the spread between these prices while facilitating liquidity and executing principal trades.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com