Bid-ask spread capture involves profiting from the difference between the buying price and selling price in a trade, while maker rebates are incentives provided by exchanges to liquidity providers who place limit orders. Traders utilizing spread capture aim to execute trades within the spread to secure gains, whereas those focusing on maker rebates benefit from reduced trading costs and additional income through exchange rewards. Explore deeper insights on optimizing trading strategies by balancing bid-ask spread capture and maker rebates.
Why it is important
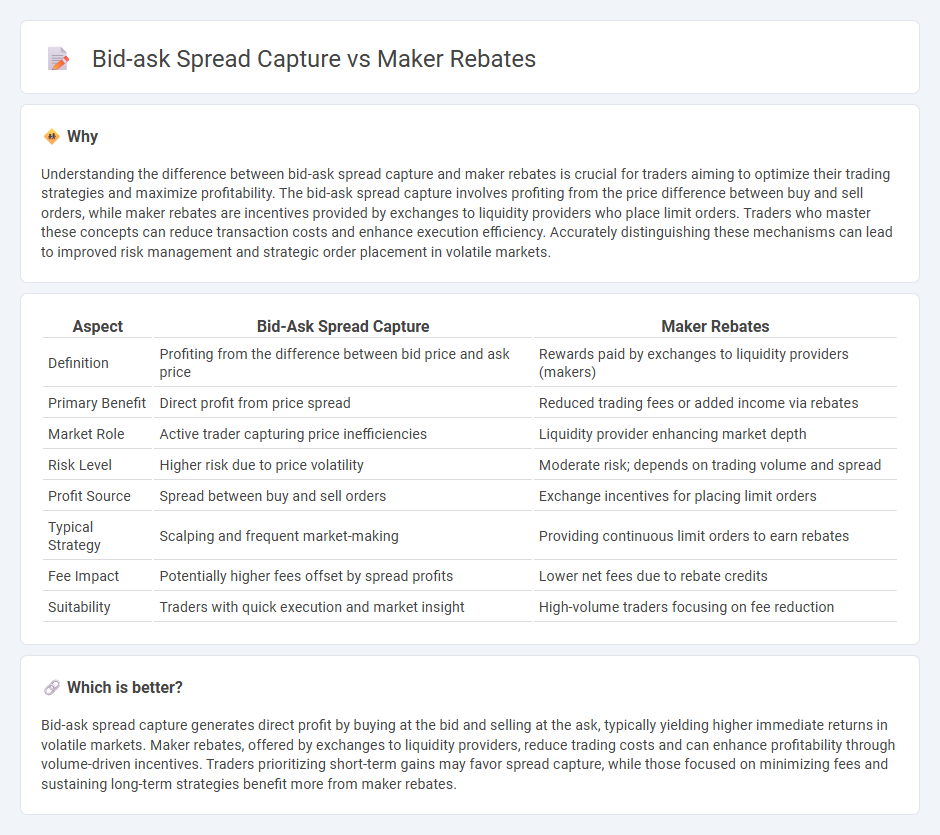
Understanding the difference between bid-ask spread capture and maker rebates is crucial for traders aiming to optimize their trading strategies and maximize profitability. The bid-ask spread capture involves profiting from the price difference between buy and sell orders, while maker rebates are incentives provided by exchanges to liquidity providers who place limit orders. Traders who master these concepts can reduce transaction costs and enhance execution efficiency. Accurately distinguishing these mechanisms can lead to improved risk management and strategic order placement in volatile markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Bid-Ask Spread Capture | Maker Rebates |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profiting from the difference between bid price and ask price | Rewards paid by exchanges to liquidity providers (makers) |
| Primary Benefit | Direct profit from price spread | Reduced trading fees or added income via rebates |
| Market Role | Active trader capturing price inefficiencies | Liquidity provider enhancing market depth |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to price volatility | Moderate risk; depends on trading volume and spread |
| Profit Source | Spread between buy and sell orders | Exchange incentives for placing limit orders |
| Typical Strategy | Scalping and frequent market-making | Providing continuous limit orders to earn rebates |
| Fee Impact | Potentially higher fees offset by spread profits | Lower net fees due to rebate credits |
| Suitability | Traders with quick execution and market insight | High-volume traders focusing on fee reduction |
Which is better?
Bid-ask spread capture generates direct profit by buying at the bid and selling at the ask, typically yielding higher immediate returns in volatile markets. Maker rebates, offered by exchanges to liquidity providers, reduce trading costs and can enhance profitability through volume-driven incentives. Traders prioritizing short-term gains may favor spread capture, while those focused on minimizing fees and sustaining long-term strategies benefit more from maker rebates.
Connection
Bid-ask spread capture occurs when traders profit from the difference between the bid and ask prices in a market, while maker rebates incentivize liquidity providers to post limit orders that tighten this spread. Market makers who add liquidity by placing buy or sell orders at the bid or ask price receive rebates, which effectively reduce their trading costs and enhance profitability. This symbiotic relationship encourages tighter spreads and improves market efficiency by increasing order book depth and reducing transaction costs for traders.
Key Terms
Liquidity provision
Maker rebates incentivize liquidity provision by rewarding limit order placements that add depth to the order book, effectively reducing transaction costs for other traders. Capturing the bid-ask spread involves executing trades at favorable prices within the spread, profiting from the difference between buying and selling prices. Explore how strategic liquidity provision through maker rebates competes and complements bid-ask spread capture in dynamic market environments.
Order book dynamics
Maker rebates provide liquidity by incentivizing limit order placements, directly impacting order book depth and narrowing bid-ask spreads through increased competitive quoting. In contrast, bid-ask spread capture strategies exploit existing order book imbalances to profit from price discrepancies without necessarily improving liquidity. Explore detailed order book dynamics and strategies to optimize trading performance.
Market making strategies
Market making strategies prioritize capturing the bid-ask spread to generate consistent profits by simultaneously posting buy and sell orders. Maker rebates, offered by exchanges as incentives for liquidity providers, can enhance market makers' profitability by offsetting transaction costs and encouraging tighter spreads. Explore detailed comparisons and practical applications of these strategies to optimize your market making approach.
Source and External Links
Maker Program | Vertex Docs - Maker rebates are earned by users who place limit orders (maker trades) and stake a minimum amount of VRTX tokens, with rebates such as 0.35 basis points available depending on the staked tier, regardless of additional eligibility criteria for other rewards.
Introduction to the Market Maker Incentive Program - Bybit - Market Makers on Bybit can earn up to 0.005% maker rebates on Spot and Derivatives trading by participating in the Market Maker Incentive Program, which also offers benefits like exclusive fee rebates and institutional loans.
Maker-Taker Model - QuestDB - The maker-taker model is a common fee structure where liquidity providers (makers) receive rebates for placing resting limit orders, typically around 0.2-0.4 basis points, while takers pay fees for removing liquidity, incentivizing liquidity on exchanges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com