Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading without intermediaries, leveraging smart contracts for secure and trustless transactions across different blockchains. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) facilitate trading through blockchain-based platforms, offering enhanced privacy and reduced counterparty risk by eliminating centralized control. Explore their unique advantages and functionalities to understand which suits your trading strategy best.
Why it is important
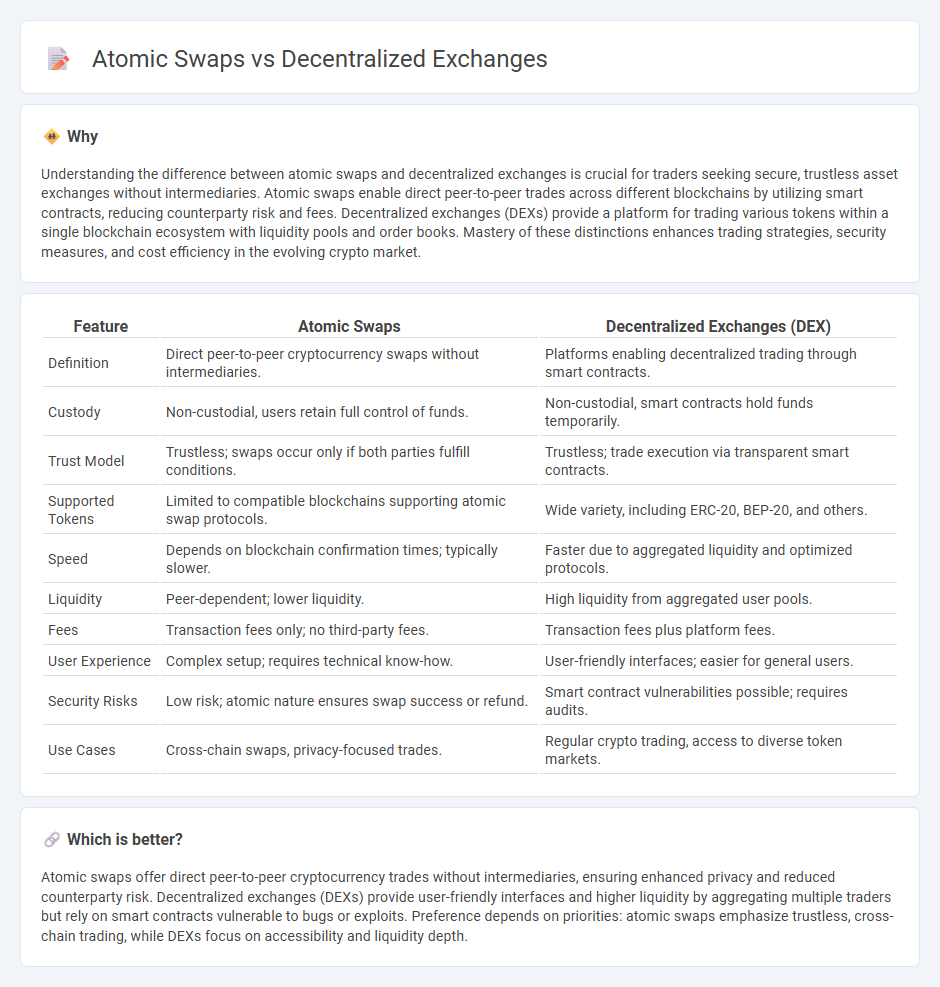
Understanding the difference between atomic swaps and decentralized exchanges is crucial for traders seeking secure, trustless asset exchanges without intermediaries. Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer trades across different blockchains by utilizing smart contracts, reducing counterparty risk and fees. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) provide a platform for trading various tokens within a single blockchain ecosystem with liquidity pools and order books. Mastery of these distinctions enhances trading strategies, security measures, and cost efficiency in the evolving crypto market.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Atomic Swaps | Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency swaps without intermediaries. | Platforms enabling decentralized trading through smart contracts. |
| Custody | Non-custodial, users retain full control of funds. | Non-custodial, smart contracts hold funds temporarily. |
| Trust Model | Trustless; swaps occur only if both parties fulfill conditions. | Trustless; trade execution via transparent smart contracts. |
| Supported Tokens | Limited to compatible blockchains supporting atomic swap protocols. | Wide variety, including ERC-20, BEP-20, and others. |
| Speed | Depends on blockchain confirmation times; typically slower. | Faster due to aggregated liquidity and optimized protocols. |
| Liquidity | Peer-dependent; lower liquidity. | High liquidity from aggregated user pools. |
| Fees | Transaction fees only; no third-party fees. | Transaction fees plus platform fees. |
| User Experience | Complex setup; requires technical know-how. | User-friendly interfaces; easier for general users. |
| Security Risks | Low risk; atomic nature ensures swap success or refund. | Smart contract vulnerabilities possible; requires audits. |
| Use Cases | Cross-chain swaps, privacy-focused trades. | Regular crypto trading, access to diverse token markets. |
Which is better?
Atomic swaps offer direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trades without intermediaries, ensuring enhanced privacy and reduced counterparty risk. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) provide user-friendly interfaces and higher liquidity by aggregating multiple traders but rely on smart contracts vulnerable to bugs or exploits. Preference depends on priorities: atomic swaps emphasize trustless, cross-chain trading, while DEXs focus on accessibility and liquidity depth.
Connection
Atomic swaps enable trustless trading of cryptocurrencies directly between users without intermediaries, forming the core technology behind decentralized exchanges (DEXs). By utilizing smart contracts and cross-chain communication protocols, atomic swaps eliminate the need for centralized custody and reduce counterparty risk in decentralized trading environments. This integration fosters enhanced liquidity and seamless cross-chain asset exchanges, driving the evolution of decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems.
Key Terms
Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools in decentralized exchanges aggregate user funds to enable seamless token swaps with minimal slippage and continuous market availability. Atomic swaps facilitate direct peer-to-peer token exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries but typically lack pooled liquidity, resulting in potential delays or higher costs for large trades. Explore how liquidity pools and atomic swaps impact decentralized trading efficiency and user experience.
Smart Contracts
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) utilize smart contracts to automate trading, custody, and settlement processes directly on the blockchain, enhancing security and transparency without intermediaries. Atomic swaps leverage smart contracts to enable trustless cross-chain token exchanges by ensuring transactions either complete fully or not at all, preventing counterparty risk. Discover how smart contracts revolutionize trustless trading in both DEXs and atomic swaps for seamless cryptocurrency transactions.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) facilitate secure trading of digital assets without intermediaries, utilizing smart contracts to manage orders on compatible blockchains. Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cross-chain transactions by executing simultaneous trades across different blockchain networks, enhancing interoperability without centralized control. Explore the benefits and technical intricacies of each method to understand their impact on seamless cross-chain asset exchange.
Source and External Links
Best DEX Decentralized exchanges - DeFi Prime - Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are cryptocurrency exchanges operating without a central authority, enabling peer-to-peer token trades through various platforms like GMX, 1inch, and Balancer that offer different features such as low fees, liquidity pools, and leverage trading directly from users' wallets.
What is a DEX? - Coinbase - A DEX is a peer-to-peer marketplace where cryptocurrency trades occur directly on the blockchain via smart contracts and liquidity pools without intermediaries, providing trustless and transparent trading of crypto tokens rather than fiat, contrasting centralized exchanges that handle orders and custody assets internally.
What Is a DEX? Decentralized Exchange Platforms - Gemini - Decentralized exchanges are non-custodial peer-to-peer crypto trading platforms where users retain control of their private keys, and trades are executed automatically through smart contracts on the blockchain, offering an alternative to centralized exchanges with benefits and trade-offs regarding control, security, and transaction trustlessness.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com