Front running and layering are two distinct trading strategies used in financial markets to gain an advantage by exploiting information asymmetry or market manipulation. Front running involves a trader executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending large transactions, aiming to profit from anticipated price movements. Explore the differences between front running and layering to understand their impact on market integrity and trading ethics.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between front running and layering is crucial for traders to avoid illegal market manipulation practices and comply with financial regulations. Front running involves executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending trades, giving unfair advantage, while layering manipulates market prices through deceptive order placements without the intent to trade. Identifying these activities protects market integrity and ensures fair trading conditions for all participants. Mastery of these distinctions helps traders maintain ethical standards and avoid legal penalties.
Comparison Table
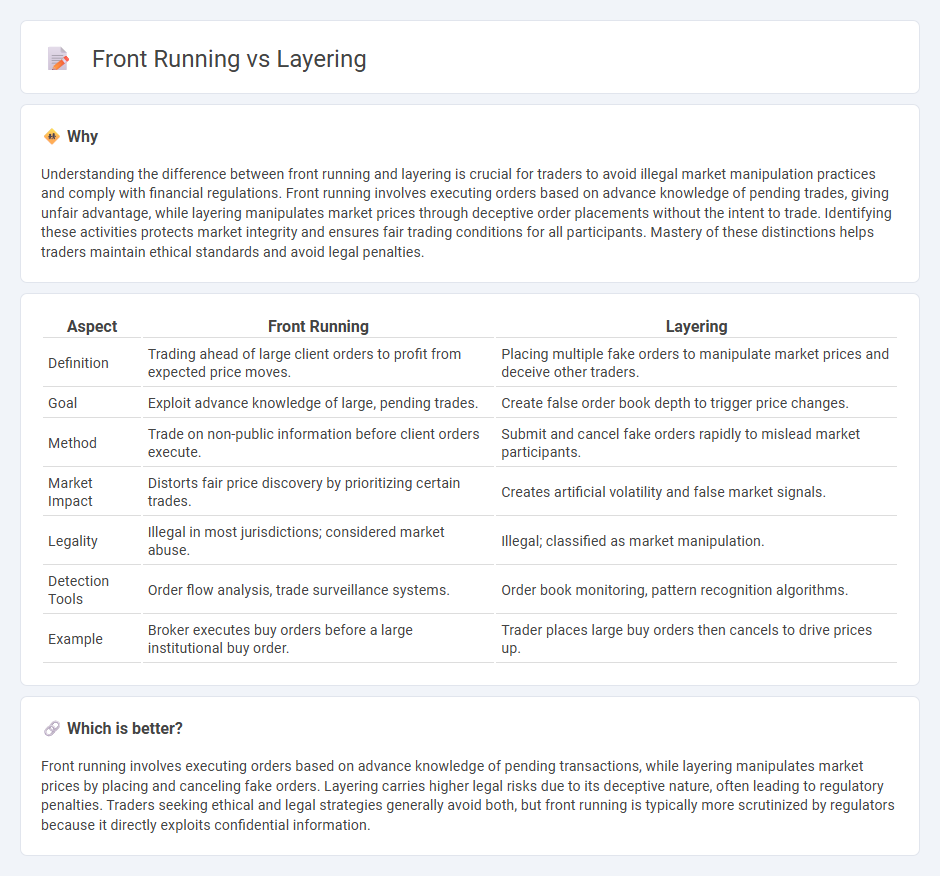
| Aspect | Front Running | Layering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading ahead of large client orders to profit from expected price moves. | Placing multiple fake orders to manipulate market prices and deceive other traders. |
| Goal | Exploit advance knowledge of large, pending trades. | Create false order book depth to trigger price changes. |
| Method | Trade on non-public information before client orders execute. | Submit and cancel fake orders rapidly to mislead market participants. |
| Market Impact | Distorts fair price discovery by prioritizing certain trades. | Creates artificial volatility and false market signals. |
| Legality | Illegal in most jurisdictions; considered market abuse. | Illegal; classified as market manipulation. |
| Detection Tools | Order flow analysis, trade surveillance systems. | Order book monitoring, pattern recognition algorithms. |
| Example | Broker executes buy orders before a large institutional buy order. | Trader places large buy orders then cancels to drive prices up. |
Which is better?
Front running involves executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending transactions, while layering manipulates market prices by placing and canceling fake orders. Layering carries higher legal risks due to its deceptive nature, often leading to regulatory penalties. Traders seeking ethical and legal strategies generally avoid both, but front running is typically more scrutinized by regulators because it directly exploits confidential information.
Connection
Front running and layering are connected through their manipulation of market orders to exploit price movements. Front running involves placing orders ahead of large pending transactions to benefit from anticipated price changes, while layering places multiple fake orders to create false market depth and mislead other traders. Both tactics disrupt fair market conditions and are considered illegal forms of market manipulation.
Key Terms
Order Book
Layering involves placing multiple false orders on one side of the order book to manipulate market perceptions and create artificial demand or supply, whereas front running exploits advance knowledge of large orders to execute trades ahead, benefiting from subsequent price movements. Both tactics distort the order book's true liquidity and depth, impacting price discovery and market integrity. Explore more about these market manipulation techniques and their detection methods in order book analysis.
Execution Priority
Layering manipulates execution priority by placing multiple non-genuine limit orders to create a false impression of demand or supply, influencing market price movements. Front running exploits privileged access to order information, allowing traders to execute orders ahead of large pending transactions to profit from anticipated price changes. Explore the detailed mechanisms of these strategies and their regulatory implications.
Market Manipulation
Layering involves placing a series of non-bona fide orders to create misleading market depth and manipulate prices before canceling them, while front running exploits prior knowledge of large pending orders to trade ahead and gain unfair profits. Both techniques disrupt market integrity by fostering artificial price movements and eroding fair trading conditions. Explore more about regulatory measures and detection methodologies targeting these manipulative practices.
Source and External Links
Layering Propagation for the Home Gardener - Layering is a plant propagation technique where a new plant forms roots while still attached to the mother plant, with methods including tip, simple, compound, mound, and air layering suitable for various plants like blackberries, roses, and vines.
Mastering the Art of Layering - Layering in fashion is a technique to create depth, texture, and dimension in an outfit by combining base layers with sweaters, cardigans, or scarves to build stylish looks for any occasion.
Layering - Layering as a propagation method works well for plants that root poorly from cuttings, involving bending shoots to the soil, wounding them, applying rooting hormone, and covering with soil until new roots develop over months.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com