Social sentiment analysis trading leverages real-time public opinion and market mood extracted from social media platforms, news, and forums to anticipate price movements. Quantitative trading relies on mathematical models, statistical analysis, and historical data to identify trading opportunities and execute automated strategies. Discover deeper insights into how these distinct approaches can enhance your trading performance.
Why it is important
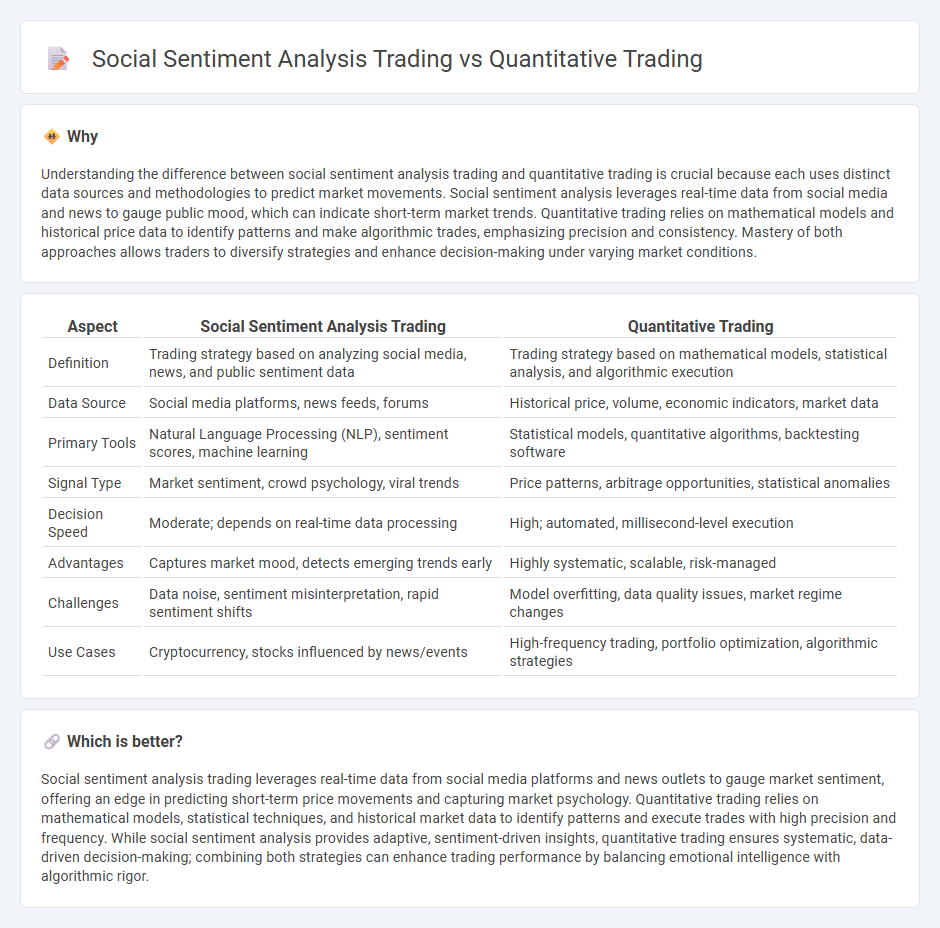
Understanding the difference between social sentiment analysis trading and quantitative trading is crucial because each uses distinct data sources and methodologies to predict market movements. Social sentiment analysis leverages real-time data from social media and news to gauge public mood, which can indicate short-term market trends. Quantitative trading relies on mathematical models and historical price data to identify patterns and make algorithmic trades, emphasizing precision and consistency. Mastery of both approaches allows traders to diversify strategies and enhance decision-making under varying market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Social Sentiment Analysis Trading | Quantitative Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading strategy based on analyzing social media, news, and public sentiment data | Trading strategy based on mathematical models, statistical analysis, and algorithmic execution |
| Data Source | Social media platforms, news feeds, forums | Historical price, volume, economic indicators, market data |
| Primary Tools | Natural Language Processing (NLP), sentiment scores, machine learning | Statistical models, quantitative algorithms, backtesting software |
| Signal Type | Market sentiment, crowd psychology, viral trends | Price patterns, arbitrage opportunities, statistical anomalies |
| Decision Speed | Moderate; depends on real-time data processing | High; automated, millisecond-level execution |
| Advantages | Captures market mood, detects emerging trends early | Highly systematic, scalable, risk-managed |
| Challenges | Data noise, sentiment misinterpretation, rapid sentiment shifts | Model overfitting, data quality issues, market regime changes |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrency, stocks influenced by news/events | High-frequency trading, portfolio optimization, algorithmic strategies |
Which is better?
Social sentiment analysis trading leverages real-time data from social media platforms and news outlets to gauge market sentiment, offering an edge in predicting short-term price movements and capturing market psychology. Quantitative trading relies on mathematical models, statistical techniques, and historical market data to identify patterns and execute trades with high precision and frequency. While social sentiment analysis provides adaptive, sentiment-driven insights, quantitative trading ensures systematic, data-driven decision-making; combining both strategies can enhance trading performance by balancing emotional intelligence with algorithmic rigor.
Connection
Social sentiment analysis trading leverages real-time data from social media and news platforms to gauge market mood, which directly influences quantitative trading models by providing sentiment indicators that improve predictive accuracy. Quantitative trading employs mathematical algorithms and statistical techniques that integrate these sentiment-derived signals to optimize trade timing and asset selection. This synergy enhances decision-making efficiency and risk management in automated trading systems.
Key Terms
Algorithmic Models
Quantitative trading relies on algorithmic models that utilize historical price data and statistical techniques to identify profitable trading opportunities through pattern recognition and risk management. Social sentiment analysis trading integrates natural language processing algorithms to gauge market sentiment from social media, news, and other textual data sources, influencing trade decisions based on collective investor mood. Explore the strengths and limitations of algorithmic models in both approaches to optimize your trading strategy.
Sentiment Data
Quantitative trading leverages mathematical models and historical price data to execute trades, while social sentiment analysis trading focuses on interpreting real-time sentiment data from social media, news, and forums to predict market movements. Sentiment data, derived from natural language processing (NLP) algorithms, captures investor emotions and public opinion, providing a complementary perspective to traditional quantitative indicators. Discover how integrating sentiment data enhances trading strategies by exploring advanced sentiment analysis techniques and analytics tools.
Backtesting
Backtesting in quantitative trading involves using historical price and volume data to validate algorithmic strategies by measuring performance metrics like Sharpe ratio and drawdown. In social sentiment analysis trading, backtesting incorporates sentiment scores derived from social media, news, and forums to predict market reactions, requiring natural language processing and sentiment quantification models. Explore the key methods and tools that enhance accuracy in backtesting for both trading strategies.
Source and External Links
How To Become a Quantitative Trader in 4 Steps (With Skills) - Indeed - A quantitative trader, or quant, uses mathematical models and large data analysis to identify and capitalize on profitable trading opportunities, often leveraging algorithmic and high-frequency trading techniques.
Quantitative analysis (finance) - Wikipedia - Quantitative trading involves using mathematical and statistical methods to analyze financial markets, developing strategies such as statistical arbitrage, algorithmic, and electronic trading, commonly practiced by specialized finance professionals known as quants.
Quantitative Trader - Jane Street - Quantitative traders work with proprietary models to trade efficiently on pricing inefficiencies, employing technology and collaborative problem-solving in a trading environment that executes millions of trades daily without requiring prior finance experience.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com