Microstructure modeling focuses on the intricate mechanisms of order flow, bid-ask spreads, and price formation within financial markets to optimize trade execution. Inventory risk modeling addresses the management of asset holdings and potential losses due to market volatility, aiming to balance profit opportunities with exposure limits. Discover how combining these approaches can enhance trading strategies and risk management.
Why it is important
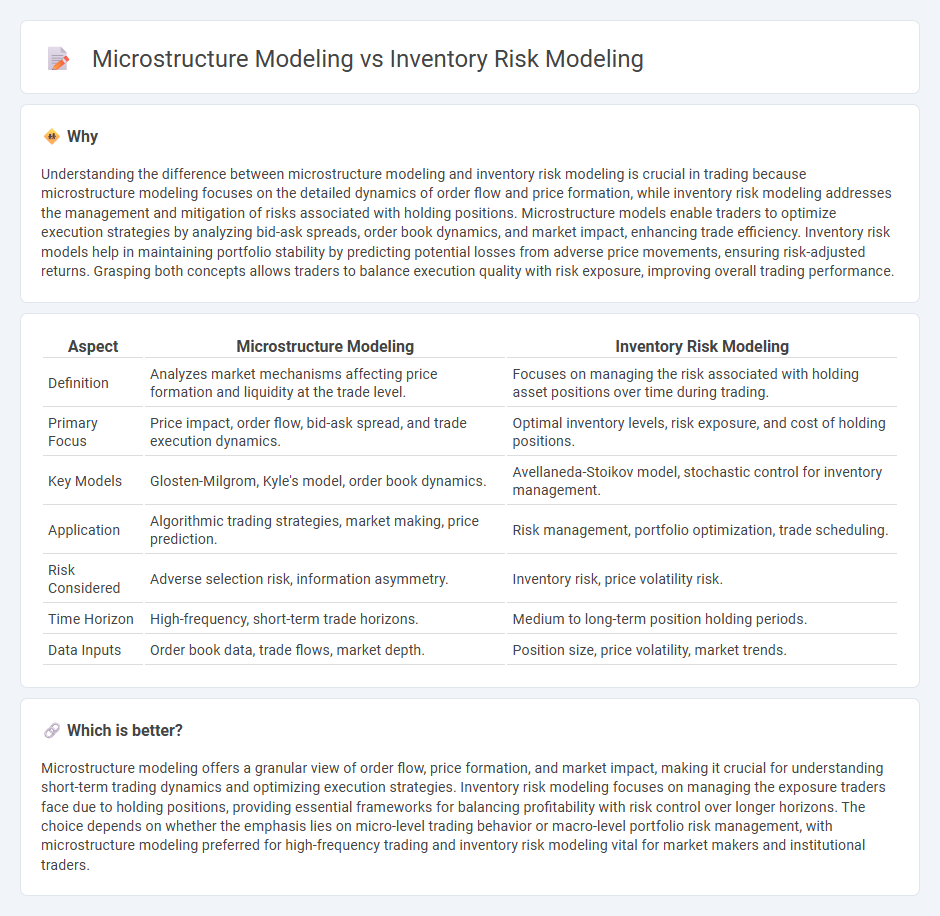
Understanding the difference between microstructure modeling and inventory risk modeling is crucial in trading because microstructure modeling focuses on the detailed dynamics of order flow and price formation, while inventory risk modeling addresses the management and mitigation of risks associated with holding positions. Microstructure models enable traders to optimize execution strategies by analyzing bid-ask spreads, order book dynamics, and market impact, enhancing trade efficiency. Inventory risk models help in maintaining portfolio stability by predicting potential losses from adverse price movements, ensuring risk-adjusted returns. Grasping both concepts allows traders to balance execution quality with risk exposure, improving overall trading performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microstructure Modeling | Inventory Risk Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes market mechanisms affecting price formation and liquidity at the trade level. | Focuses on managing the risk associated with holding asset positions over time during trading. |
| Primary Focus | Price impact, order flow, bid-ask spread, and trade execution dynamics. | Optimal inventory levels, risk exposure, and cost of holding positions. |
| Key Models | Glosten-Milgrom, Kyle's model, order book dynamics. | Avellaneda-Stoikov model, stochastic control for inventory management. |
| Application | Algorithmic trading strategies, market making, price prediction. | Risk management, portfolio optimization, trade scheduling. |
| Risk Considered | Adverse selection risk, information asymmetry. | Inventory risk, price volatility risk. |
| Time Horizon | High-frequency, short-term trade horizons. | Medium to long-term position holding periods. |
| Data Inputs | Order book data, trade flows, market depth. | Position size, price volatility, market trends. |
Which is better?
Microstructure modeling offers a granular view of order flow, price formation, and market impact, making it crucial for understanding short-term trading dynamics and optimizing execution strategies. Inventory risk modeling focuses on managing the exposure traders face due to holding positions, providing essential frameworks for balancing profitability with risk control over longer horizons. The choice depends on whether the emphasis lies on micro-level trading behavior or macro-level portfolio risk management, with microstructure modeling preferred for high-frequency trading and inventory risk modeling vital for market makers and institutional traders.
Connection
Microstructure modeling analyzes the detailed processes within financial markets, including order flow and price formation, which directly impact liquidity and trading costs. Inventory risk modeling focuses on the risks traders face from holding assets amid price fluctuations, influenced by market microstructure dynamics. These models connect by capturing how order execution and market depth affect traders' inventory decisions and risk management strategies in high-frequency trading environments.
Key Terms
**Inventory Risk Modeling:**
Inventory risk modeling quantifies the potential losses traders face due to holding inventory in volatile markets, employing stochastic processes and dynamic optimization techniques to manage price impact and adverse selection. It integrates market liquidity measures, order flow dynamics, and price volatility to minimize costs associated with holding positions over time. Explore detailed methodologies and applications to enhance risk management strategies in high-frequency trading environments.
Position Limits
Inventory risk modeling prioritizes managing position limits to mitigate financial exposure by quantifying potential losses and capital requirements based on asset holdings. Microstructure modeling examines market mechanisms and order flows, incorporating position limits to analyze their impact on liquidity, price dynamics, and trading strategies. Explore deeper to understand how these approaches influence risk control and market behavior under varying regulatory constraints.
Risk Aversion
Inventory risk modeling centers on quantifying and managing the risk that a trader's inventory will lead to financial losses due to price fluctuations, particularly emphasizing how risk aversion influences optimal inventory levels and trading strategies. Microstructure modeling examines price formation and order book dynamics, analyzing how risk-averse traders adjust order submissions and cancellations in response to market signals to minimize adverse selection and inventory risks. Explore further to understand the nuanced impact of risk aversion in shaping both inventory risk management and market microstructure behaviors.
Source and External Links
Risk Aversion in Inventory Management - This paper proposes a framework that incorporates risk aversion into multiperiod inventory and pricing models, showing optimal policies that consider the decision maker's risk tolerance and possible financial hedging to manage inventory risk effectively.
What is Inventory Risk? + Management and Solutions - ShipBob - Inventory risk refers to the chance that products may not sell or lose value, with key causes like improper demand forecasting and product shelf life, and can be managed through data-driven software that improves inventory planning and demand prediction.
Understanding Inventory Risk: What It Is and How To Manage It - Inventory risk is the uncertainty in product availability and demand that can cause overstock or stockouts, and managing it requires balancing inventory levels to optimize supply and demand for reducing financial losses and improving customer satisfaction.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com