Delta hedging involves managing the directional risk of an option by offsetting changes in the underlying asset's price to maintain a neutral position. Gamma hedging focuses on controlling the rate of change of the delta itself, addressing the curvature risk associated with large price movements in the underlying. Explore detailed strategies and practical applications to enhance your risk management techniques in options trading.
Why it is important
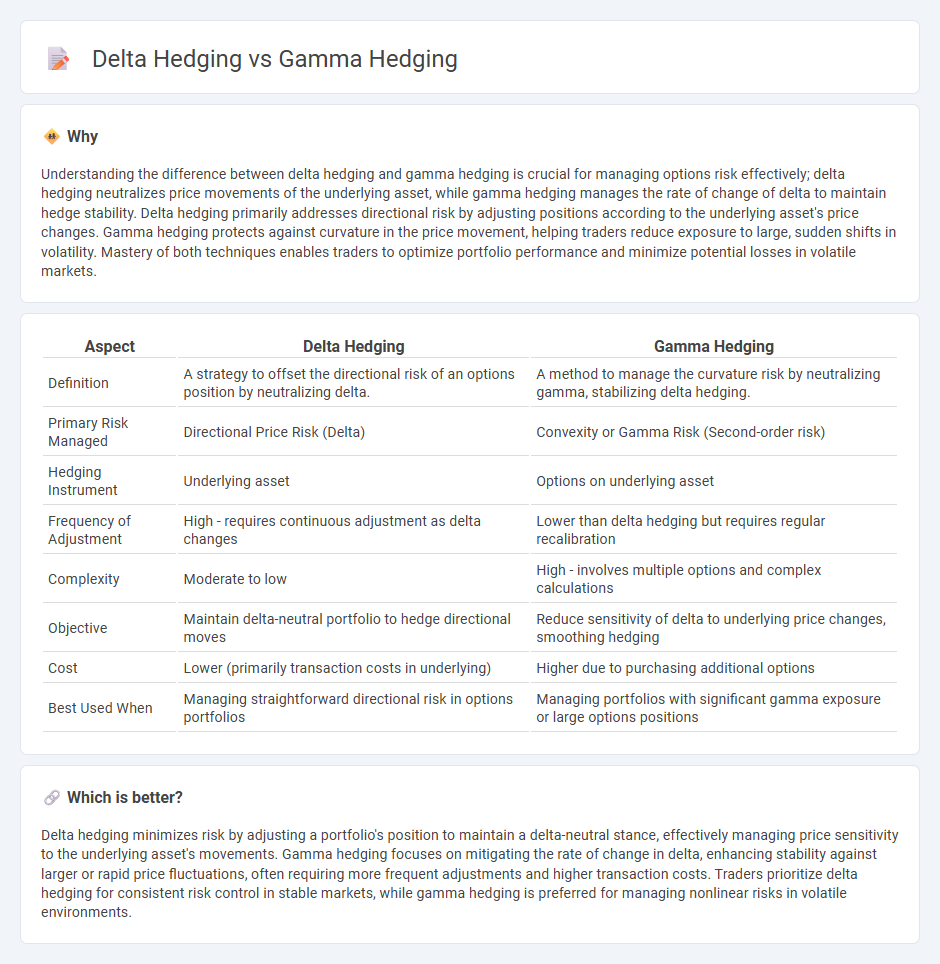
Understanding the difference between delta hedging and gamma hedging is crucial for managing options risk effectively; delta hedging neutralizes price movements of the underlying asset, while gamma hedging manages the rate of change of delta to maintain hedge stability. Delta hedging primarily addresses directional risk by adjusting positions according to the underlying asset's price changes. Gamma hedging protects against curvature in the price movement, helping traders reduce exposure to large, sudden shifts in volatility. Mastery of both techniques enables traders to optimize portfolio performance and minimize potential losses in volatile markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Delta Hedging | Gamma Hedging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A strategy to offset the directional risk of an options position by neutralizing delta. | A method to manage the curvature risk by neutralizing gamma, stabilizing delta hedging. |
| Primary Risk Managed | Directional Price Risk (Delta) | Convexity or Gamma Risk (Second-order risk) |
| Hedging Instrument | Underlying asset | Options on underlying asset |
| Frequency of Adjustment | High - requires continuous adjustment as delta changes | Lower than delta hedging but requires regular recalibration |
| Complexity | Moderate to low | High - involves multiple options and complex calculations |
| Objective | Maintain delta-neutral portfolio to hedge directional moves | Reduce sensitivity of delta to underlying price changes, smoothing hedging |
| Cost | Lower (primarily transaction costs in underlying) | Higher due to purchasing additional options |
| Best Used When | Managing straightforward directional risk in options portfolios | Managing portfolios with significant gamma exposure or large options positions |
Which is better?
Delta hedging minimizes risk by adjusting a portfolio's position to maintain a delta-neutral stance, effectively managing price sensitivity to the underlying asset's movements. Gamma hedging focuses on mitigating the rate of change in delta, enhancing stability against larger or rapid price fluctuations, often requiring more frequent adjustments and higher transaction costs. Traders prioritize delta hedging for consistent risk control in stable markets, while gamma hedging is preferred for managing nonlinear risks in volatile environments.
Connection
Delta hedging and gamma hedging are interconnected risk management strategies used to mitigate the exposure of options portfolios to price movements of the underlying asset. Delta hedging involves adjusting the position to maintain a neutral delta, while gamma hedging focuses on controlling the rate of change of delta by using additional derivatives to stabilize portfolio sensitivity. Effective integration of delta and gamma hedging allows traders to maintain more precise control over directional risk and the curvature risk of options positions.
Key Terms
Delta
Delta hedging involves maintaining a neutral position by offsetting the delta risk of an option portfolio, thereby minimizing sensitivity to small price movements in the underlying asset. Gamma hedging complements this by targeting the gamma exposure to stabilize delta over larger price changes, but delta remains the primary metric for immediate risk management. Explore deeper insights into how delta hedging forms the foundation of effective options risk strategies.
Gamma
Gamma hedging involves managing the rate of change of an option's delta to maintain a stable portfolio sensitivity as the underlying asset price fluctuates. Unlike delta hedging, which neutralizes directional exposure by adjusting for the first derivative of the option price, gamma hedging targets the second derivative, reducing the risk from large price movements. Explore the intricacies of gamma hedging strategies and their impact on dynamic risk management.
Option Position
Gamma hedging involves managing the rate of change of delta in an option position to maintain a stable hedge as the underlying asset price fluctuates, while delta hedging focuses on neutralizing the immediate price risk by balancing the delta exposure. Option traders implement gamma hedging by frequently adjusting their delta hedges to control curvature risk, whereas delta hedging requires fewer adjustments but is less effective during volatile markets. Explore more about how these dynamic hedging strategies impact option portfolio risk management and trading performance.
Source and External Links
Delta Hedging vs Gamma Hedging - QuestDB - Gamma hedging is a dynamic risk management strategy in options trading that manages the rate of change in delta itself, using options to counteract gamma exposure and providing more comprehensive protection against market movements beyond delta hedging.
Gamma Options: What is Gamma in Options Trading? - tastylive - Gamma hedging involves maintaining delta hedges as the underlying asset price changes, focusing on managing how delta itself changes with price moves, and is typically used alongside delta-neutral strategies to reduce portfolio gamma risk.
Deep Gamma Hedging - arXiv - Gamma hedging replicates derivatives by using multiple instruments to make a portfolio gamma neutral, balancing gamma exposure with one option while adjusting delta neutrality with another.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com