Order book imbalance measures the difference between buy and sell orders at various price levels, providing insight into market sentiment and potential price movements. VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) represents the average trading price throughout the day, weighted by volume, serving as a benchmark for trade execution quality. Explore the relationship between order book imbalance and VWAP to enhance trading strategies and market timing.
Why it is important
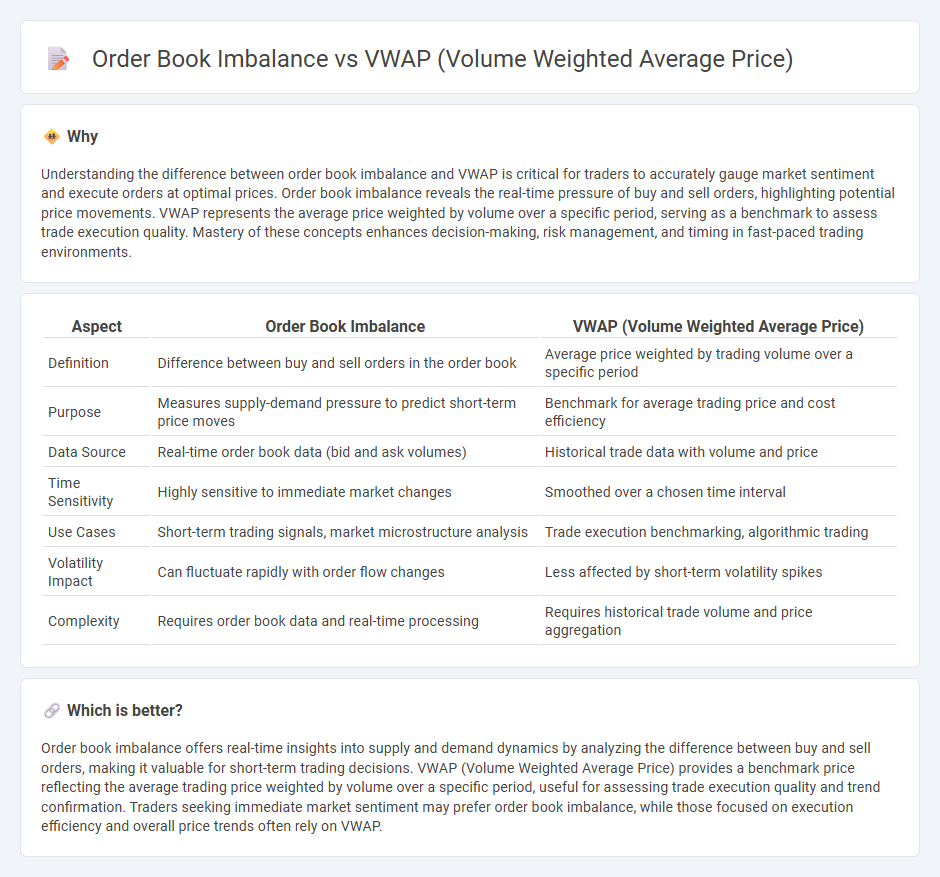
Understanding the difference between order book imbalance and VWAP is critical for traders to accurately gauge market sentiment and execute orders at optimal prices. Order book imbalance reveals the real-time pressure of buy and sell orders, highlighting potential price movements. VWAP represents the average price weighted by volume over a specific period, serving as a benchmark to assess trade execution quality. Mastery of these concepts enhances decision-making, risk management, and timing in fast-paced trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Order Book Imbalance | VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Difference between buy and sell orders in the order book | Average price weighted by trading volume over a specific period |
| Purpose | Measures supply-demand pressure to predict short-term price moves | Benchmark for average trading price and cost efficiency |
| Data Source | Real-time order book data (bid and ask volumes) | Historical trade data with volume and price |
| Time Sensitivity | Highly sensitive to immediate market changes | Smoothed over a chosen time interval |
| Use Cases | Short-term trading signals, market microstructure analysis | Trade execution benchmarking, algorithmic trading |
| Volatility Impact | Can fluctuate rapidly with order flow changes | Less affected by short-term volatility spikes |
| Complexity | Requires order book data and real-time processing | Requires historical trade volume and price aggregation |
Which is better?
Order book imbalance offers real-time insights into supply and demand dynamics by analyzing the difference between buy and sell orders, making it valuable for short-term trading decisions. VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) provides a benchmark price reflecting the average trading price weighted by volume over a specific period, useful for assessing trade execution quality and trend confirmation. Traders seeking immediate market sentiment may prefer order book imbalance, while those focused on execution efficiency and overall price trends often rely on VWAP.
Connection
Order book imbalance reflects the disparity between buy and sell orders, signaling potential price movements, while VWAP provides the average trading price weighted by volume over a specific period. Traders analyze order book imbalance to anticipate short-term market pressure, using VWAP as a benchmark to assess execution quality and identify optimal entry or exit points. Combining order book imbalance with VWAP enhances trading strategies by aligning supply-demand dynamics with volume-based price levels for improved decision-making.
Key Terms
Liquidity
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) represents the average price of a security weighted by trading volume, serving as a critical benchmark for assessing execution quality and market liquidity. Order book imbalance measures the difference between buy and sell orders, providing insights into supply-demand dynamics and potential price movements in high-frequency trading contexts. Explore the nuances of VWAP and order book imbalance to enhance your strategies for liquidity management and optimal trade execution.
Market Impact
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) provides a benchmark for the average price at which a security is traded, weighted by volume, reflecting the true cost of executing large orders over a period; order book imbalance measures the disparity between buy and sell orders, indicating potential supply-demand pressure and short-term price movements. Market impact refers to the effect large trades have on price, where significant deviations from VWAP or skewed order book imbalance can signal liquidity constraints and increased trading costs. Explore how integrating VWAP strategies with real-time order book imbalance analysis can optimize execution and minimize market impact.
Price Discovery
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) consolidates trading volume and price to provide a benchmark reflecting the average price at which a security traded throughout the day, highlighting liquidity and execution quality. Order book imbalance measures the difference between buy and sell orders at various price levels, offering real-time insights into market pressure and potential price movements. Explore the nuances of how VWAP and order book imbalance interact to enhance effective price discovery strategies.
Source and External Links
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) - TradingView - VWAP is a technical analysis tool measuring the average price weighted by volume, primarily used with intraday charts to gauge the general direction of prices and calculated by dividing the cumulative typical price-volume products by cumulative volume.
Volume Weighted Adjusted Price (VWAP) - Corporate Finance Institute - VWAP is the average price of a stock weighted by total trading volume, calculated intraday, and used by investors as a benchmark to compare current stock prices for better timing of trades.
Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP) - ChartSchool - VWAP equals the dollar value of all trading periods divided by total volume for the day, typically calculated from tick or intraday data, and used mostly for intraday trading analysis rather than longer periods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com