Delta hedging is a risk management strategy focusing on neutralizing the directional risk of an options portfolio by balancing its delta exposure. Dynamic hedging, a more comprehensive technique, continuously adjusts the hedge ratio as market conditions and underlying asset prices fluctuate. Explore the nuances of these hedging methods to optimize your trading strategy and risk mitigation.
Why it is important
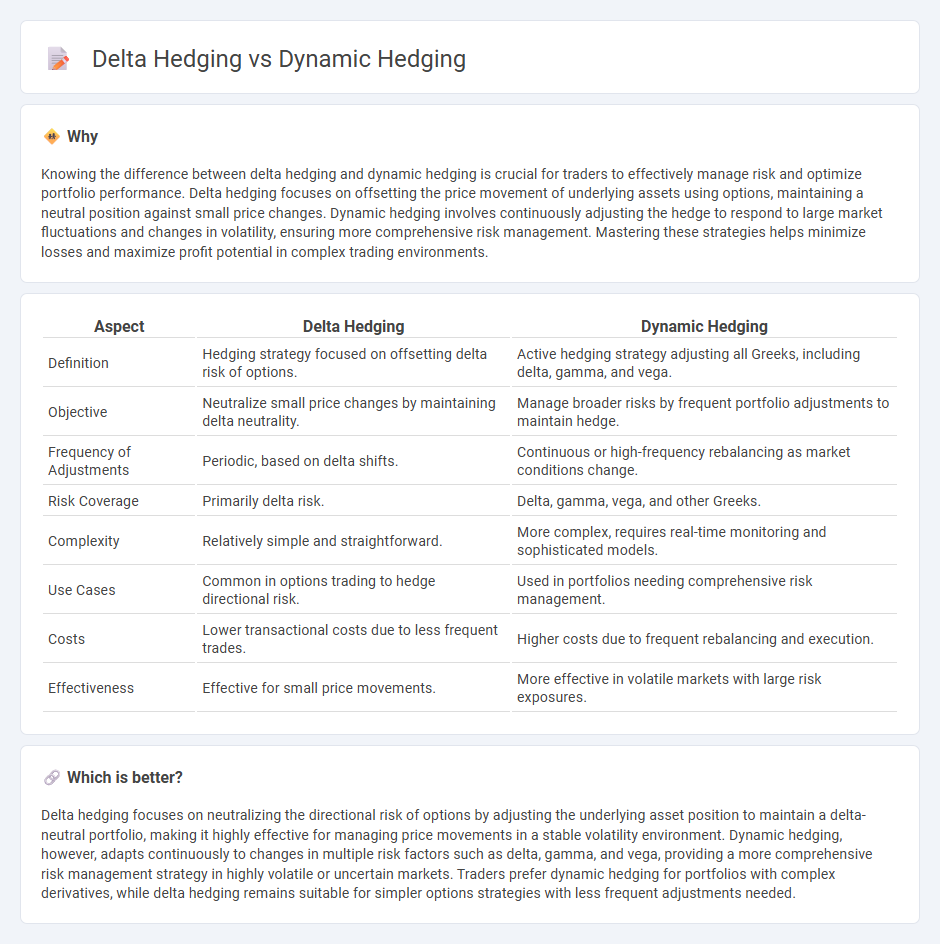
Knowing the difference between delta hedging and dynamic hedging is crucial for traders to effectively manage risk and optimize portfolio performance. Delta hedging focuses on offsetting the price movement of underlying assets using options, maintaining a neutral position against small price changes. Dynamic hedging involves continuously adjusting the hedge to respond to large market fluctuations and changes in volatility, ensuring more comprehensive risk management. Mastering these strategies helps minimize losses and maximize profit potential in complex trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Delta Hedging | Dynamic Hedging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hedging strategy focused on offsetting delta risk of options. | Active hedging strategy adjusting all Greeks, including delta, gamma, and vega. |
| Objective | Neutralize small price changes by maintaining delta neutrality. | Manage broader risks by frequent portfolio adjustments to maintain hedge. |
| Frequency of Adjustments | Periodic, based on delta shifts. | Continuous or high-frequency rebalancing as market conditions change. |
| Risk Coverage | Primarily delta risk. | Delta, gamma, vega, and other Greeks. |
| Complexity | Relatively simple and straightforward. | More complex, requires real-time monitoring and sophisticated models. |
| Use Cases | Common in options trading to hedge directional risk. | Used in portfolios needing comprehensive risk management. |
| Costs | Lower transactional costs due to less frequent trades. | Higher costs due to frequent rebalancing and execution. |
| Effectiveness | Effective for small price movements. | More effective in volatile markets with large risk exposures. |
Which is better?
Delta hedging focuses on neutralizing the directional risk of options by adjusting the underlying asset position to maintain a delta-neutral portfolio, making it highly effective for managing price movements in a stable volatility environment. Dynamic hedging, however, adapts continuously to changes in multiple risk factors such as delta, gamma, and vega, providing a more comprehensive risk management strategy in highly volatile or uncertain markets. Traders prefer dynamic hedging for portfolios with complex derivatives, while delta hedging remains suitable for simpler options strategies with less frequent adjustments needed.
Connection
Delta hedging is a specific form of dynamic hedging focused on managing the risk of options portfolios by neutralizing the delta, or price sensitivity to the underlying asset. Dynamic hedging involves continuously adjusting hedge positions in response to changes in market conditions, with delta hedging being a practical application that targets delta neutrality. Both methods aim to minimize exposure to price movements, enhancing risk management efficiency in derivative trading.
Key Terms
Option Greeks
Dynamic hedging actively adjusts option positions based on real-time movements in the underlying asset to maintain a desired risk profile, utilizing multiple Option Greeks such as gamma and vega to manage volatility and time decay risks. Delta hedging specifically targets neutralizing the delta of an option position to limit exposure to price changes in the underlying asset, primarily focusing on maintaining a delta-neutral portfolio. Explore deeper insights into how dynamic and delta hedging strategies leverage Option Greeks for optimized portfolio risk management.
Volatility
Dynamic hedging continuously adjusts the hedge ratio to manage the changing delta of an option, effectively responding to market volatility and minimizing risk exposure. Delta hedging, a subset of dynamic hedging, specifically targets neutralizing delta at one point in time but requires frequent rebalancing as volatility impacts option Greeks. Explore more to understand how volatility-driven adjustments optimize hedging strategies.
Rebalancing frequency
Dynamic hedging involves continuously adjusting a portfolio's hedge ratio to maintain optimal risk exposure, requiring frequent rebalancing based on market movements and volatility shifts. Delta hedging, a subset of dynamic hedging, specifically targets neutralizing the delta risk of options by adjusting positions as the underlying asset price changes, often requiring multiple rebalancing intervals within trading sessions. Explore detailed strategies and implications of rebalancing frequencies to enhance your risk management approach.
Source and External Links
Dynamic Hedging - QuestDB - Dynamic hedging is a risk management strategy where traders continuously adjust hedge positions in response to market changes, particularly used to maintain risk profiles for complex instruments like options by monitoring Greeks such as delta, gamma, and vega, requiring frequent rebalancing to maintain hedge accuracy.
ECON 251 - Lecture 20 - Dynamic Hedging | Open Yale Courses - Dynamic hedging involves adjusting a hedge annually to account for changing conditions, simplifying the hedging challenge over long periods by focusing on what can happen in the next year, thus reducing complex risk management into manageable steps.
Dynamic hedging Definition - Nasdaq - Dynamic hedging is a strategy that involves regularly rebalancing hedge positions as market conditions change to protect the value of a portfolio through synthetic instruments or other hedging techniques.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com