Gamma squeeze occurs when rapid buying of options forces market makers to buy the underlying stock, driving prices sharply higher and creating intense volatility. Bull trap deceives traders by signaling a false breakout, causing premature purchases before the price reverses downward. Explore the key differences and strategies to identify these market phenomena effectively.
Why it is important
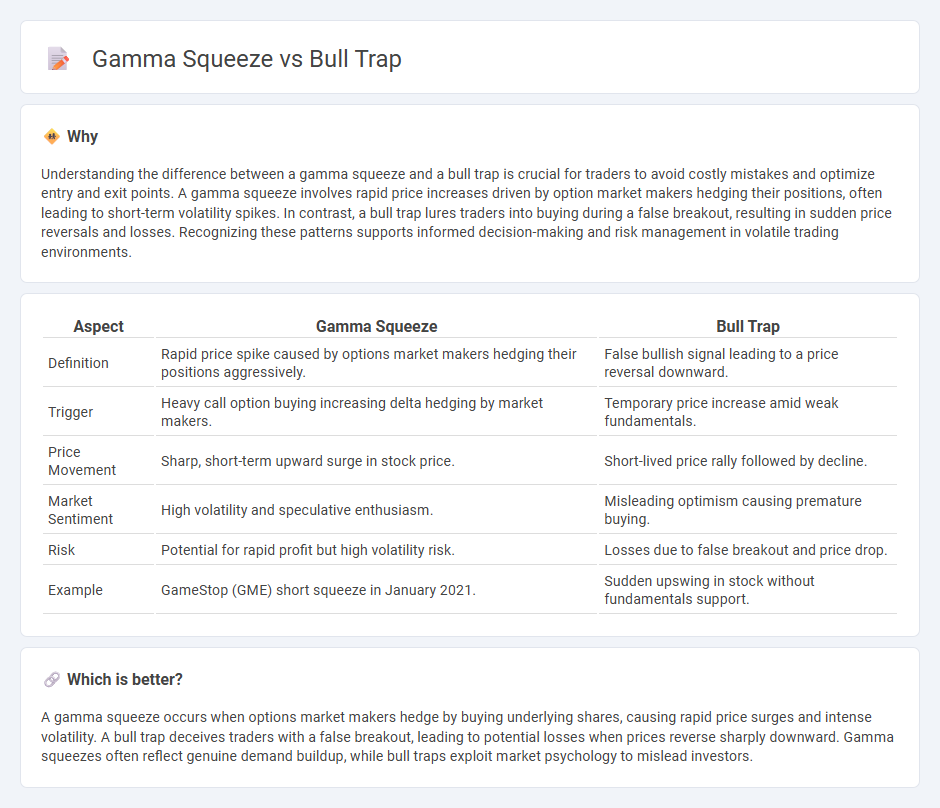
Understanding the difference between a gamma squeeze and a bull trap is crucial for traders to avoid costly mistakes and optimize entry and exit points. A gamma squeeze involves rapid price increases driven by option market makers hedging their positions, often leading to short-term volatility spikes. In contrast, a bull trap lures traders into buying during a false breakout, resulting in sudden price reversals and losses. Recognizing these patterns supports informed decision-making and risk management in volatile trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gamma Squeeze | Bull Trap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid price spike caused by options market makers hedging their positions aggressively. | False bullish signal leading to a price reversal downward. |
| Trigger | Heavy call option buying increasing delta hedging by market makers. | Temporary price increase amid weak fundamentals. |
| Price Movement | Sharp, short-term upward surge in stock price. | Short-lived price rally followed by decline. |
| Market Sentiment | High volatility and speculative enthusiasm. | Misleading optimism causing premature buying. |
| Risk | Potential for rapid profit but high volatility risk. | Losses due to false breakout and price drop. |
| Example | GameStop (GME) short squeeze in January 2021. | Sudden upswing in stock without fundamentals support. |
Which is better?
A gamma squeeze occurs when options market makers hedge by buying underlying shares, causing rapid price surges and intense volatility. A bull trap deceives traders with a false breakout, leading to potential losses when prices reverse sharply downward. Gamma squeezes often reflect genuine demand buildup, while bull traps exploit market psychology to mislead investors.
Connection
Gamma squeezes cause rapid price spikes as options market makers buy underlying stocks to hedge their positions, creating intense upward momentum. Bull traps occur when these sharp gains lure traders into buying, only for prices to reverse sharply afterward. This connection highlights the risk of mistaking gamma squeeze-driven rallies for sustainable market trends.
Key Terms
False breakout (Bull Trap)
A bull trap occurs when a stock price falsely breaks above a key resistance level, luring traders into buying before the price sharply reverses downward, causing losses. It differs from a gamma squeeze, where options market dynamics drive a rapid price increase due to dealers hedging their exposure, often creating a short-lived rally. Explore how identifying false breakouts can help protect your portfolio from costly bull traps.
Options delta hedging (Gamma Squeeze)
A bull trap occurs when investors mistake a temporary market rally for a genuine upward trend, leading to premature buying before prices decline again, while a gamma squeeze arises from options delta hedging, where market makers must buy the underlying stock aggressively as the price approaches the strike, causing rapid price spikes. Delta hedging involves adjusting option positions to remain delta-neutral, and gamma squeeze intensifies buying pressure due to the convexity of gamma near the money options. Explore detailed mechanisms of gamma squeeze and its impact on market volatility to enhance trading strategies.
Short covering
A bull trap occurs when investors mistakenly believe a downtrend has reversed, leading to a short covering rally that quickly reverses, causing losses for traders positioned for continued gains. A gamma squeeze involves options market makers hedging by buying underlying stocks as prices rise, fueling a self-reinforcing upward momentum that forces shorts to cover rapidly. Explore the detailed mechanics and implications behind short covering in both phenomena to enhance trading strategies.
Source and External Links
What is a Bull Trap? - A Complete Guide - CenterPoint Securities - A bull trap is a deceptive upward price movement that tricks bullish investors into thinking a stock's price will rise, but the increase is short-lived and followed by a continued downtrend causing losses for those caught in the trap.
Bull Trap Trading Guide: How to Identify And Escape - Mitrade - A bull trap occurs when a price breaks above a resistance level, giving false confirmation of a bullish breakout, only to sharply reverse and trap buyers in losing trades shortly thereafter.
What is a Bull Trap & How Do I Avoid It? - CMC Markets - Bull traps happen when the price rises above resistance, luring buyers expecting a rally, but the move quickly reverses and the price falls, often happening in downtrends or flat markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com