Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies through automated trading algorithms within a single market or similar asset classes, enabling rapid execution and reduced market risk. Cross-asset arbitrage involves identifying inefficiencies between different asset classes, such as equities and bonds, capitalizing on relative value disparities across markets. Discover more about how these trading strategies can enhance portfolio diversification and profitability.
Why it is important
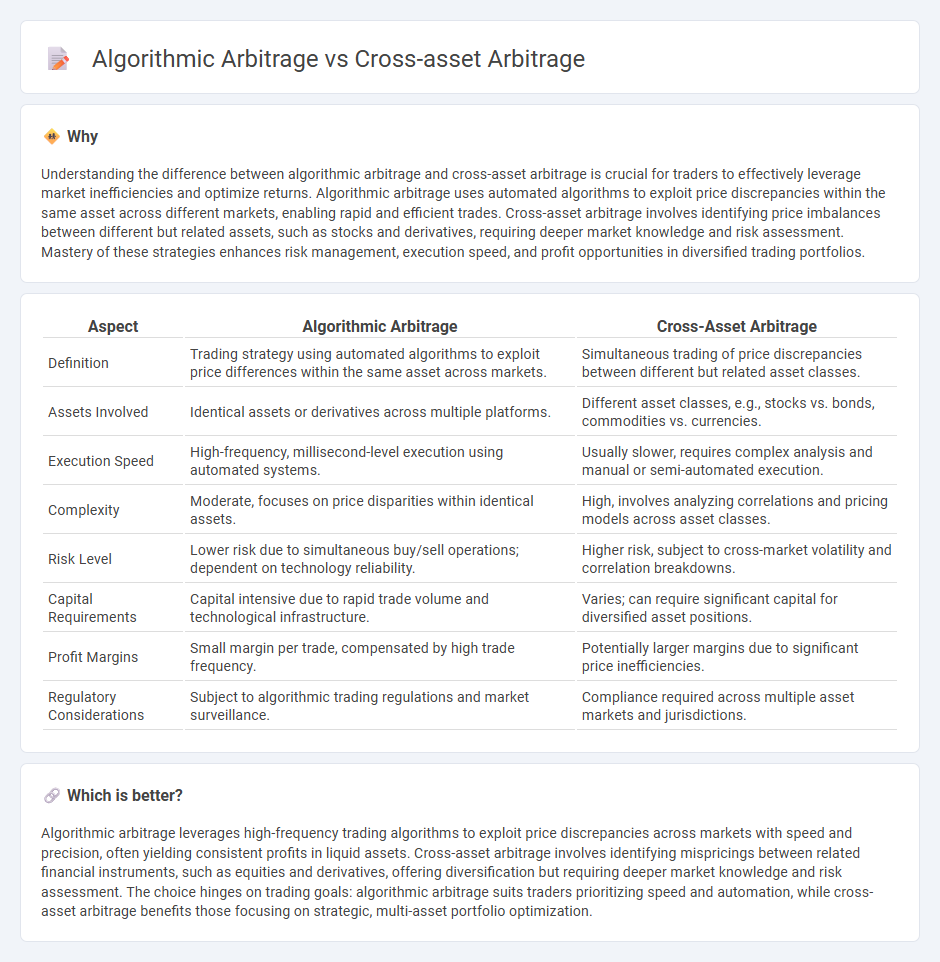
Understanding the difference between algorithmic arbitrage and cross-asset arbitrage is crucial for traders to effectively leverage market inefficiencies and optimize returns. Algorithmic arbitrage uses automated algorithms to exploit price discrepancies within the same asset across different markets, enabling rapid and efficient trades. Cross-asset arbitrage involves identifying price imbalances between different but related assets, such as stocks and derivatives, requiring deeper market knowledge and risk assessment. Mastery of these strategies enhances risk management, execution speed, and profit opportunities in diversified trading portfolios.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Arbitrage | Cross-Asset Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading strategy using automated algorithms to exploit price differences within the same asset across markets. | Simultaneous trading of price discrepancies between different but related asset classes. |
| Assets Involved | Identical assets or derivatives across multiple platforms. | Different asset classes, e.g., stocks vs. bonds, commodities vs. currencies. |
| Execution Speed | High-frequency, millisecond-level execution using automated systems. | Usually slower, requires complex analysis and manual or semi-automated execution. |
| Complexity | Moderate, focuses on price disparities within identical assets. | High, involves analyzing correlations and pricing models across asset classes. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to simultaneous buy/sell operations; dependent on technology reliability. | Higher risk, subject to cross-market volatility and correlation breakdowns. |
| Capital Requirements | Capital intensive due to rapid trade volume and technological infrastructure. | Varies; can require significant capital for diversified asset positions. |
| Profit Margins | Small margin per trade, compensated by high trade frequency. | Potentially larger margins due to significant price inefficiencies. |
| Regulatory Considerations | Subject to algorithmic trading regulations and market surveillance. | Compliance required across multiple asset markets and jurisdictions. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic arbitrage leverages high-frequency trading algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across markets with speed and precision, often yielding consistent profits in liquid assets. Cross-asset arbitrage involves identifying mispricings between related financial instruments, such as equities and derivatives, offering diversification but requiring deeper market knowledge and risk assessment. The choice hinges on trading goals: algorithmic arbitrage suits traders prioritizing speed and automation, while cross-asset arbitrage benefits those focusing on strategic, multi-asset portfolio optimization.
Connection
Algorithmic arbitrage leverages automated trading algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across different markets, including cross-asset arbitrage, which specifically targets inefficiencies between related financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives. Both strategies depend on real-time data analysis and rapid execution to capitalize on transient arbitrage opportunities before market prices converge. The integration of algorithmic techniques enhances the efficiency and accuracy of identifying and executing cross-asset arbitrage trades, maximizing profitability in complex, multi-asset environments.
Key Terms
Cross-asset arbitrage:
Cross-asset arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between different asset classes such as equities, bonds, and commodities, aiming to capitalize on market inefficiencies by simultaneously buying undervalued assets and selling overvalued ones. This strategy requires advanced analytical tools and real-time data to identify correlations and divergences across heterogeneous financial instruments. Explore the latest techniques and tools to master cross-asset arbitrage opportunities.
Price convergence
Cross-asset arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between related but different financial instruments, aiming to profit as their prices converge due to underlying economic relations. Algorithmic arbitrage leverages high-frequency trading algorithms to identify and capitalize on fleeting price inefficiencies across multiple assets within milliseconds, accelerating the price convergence process through automated execution. Explore more to understand how these arbitrage strategies impact market efficiency and convergence dynamics.
Correlation
Cross-asset arbitrage exploits price inefficiencies between related but different asset classes by leveraging their statistical correlation, such as equities and fixed income, to generate risk-adjusted returns. Algorithmic arbitrage employs automated, high-speed trading algorithms to detect and act upon short-term, often intra-market price discrepancies, where correlation plays a secondary role to execution speed and pattern recognition. Explore how correlation influences strategy effectiveness and risk management in these arbitrage techniques.
Source and External Links
An experimental analysis on cross-asset arbitrage opportunity and ... - This research experimentally shows how arbitrage opportunities across different assets reduce price discrepancies and mispricing by encouraging traders to consider alternate asset prices during transactions.
Multi-Asset Volatility Arbitrage (Trading Strategy) - DayTrading.com - Multi-asset volatility arbitrage is a strategy where traders identify volatility differences across assets, take long and short positions accordingly, and profit from mean reversion in price differentials.
Cross-Asset Trading: Opportunities and Challenges in a Diversified Portfolio - Cross-asset arbitrage exploits price inefficiencies across different asset classes affected by variables like interest rates, allowing traders to capture arbitrage in global financial markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com