Front running involves a trader executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending large trades to capitalize on price movements, often raising ethical and legal concerns in financial markets. Churning refers to excessive trading by brokers within a client's account primarily to generate commissions, which can harm investors by increasing costs without improving returns. Explore the key differences and implications of front running versus churning to better understand their impact on trading integrity and investor protection.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between front running and churning is crucial for traders to avoid illegal and unethical practices that can lead to severe regulatory penalties. Front running involves exploiting non-public information about upcoming trades to gain unfair advantage, while churning refers to excessive trading primarily to generate commissions rather than benefiting the client. Recognizing these behaviors helps maintain market integrity and protects investors' interests. Awareness of these distinctions enhances compliance with financial regulations such as SEC and FINRA rules.
Comparison Table
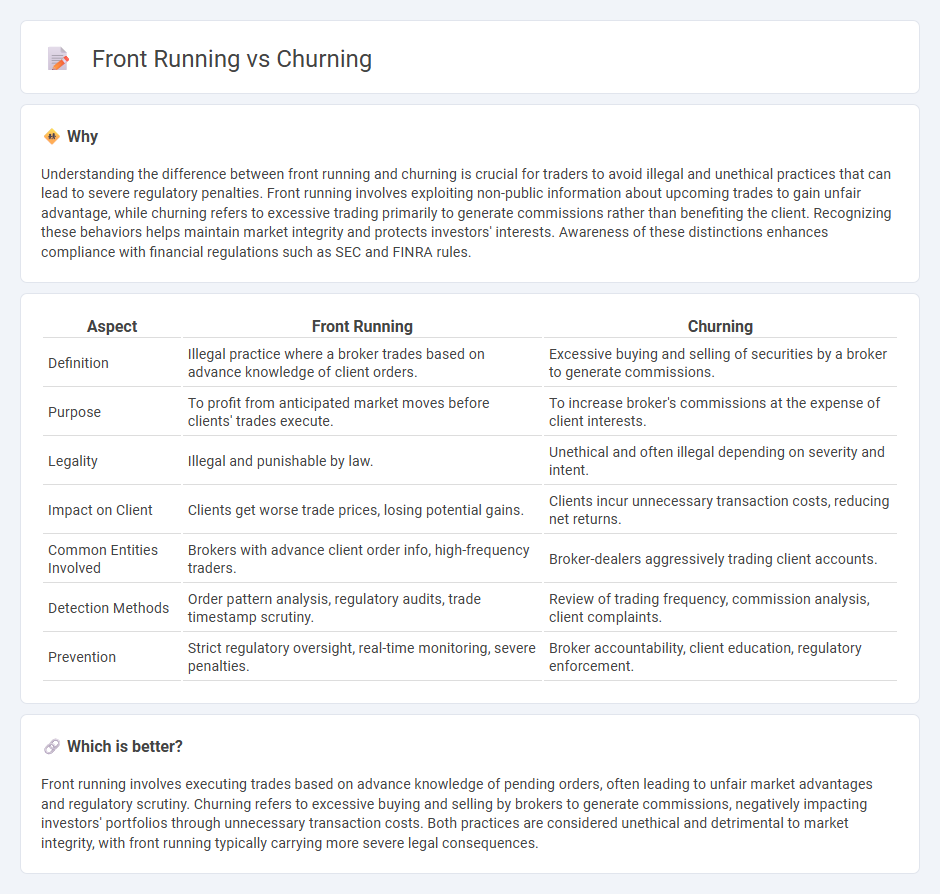
| Aspect | Front Running | Churning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegal practice where a broker trades based on advance knowledge of client orders. | Excessive buying and selling of securities by a broker to generate commissions. |
| Purpose | To profit from anticipated market moves before clients' trades execute. | To increase broker's commissions at the expense of client interests. |
| Legality | Illegal and punishable by law. | Unethical and often illegal depending on severity and intent. |
| Impact on Client | Clients get worse trade prices, losing potential gains. | Clients incur unnecessary transaction costs, reducing net returns. |
| Common Entities Involved | Brokers with advance client order info, high-frequency traders. | Broker-dealers aggressively trading client accounts. |
| Detection Methods | Order pattern analysis, regulatory audits, trade timestamp scrutiny. | Review of trading frequency, commission analysis, client complaints. |
| Prevention | Strict regulatory oversight, real-time monitoring, severe penalties. | Broker accountability, client education, regulatory enforcement. |
Which is better?
Front running involves executing trades based on advance knowledge of pending orders, often leading to unfair market advantages and regulatory scrutiny. Churning refers to excessive buying and selling by brokers to generate commissions, negatively impacting investors' portfolios through unnecessary transaction costs. Both practices are considered unethical and detrimental to market integrity, with front running typically carrying more severe legal consequences.
Connection
Front running and churning are connected as unethical trading practices that exploit investor assets for broker or trader profit. Front running involves executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending large trades, while churning entails excessive trading to generate commissions without regard to client benefit. Both behaviors violate fiduciary duties and can lead to significant financial harm and regulatory penalties.
Key Terms
Excessive Trading (Churning)
Excessive trading, or churning, occurs when a broker executes an unusually high number of trades in a client's account primarily to generate commissions rather than to benefit the client. This practice violates fiduciary duties and can result in substantial financial harm due to unnecessary fees and increased tax liabilities. Learn more about identifying and protecting yourself from churning to ensure your investments are managed ethically.
Insider Knowledge (Front Running)
Front running involves exploiting insider knowledge by executing trades based on advance information about pending large orders to gain unfair market advantage. This unethical practice undermines market integrity and is strictly prohibited by regulatory authorities like the SEC and FINRA. Explore more to understand the legal implications and detection methods of front running.
Fiduciary Duty
Churning involves excessive buying and selling of securities by a broker primarily to generate commissions, breaching fiduciary duty by prioritizing personal gain over client interests. Front running occurs when a broker executes orders on a security for its own account while taking advantage of advance knowledge of pending orders from its clients, violating the duty of loyalty and trust. Explore further to understand how fiduciary duty is legally upheld in cases of churning and front running.
Source and External Links
Churning (finance) - Churning is the illegal practice of excessive buying and selling of securities by a broker in a customer's account to generate commission, often harming the investor's portfolio.
churning | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - Churning refers to excessive trading by a stock broker to benefit personally via commissions, violating federal securities law and the broker's fiduciary duty.
What Is Credit Card Churning? - Credit card churning is the practice of opening and closing multiple credit card accounts to earn sign-up bonuses and rewards but carries risks such as damaging credit scores.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com