Execution algorithms enhance trading efficiency by systematically breaking large orders into smaller slices, minimizing market impact and reducing transaction costs. Basket trading, on the other hand, involves simultaneously buying or selling a group of securities, optimizing portfolio adjustments and quick rebalancing across multiple assets. Explore these strategies further to understand their distinct advantages in modern trading.
Why it is important
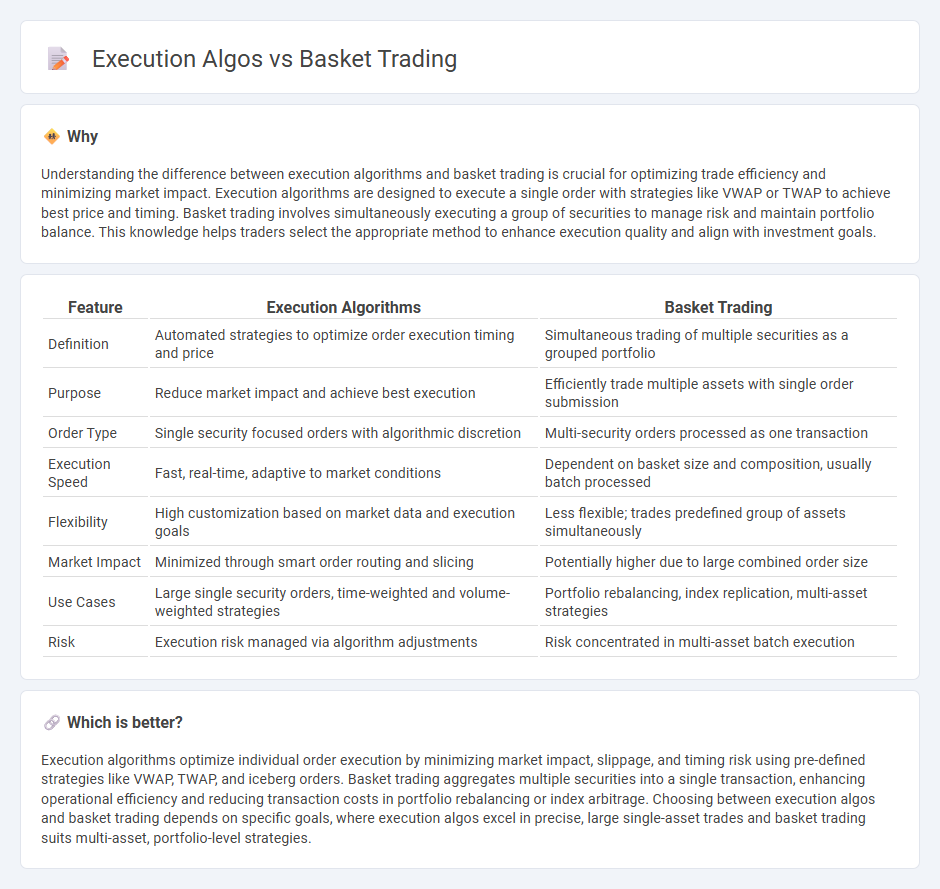
Understanding the difference between execution algorithms and basket trading is crucial for optimizing trade efficiency and minimizing market impact. Execution algorithms are designed to execute a single order with strategies like VWAP or TWAP to achieve best price and timing. Basket trading involves simultaneously executing a group of securities to manage risk and maintain portfolio balance. This knowledge helps traders select the appropriate method to enhance execution quality and align with investment goals.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Execution Algorithms | Basket Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated strategies to optimize order execution timing and price | Simultaneous trading of multiple securities as a grouped portfolio |
| Purpose | Reduce market impact and achieve best execution | Efficiently trade multiple assets with single order submission |
| Order Type | Single security focused orders with algorithmic discretion | Multi-security orders processed as one transaction |
| Execution Speed | Fast, real-time, adaptive to market conditions | Dependent on basket size and composition, usually batch processed |
| Flexibility | High customization based on market data and execution goals | Less flexible; trades predefined group of assets simultaneously |
| Market Impact | Minimized through smart order routing and slicing | Potentially higher due to large combined order size |
| Use Cases | Large single security orders, time-weighted and volume-weighted strategies | Portfolio rebalancing, index replication, multi-asset strategies |
| Risk | Execution risk managed via algorithm adjustments | Risk concentrated in multi-asset batch execution |
Which is better?
Execution algorithms optimize individual order execution by minimizing market impact, slippage, and timing risk using pre-defined strategies like VWAP, TWAP, and iceberg orders. Basket trading aggregates multiple securities into a single transaction, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing transaction costs in portfolio rebalancing or index arbitrage. Choosing between execution algos and basket trading depends on specific goals, where execution algos excel in precise, large single-asset trades and basket trading suits multi-asset, portfolio-level strategies.
Connection
Execution algorithms optimize order placement by breaking large trades into smaller fragments to reduce market impact and slippage. Basket trading involves simultaneously buying or selling a group of securities, and execution algos enhance this process by efficiently managing the timing and sequencing of multiple orders within the basket. Combining execution algorithms with basket trading improves cost efficiency, price synchronization, and execution speed in multi-asset portfolios.
Key Terms
Diversification
Basket trading allows investors to simultaneously execute multiple securities, enhancing portfolio diversification through efficient allocation across various asset classes without repeated manual orders. Execution algorithms optimize trade timing and reduce market impact by slicing large orders into smaller tranches, ensuring precise control and cost efficiency in portfolio rebalancing. Discover how integrating basket trading with advanced execution algos can elevate diversification strategies and portfolio performance.
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price)
Basket trading involves executing multiple securities simultaneously to achieve efficient market exposure, often improving liquidity management. Execution algorithms like VWAP focus on minimizing market impact by distributing trades proportionally to volume patterns throughout the trading day, optimizing the average price paid or received. Explore how VWAP algorithms enhance portfolio execution and reduce slippage in dynamic markets.
Slippage
Basket trading involves simultaneously executing multiple securities to achieve a specific portfolio allocation, often targeting minimal market impact. Execution algorithms are designed to optimize trade timing and order slicing, aiming to reduce slippage--the difference between expected and actual trade prices--by adapting to real-time market conditions. Explore how mastering slippage control can elevate your trading strategy by learning more about advanced execution techniques.
Source and External Links
Basket Trading: What it is, key aspects & examples. - Equirus Wealth - Basket trading is a strategy where you buy or sell a group of securities as one unit, enabling diversification, risk management, and simplified, flexible trading across various assets like stocks, commodities, and currencies.
What is Basket Trading? Types, Advantages, and Challenges ... - Motilal Oswal - Basket trading allows simultaneous buying or selling of multiple assets in proportion to a benchmark index to achieve portfolio goals with reduced risk and higher efficiency.
Pro Guide to Mastering Basket Trades - Tradetron - Basket trading enables professional traders to manage portfolios efficiently by consolidating multiple trades into one, reducing transaction costs while supporting goal-oriented investment strategies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com