Dark pool prints reveal large, non-displayed trades executed away from public exchanges, offering insights into institutional trading activity that may not impact market maker quotes immediately. Market maker quotes provide real-time bid and ask prices, reflecting liquidity and short-term supply-demand dynamics on public exchanges. Explore the distinctions between dark pool prints and market maker quotes to enhance your trading strategy.
Why it is important
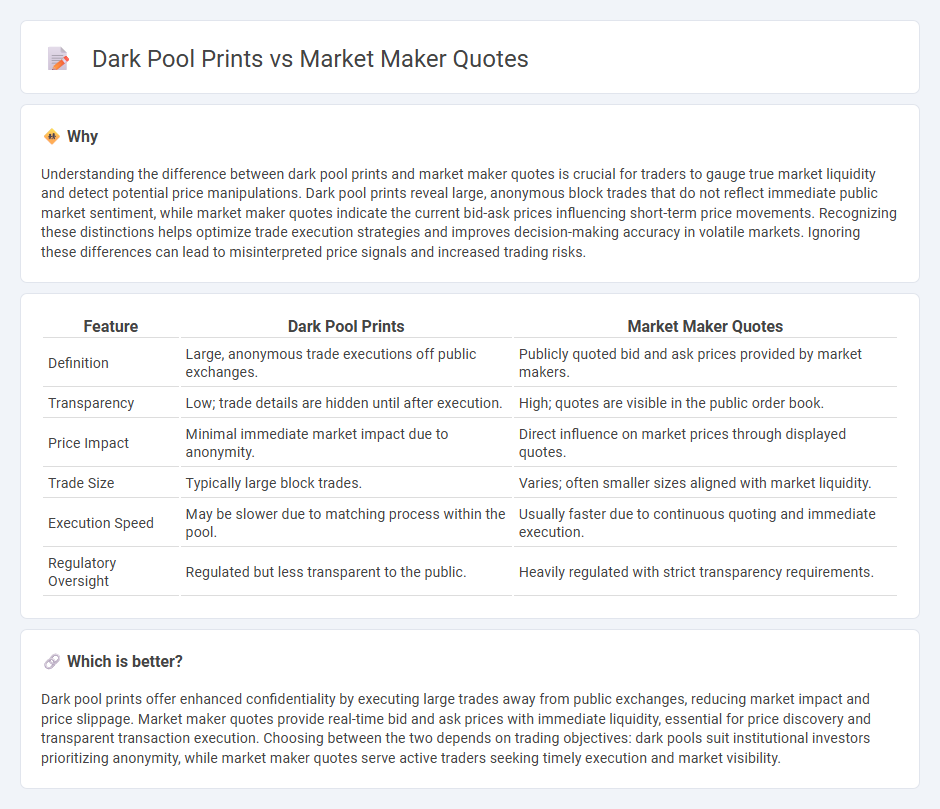
Understanding the difference between dark pool prints and market maker quotes is crucial for traders to gauge true market liquidity and detect potential price manipulations. Dark pool prints reveal large, anonymous block trades that do not reflect immediate public market sentiment, while market maker quotes indicate the current bid-ask prices influencing short-term price movements. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize trade execution strategies and improves decision-making accuracy in volatile markets. Ignoring these differences can lead to misinterpreted price signals and increased trading risks.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dark Pool Prints | Market Maker Quotes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large, anonymous trade executions off public exchanges. | Publicly quoted bid and ask prices provided by market makers. |
| Transparency | Low; trade details are hidden until after execution. | High; quotes are visible in the public order book. |
| Price Impact | Minimal immediate market impact due to anonymity. | Direct influence on market prices through displayed quotes. |
| Trade Size | Typically large block trades. | Varies; often smaller sizes aligned with market liquidity. |
| Execution Speed | May be slower due to matching process within the pool. | Usually faster due to continuous quoting and immediate execution. |
| Regulatory Oversight | Regulated but less transparent to the public. | Heavily regulated with strict transparency requirements. |
Which is better?
Dark pool prints offer enhanced confidentiality by executing large trades away from public exchanges, reducing market impact and price slippage. Market maker quotes provide real-time bid and ask prices with immediate liquidity, essential for price discovery and transparent transaction execution. Choosing between the two depends on trading objectives: dark pools suit institutional investors prioritizing anonymity, while market maker quotes serve active traders seeking timely execution and market visibility.
Connection
Dark pool prints reflect large, non-public trades executed away from traditional exchanges, providing market makers with discreet liquidity information. Market maker quotes adjust dynamically based on these hidden transactions to manage inventory risk and maintain market efficiency. This interplay influences price discovery by incorporating off-exchange trade data into public bid-ask spreads.
Key Terms
Bid-Ask Spread
Market maker quotes represent the displayed bid-ask spread, providing transparent liquidity and facilitating price discovery in public exchanges. Dark pool prints occur off-exchange and reveal trades executed at prices within or outside the visible spread, often at midpoints, reducing market impact and signaling iceberg orders. Explore how bid-ask spreads influence trading strategies and market efficiency in depth.
Liquidity
Market maker quotes provide transparent bid and ask prices, enabling visible liquidity in public exchanges, whereas dark pool prints represent executed trades in private venues, hiding liquidity to prevent market impact. Market makers facilitate continuous liquidity, supporting price discovery, while dark pools allow large investors to trade sizeable blocks without revealing intentions. Explore our analysis to understand how these liquidity sources influence market dynamics and trading strategies.
Trade Transparency
Market maker quotes provide visible bid-ask prices reflecting real-time market liquidity, enhancing price discovery in transparent trading environments. Dark pool prints, however, represent large trade executions hidden from public view until after completion, reducing market impact but limiting real-time transparency. Explore the balance between these mechanisms and their implications for trade transparency to better understand modern market dynamics.
Source and External Links
Market maker: What it is, importance, benefits & examples - StoneX - A market maker is a financial institution that actively quotes both bids (buy prices) and offers (sell prices) to provide liquidity in financial markets and profits from the spread between them.
What does a market maker mean if they post a quote stating 1000-1010 25x10? - Market maker quotes show the bid price, ask price, and the sizes (quantity available) at each price, e.g., a quote of 10.00-10.10 [25x10] means willingness to buy 25 units at $10.00 and sell 10 units at $10.10.
Bids & offers | Trading securities | Recommendations & strategies - Market maker quotes display how many round lots they are willing to buy or sell at a set bid and ask price, with the difference called the "spread," from which they make a profit, often trading thousands of times daily.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com