Trading on modular blockchains leverages specialized layers for execution and settlement, enhancing scalability and customization compared to monolithic systems. Automated Market Makers (AMMs) use algorithmic formulas to provide liquidity, enabling decentralized trading without traditional order books. Explore the advantages and challenges of each to optimize your trading strategy in the evolving blockchain ecosystem.
Why it is important
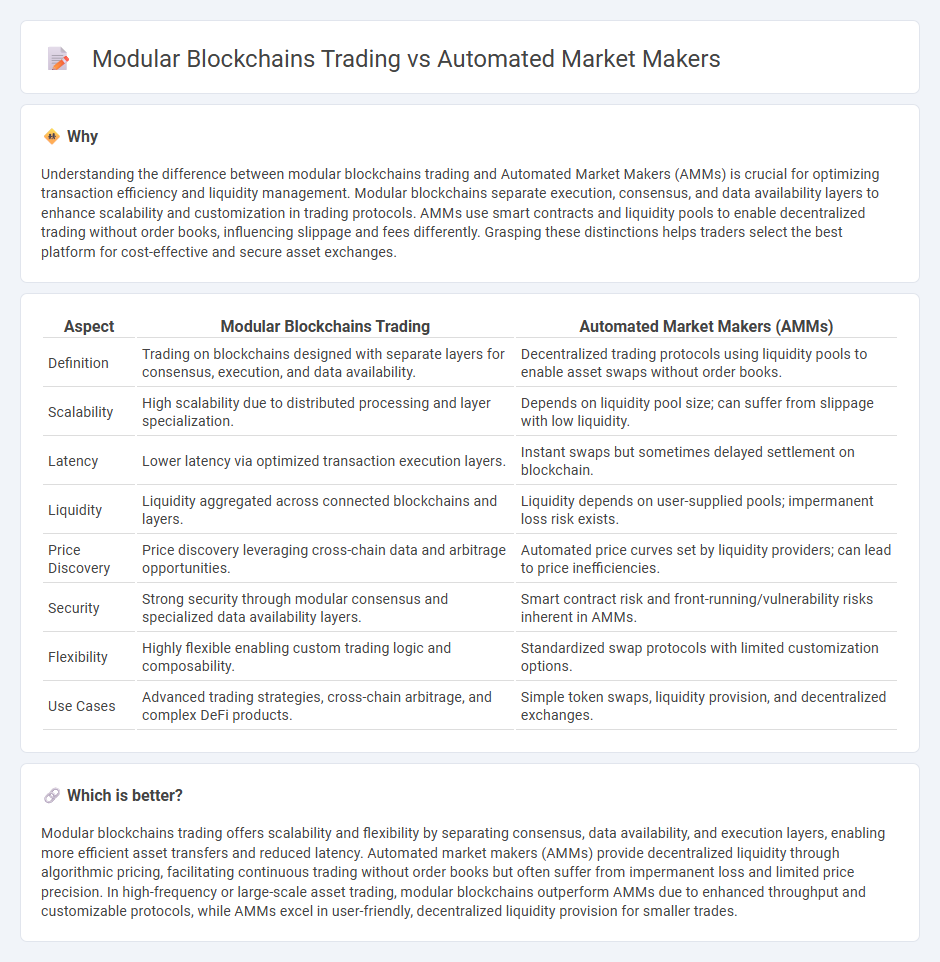
Understanding the difference between modular blockchains trading and Automated Market Makers (AMMs) is crucial for optimizing transaction efficiency and liquidity management. Modular blockchains separate execution, consensus, and data availability layers to enhance scalability and customization in trading protocols. AMMs use smart contracts and liquidity pools to enable decentralized trading without order books, influencing slippage and fees differently. Grasping these distinctions helps traders select the best platform for cost-effective and secure asset exchanges.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Modular Blockchains Trading | Automated Market Makers (AMMs) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading on blockchains designed with separate layers for consensus, execution, and data availability. | Decentralized trading protocols using liquidity pools to enable asset swaps without order books. |
| Scalability | High scalability due to distributed processing and layer specialization. | Depends on liquidity pool size; can suffer from slippage with low liquidity. |
| Latency | Lower latency via optimized transaction execution layers. | Instant swaps but sometimes delayed settlement on blockchain. |
| Liquidity | Liquidity aggregated across connected blockchains and layers. | Liquidity depends on user-supplied pools; impermanent loss risk exists. |
| Price Discovery | Price discovery leveraging cross-chain data and arbitrage opportunities. | Automated price curves set by liquidity providers; can lead to price inefficiencies. |
| Security | Strong security through modular consensus and specialized data availability layers. | Smart contract risk and front-running/vulnerability risks inherent in AMMs. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible enabling custom trading logic and composability. | Standardized swap protocols with limited customization options. |
| Use Cases | Advanced trading strategies, cross-chain arbitrage, and complex DeFi products. | Simple token swaps, liquidity provision, and decentralized exchanges. |
Which is better?
Modular blockchains trading offers scalability and flexibility by separating consensus, data availability, and execution layers, enabling more efficient asset transfers and reduced latency. Automated market makers (AMMs) provide decentralized liquidity through algorithmic pricing, facilitating continuous trading without order books but often suffer from impermanent loss and limited price precision. In high-frequency or large-scale asset trading, modular blockchains outperform AMMs due to enhanced throughput and customizable protocols, while AMMs excel in user-friendly, decentralized liquidity provision for smaller trades.
Connection
Modular blockchains enhance trading by enabling scalability and specialization through distinct layers for execution, consensus, and data availability, allowing Automated Market Makers (AMMs) to operate efficiently on the execution layer. AMMs leverage these modular frameworks to facilitate decentralized liquidity provision and real-time asset swaps without relying on traditional order books. The separation of concerns in modular blockchains reduces congestion and transaction fees, optimizing AMM performance and user experience in decentralized finance (DeFi).
Key Terms
Liquidity Pools
Automated market makers (AMMs) utilize liquidity pools to enable decentralized trading by allowing users to trade assets directly from pools without relying on traditional order books. Modular blockchains enhance this process by separating transaction execution, settlement, and consensus layers, increasing scalability and efficiency in managing liquidity pools. Explore the nuances of liquidity pool dynamics in AMMs and modular blockchain architectures to understand their impact on decentralized finance.
Smart Contracts
Automated market makers (AMMs) utilize smart contracts to facilitate decentralized trading by automatically adjusting asset prices based on liquidity pool ratios, ensuring continuous market availability without order books. Modular blockchains enhance this process by separating consensus, data availability, and execution layers, enabling more scalable and customizable smart contract deployment tailored to specific trading strategies. Explore how these innovations optimize decentralized finance and trading efficiency by diving deeper into their technological foundations.
Interoperability
Automated market makers (AMMs) facilitate decentralized trading by using liquidity pools and algorithms to set prices without order books, optimizing efficiency within a single blockchain. Modular blockchains enhance interoperability by separating consensus, data availability, and execution layers, allowing diverse chains to communicate and trade seamlessly. Explore the evolving landscape of blockchain interoperability to understand how these technologies transform decentralized finance.
Source and External Links
What is an Automated Market Maker? - An automated market maker (AMM) is a decentralized exchange protocol running on smart contracts that prices and processes crypto trades automatically using math formulas instead of order books, allowing 24/7, permissionless, fast trading and enabling liquidity providers to earn fees by supplying assets to liquidity pools.
What is an Automated Market Maker (AMM)? - AMMs are autonomous blockchain protocols that facilitate crypto trades against liquidity pools via smart contracts without needing a counterparty, using algorithms like the constant product formula (x * y = k) to determine prices algorithmically and eliminate wait times for matching buyers and sellers.
What Is an Automated Market Maker (AMM)? - Gemini - AMMs maintain continuous market liquidity by allowing users to trade digital assets automatically using liquidity pools, with prices set by algorithms based on the pool's token ratios, supporting a decentralized, permissionless trading environment without traditional order books.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com