Flash loans enable traders to borrow large amounts of capital instantly without collateral, facilitating arbitrage and quick profit opportunities within a single transaction. Margin trading involves borrowing funds to increase position size, allowing greater exposure but carrying higher risk due to potential liquidation. Discover more about the advantages and risks of flash loans and margin trading strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between flash loans and margin trading is essential for managing risk and maximizing profits in cryptocurrency markets. Flash loans offer instant, uncollateralized borrowing within a single transaction, facilitating arbitrage and complex trades without upfront capital. Margin trading involves borrowing funds over a longer term, leveraging assets to amplify gains but increasing exposure to liquidation risk. Knowing these distinctions helps traders choose the appropriate strategy for their risk tolerance and investment goals.
Comparison Table
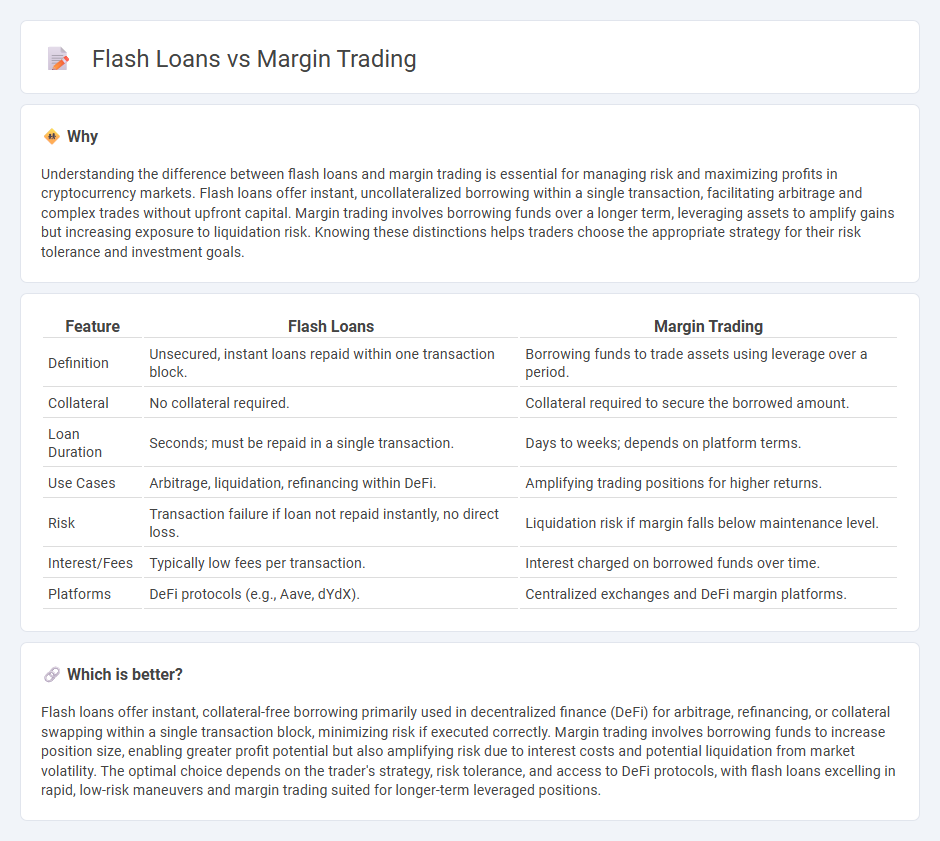
| Feature | Flash Loans | Margin Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unsecured, instant loans repaid within one transaction block. | Borrowing funds to trade assets using leverage over a period. |
| Collateral | No collateral required. | Collateral required to secure the borrowed amount. |
| Loan Duration | Seconds; must be repaid in a single transaction. | Days to weeks; depends on platform terms. |
| Use Cases | Arbitrage, liquidation, refinancing within DeFi. | Amplifying trading positions for higher returns. |
| Risk | Transaction failure if loan not repaid instantly, no direct loss. | Liquidation risk if margin falls below maintenance level. |
| Interest/Fees | Typically low fees per transaction. | Interest charged on borrowed funds over time. |
| Platforms | DeFi protocols (e.g., Aave, dYdX). | Centralized exchanges and DeFi margin platforms. |
Which is better?
Flash loans offer instant, collateral-free borrowing primarily used in decentralized finance (DeFi) for arbitrage, refinancing, or collateral swapping within a single transaction block, minimizing risk if executed correctly. Margin trading involves borrowing funds to increase position size, enabling greater profit potential but also amplifying risk due to interest costs and potential liquidation from market volatility. The optimal choice depends on the trader's strategy, risk tolerance, and access to DeFi protocols, with flash loans excelling in rapid, low-risk maneuvers and margin trading suited for longer-term leveraged positions.
Connection
Flash loans enable traders to borrow large amounts of cryptocurrency instantly without collateral, facilitating complex arbitrage and liquidation strategies within a single transaction. Margin trading relies on borrowed funds to amplify potential returns, where flash loans can provide the necessary capital quickly to enter or exit leveraged positions. The synergy between flash loans and margin trading enhances liquidity and enables more efficient market opportunities for skilled traders.
Key Terms
Leverage
Margin trading allows investors to borrow funds from brokers to amplify their trading position, often with leverage ratios ranging from 2x to 10x, depending on the asset and platform. Flash loans provide uncollateralized, instant loans within a single blockchain transaction, enabling temporary leverage without upfront capital but requiring repayment within the same block. Explore the risks, benefits, and use cases of margin trading and flash loans to understand which leverage method suits your strategy best.
Collateral
Margin trading involves borrowing funds using collateral such as cryptocurrencies or assets to increase trading positions, with liquidation risk if collateral value drops below maintenance margin. Flash loans, unique to DeFi, provide unsecured, instant loans that must be repaid within the same transaction block, eliminating traditional collateral requirements but relying on atomic execution to prevent default. Explore how collateral mechanisms impact capital efficiency and risk management in decentralized finance platforms.
Liquidation
Margin trading involves borrowing funds to increase exposure, with liquidation occurring if asset value falls below maintenance margin, triggering forced asset sale to cover debts. Flash loans are uncollateralized, instant loans executed within a single blockchain transaction, with automatic liquidation if funds are not repaid immediately, eliminating traditional risk of partial liquidation. Explore the mechanics and risks of liquidation in both tools to better manage trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Basics of Margin Trading for Investors | Charles Schwab - Margin trading means borrowing money from a broker to purchase stocks, allowing you to buy more than with your cash alone, which can magnify both gains and losses.
What is Margin Trading and How Do You Trade On It? - IG - Margin trading, also known as leveraged trading, involves putting up a portion of the full trade value (initial margin) to open a position, with maintenance margin ensuring enough funds to cover potential losses.
Margin (finance) - Wikipedia - Margin is collateral deposited with a broker to cover credit risk from borrowing money or securities and can involve loan accounts where the broker may issue margin calls if equity falls below required levels.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com