Volatility harvesting leverages market fluctuations to generate consistent returns by strategically reallocating assets during periods of price changes, optimizing portfolio performance. Algorithmic trading employs automated systems and complex mathematical models to execute trades with speed and precision, reducing human error and enhancing market efficiency. Discover how these distinct trading strategies can transform your investment approach.
Why it is important
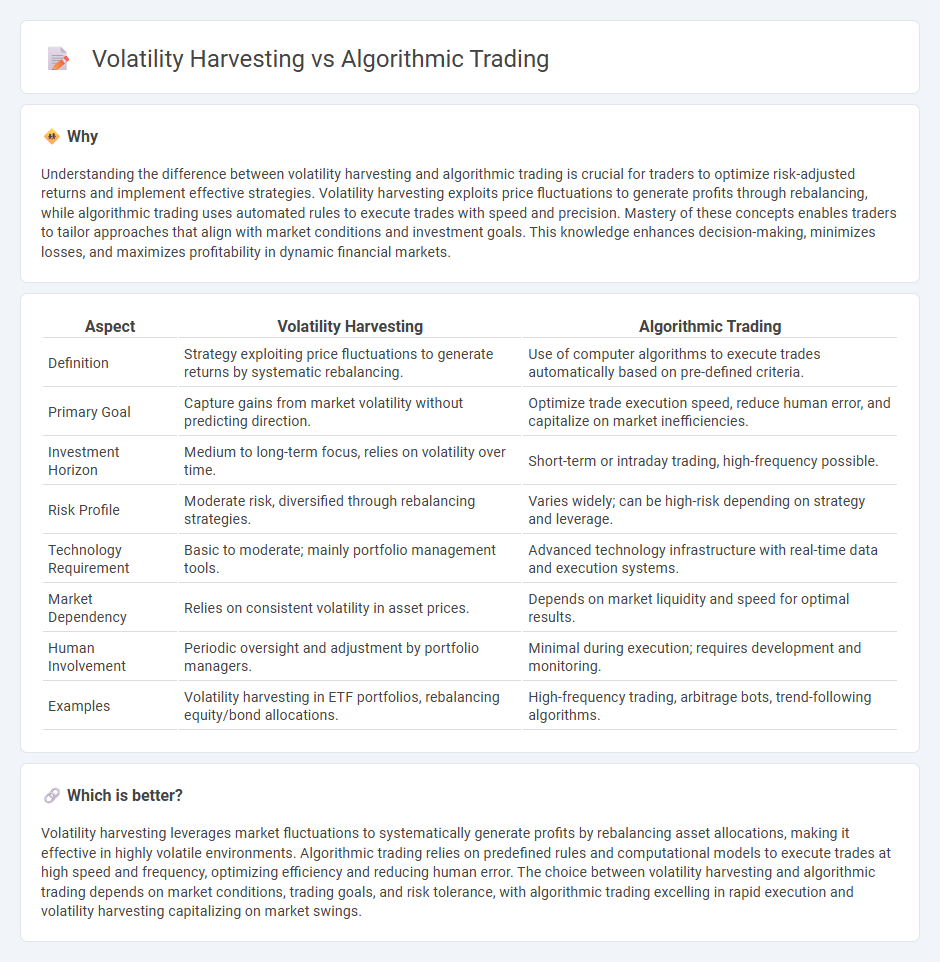
Understanding the difference between volatility harvesting and algorithmic trading is crucial for traders to optimize risk-adjusted returns and implement effective strategies. Volatility harvesting exploits price fluctuations to generate profits through rebalancing, while algorithmic trading uses automated rules to execute trades with speed and precision. Mastery of these concepts enables traders to tailor approaches that align with market conditions and investment goals. This knowledge enhances decision-making, minimizes losses, and maximizes profitability in dynamic financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Volatility Harvesting | Algorithmic Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy exploiting price fluctuations to generate returns by systematic rebalancing. | Use of computer algorithms to execute trades automatically based on pre-defined criteria. |
| Primary Goal | Capture gains from market volatility without predicting direction. | Optimize trade execution speed, reduce human error, and capitalize on market inefficiencies. |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long-term focus, relies on volatility over time. | Short-term or intraday trading, high-frequency possible. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk, diversified through rebalancing strategies. | Varies widely; can be high-risk depending on strategy and leverage. |
| Technology Requirement | Basic to moderate; mainly portfolio management tools. | Advanced technology infrastructure with real-time data and execution systems. |
| Market Dependency | Relies on consistent volatility in asset prices. | Depends on market liquidity and speed for optimal results. |
| Human Involvement | Periodic oversight and adjustment by portfolio managers. | Minimal during execution; requires development and monitoring. |
| Examples | Volatility harvesting in ETF portfolios, rebalancing equity/bond allocations. | High-frequency trading, arbitrage bots, trend-following algorithms. |
Which is better?
Volatility harvesting leverages market fluctuations to systematically generate profits by rebalancing asset allocations, making it effective in highly volatile environments. Algorithmic trading relies on predefined rules and computational models to execute trades at high speed and frequency, optimizing efficiency and reducing human error. The choice between volatility harvesting and algorithmic trading depends on market conditions, trading goals, and risk tolerance, with algorithmic trading excelling in rapid execution and volatility harvesting capitalizing on market swings.
Connection
Volatility harvesting leverages price fluctuations to generate alpha by systematically rebalancing portfolios, a process enhanced through algorithmic trading's precision and speed. Algorithmic trading executes volatility-based strategies by automatically adjusting positions in response to real-time market volatility metrics such as the VIX index. This synergy enables traders to capitalize on short-term price movements while managing risk with data-driven algorithms.
Key Terms
**Algorithmic Trading:**
Algorithmic trading uses computer algorithms to execute trades based on pre-defined criteria, aiming to optimize execution speed and accuracy in various markets such as equities, forex, and commodities. It leverages high-frequency trading, statistical arbitrage, and machine learning models to capitalize on market inefficiencies and real-time data analysis. Explore the nuances and strategic advantages of algorithmic trading to enhance your market performance.
Backtesting
Algorithmic trading leverages predefined rules and statistical models to execute trades automatically, enhancing precision and speed in volatile markets. Volatility harvesting exploits price fluctuations to generate returns by systematically buying low and selling high, often requiring robust backtesting to validate strategies under varying market conditions. Explore detailed backtesting techniques to optimize both algorithmic trading and volatility harvesting strategies effectively.
Execution algorithms
Execution algorithms in algorithmic trading optimize order placement to minimize market impact and transaction costs, leveraging real-time data and sophisticated models. Volatility harvesting strategies utilize these algorithms to exploit price fluctuations by systematically buying low and selling high within short timeframes. Explore detailed methodologies and performance metrics to understand the nuances of execution algorithms in both approaches.
Source and External Links
What is Algorithmic Trading and How Do You Get Started? - IG - Algorithmic trading uses computer codes to open and close trades based on set rules like price movements, with key strategies including price action, technical analysis, and a combination of both, allowing traders to automate buying or selling at specific price levels or technical indicator triggers.
Algorithmic Trading - Definition, Example, Pros, Cons - Algorithmic trading involves pre-programmed rules to automatically execute trades when conditions, such as price crossing a moving average, are met, enabling efficient handling of large orders by breaking them into smaller batches to avoid market impact.
Algorithmic trading - Wikipedia - Algorithmic trading has evolved from fixed-rule systems based on technical indicators to incorporating advanced machine learning methods like deep reinforcement learning and directional change algorithms, which adapt dynamically to market conditions and improve trade timing in volatile environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com