Grid trading involves placing buy and sell orders at preset intervals around a base price, capitalizing on market volatility to generate profits through repeated trades. Position trading focuses on holding assets for longer periods, relying on fundamental analysis to capture substantial price movements and trends. Discover more about the strategic differences and applications of grid trading versus position trading.
Why it is important
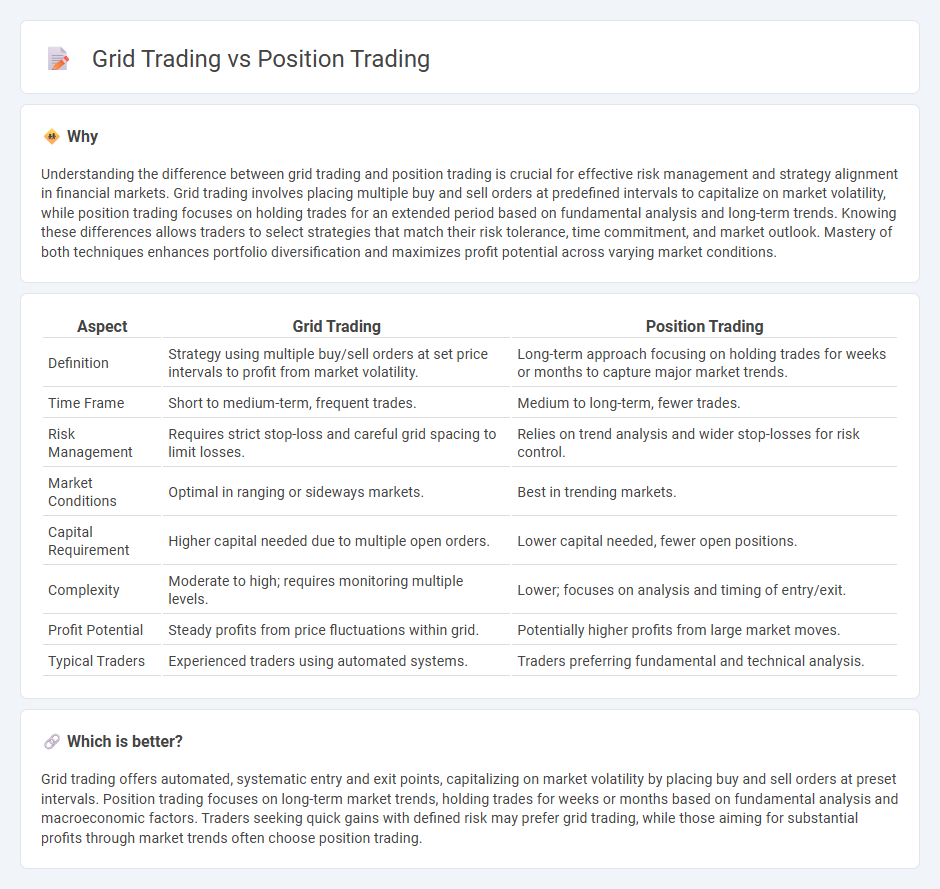
Understanding the difference between grid trading and position trading is crucial for effective risk management and strategy alignment in financial markets. Grid trading involves placing multiple buy and sell orders at predefined intervals to capitalize on market volatility, while position trading focuses on holding trades for an extended period based on fundamental analysis and long-term trends. Knowing these differences allows traders to select strategies that match their risk tolerance, time commitment, and market outlook. Mastery of both techniques enhances portfolio diversification and maximizes profit potential across varying market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Grid Trading | Position Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy using multiple buy/sell orders at set price intervals to profit from market volatility. | Long-term approach focusing on holding trades for weeks or months to capture major market trends. |
| Time Frame | Short to medium-term, frequent trades. | Medium to long-term, fewer trades. |
| Risk Management | Requires strict stop-loss and careful grid spacing to limit losses. | Relies on trend analysis and wider stop-losses for risk control. |
| Market Conditions | Optimal in ranging or sideways markets. | Best in trending markets. |
| Capital Requirement | Higher capital needed due to multiple open orders. | Lower capital needed, fewer open positions. |
| Complexity | Moderate to high; requires monitoring multiple levels. | Lower; focuses on analysis and timing of entry/exit. |
| Profit Potential | Steady profits from price fluctuations within grid. | Potentially higher profits from large market moves. |
| Typical Traders | Experienced traders using automated systems. | Traders preferring fundamental and technical analysis. |
Which is better?
Grid trading offers automated, systematic entry and exit points, capitalizing on market volatility by placing buy and sell orders at preset intervals. Position trading focuses on long-term market trends, holding trades for weeks or months based on fundamental analysis and macroeconomic factors. Traders seeking quick gains with defined risk may prefer grid trading, while those aiming for substantial profits through market trends often choose position trading.
Connection
Grid trading and position trading are connected through their strategic use of market trends and price fluctuations to maximize profit. Grid trading involves placing buy and sell orders at predetermined intervals to capitalize on market volatility, while position trading focuses on holding assets over longer periods to benefit from sustained price movements. Both methods require careful analysis of market patterns and risk management techniques to optimize trading performance.
Key Terms
Holding Period
Position trading involves maintaining trades over weeks to months based on long-term market trends and fundamental analysis, emphasizing patience and minimal trade frequency. Grid trading operates through a series of buy and sell orders at fixed intervals within a defined price range, often resulting in short to medium holding periods driven by market volatility. Explore how differing holding periods impact strategy effectiveness and risk management.
Entry/Exit Strategy
Position trading emphasizes long-term market trends by entering trades based on fundamental analysis and exiting when significant price movements confirm trend reversals, focusing on minimal trade frequency and maximizing profit potential. Grid trading employs a systematic entry and exit strategy by placing buy and sell orders at predetermined intervals to capitalize on market volatility without predicting direction, maintaining a neutral stance through multiple open positions. Explore detailed comparisons and strategy optimization to determine which suits your trading style best.
Risk Management
Position trading emphasizes long-term market trends to minimize risk exposure by holding trades for weeks or months, allowing for strategic entry and exit points based on fundamental analysis. Grid trading involves placing multiple buy and sell orders at set intervals to capitalize on market volatility but requires strict risk management to avoid significant losses during trending markets. Explore more to understand which strategy aligns best with your risk tolerance and investment goals.
Source and External Links
A guide to position trading: definition, examples and strategies - Position trading is a style focused on identifying ongoing trends to benefit from the majority of that movement, typically holding positions for weeks or months and using strategies like trend trading, breakout trading, and pullback trading.
A Beginners Guide for Position Traders: What Is Position Trading? - Position trading is a long-term approach where traders hold positions over an extended period to capture market trends, often relying on fundamental analysis combined with technical indicators such as moving averages and RSI.
Position Trading 101: A Beginner's Guide With Examples - Position trading involves holding trades from weeks to months to ride market trends, differing from buy-and-hold investing by allowing both long and short positions and focusing on exiting when trends reverse for active profit-taking.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com