Sovereign cloud offers enhanced data control and compliance by keeping information within specific national or organizational boundaries, ensuring stringent privacy and security standards. Federated cloud integrates multiple independent cloud systems, enabling shared resources and collaboration while maintaining individual autonomy over data governance. Explore the differences and benefits of sovereign and federated clouds to determine the best fit for your organization's technology strategy.
Why it is important
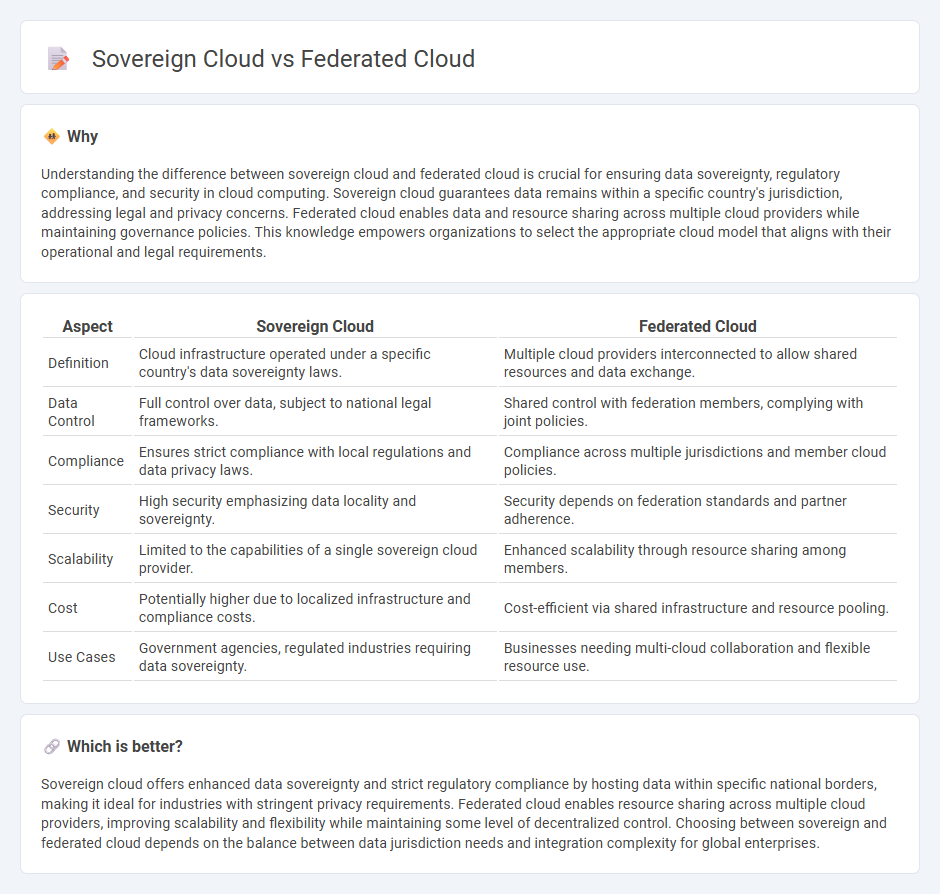
Understanding the difference between sovereign cloud and federated cloud is crucial for ensuring data sovereignty, regulatory compliance, and security in cloud computing. Sovereign cloud guarantees data remains within a specific country's jurisdiction, addressing legal and privacy concerns. Federated cloud enables data and resource sharing across multiple cloud providers while maintaining governance policies. This knowledge empowers organizations to select the appropriate cloud model that aligns with their operational and legal requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sovereign Cloud | Federated Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud infrastructure operated under a specific country's data sovereignty laws. | Multiple cloud providers interconnected to allow shared resources and data exchange. |
| Data Control | Full control over data, subject to national legal frameworks. | Shared control with federation members, complying with joint policies. |
| Compliance | Ensures strict compliance with local regulations and data privacy laws. | Compliance across multiple jurisdictions and member cloud policies. |
| Security | High security emphasizing data locality and sovereignty. | Security depends on federation standards and partner adherence. |
| Scalability | Limited to the capabilities of a single sovereign cloud provider. | Enhanced scalability through resource sharing among members. |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to localized infrastructure and compliance costs. | Cost-efficient via shared infrastructure and resource pooling. |
| Use Cases | Government agencies, regulated industries requiring data sovereignty. | Businesses needing multi-cloud collaboration and flexible resource use. |
Which is better?
Sovereign cloud offers enhanced data sovereignty and strict regulatory compliance by hosting data within specific national borders, making it ideal for industries with stringent privacy requirements. Federated cloud enables resource sharing across multiple cloud providers, improving scalability and flexibility while maintaining some level of decentralized control. Choosing between sovereign and federated cloud depends on the balance between data jurisdiction needs and integration complexity for global enterprises.
Connection
Sovereign cloud and federated cloud are connected through their emphasis on data sovereignty and regulatory compliance across distributed environments. Sovereign clouds ensure data residency and control within specific jurisdictions, while federated clouds enable multiple sovereign clouds to interoperate securely, sharing resources without compromising local governance. This integration fosters a collaborative yet compliant cloud ecosystem optimized for public sector and regulated industries.
Key Terms
Data Localization
Federated cloud architectures distribute data storage and processing across multiple jurisdictions, balancing compliance with global data protection regulations but may face challenges ensuring strict data localization. Sovereign cloud solutions emphasize full data residency within specific national boundaries, offering enhanced control and compliance with local data sovereignty laws to meet stringent regulatory requirements. Explore the differences in data localization strategies to determine which cloud model aligns best with your organization's governance needs.
Multi-cloud Architecture
Federated cloud involves multiple cloud providers collaborating to share resources while maintaining their autonomy, enhancing flexible multi-cloud architecture by enabling seamless workload portability and data interoperability. Sovereign cloud prioritizes data sovereignty and compliance with local regulations, ensuring sensitive information stays within geographic or jurisdictional boundaries, which is crucial for regulated industries adopting multi-cloud strategies. Explore the differences between federated and sovereign cloud models to optimize your multi-cloud architecture effectively.
Regulatory Compliance
Federated cloud integrates multiple cloud services across distinct organizations while maintaining regulatory compliance through shared governance and data sovereignty protocols. Sovereign cloud specifically addresses data residency and strict regulatory adherence by confining data storage and processing within national boundaries, ensuring compliance with local laws such as GDPR or HIPAA. Explore the differences in regulatory compliance frameworks to determine the best cloud strategy for your organization.
Source and External Links
What is cloud federation? - Milvus - Federated cloud allows multiple cloud environments from different providers to work as a single unified system, enabling seamless resource sharing, workload distribution, and unified identity management without users managing each cloud separately.
What is Cloud Federation? - GeeksforGeeks - Federated cloud integrates private, community, and public clouds using common standards, involving components like cloud exchange, cloud coordinator, and cloud broker to manage requests and resources across clouds.
Is Federation the Future of the Cloud? | Hyve Managed Hosting - Federated cloud connects different cloud services through standard APIs into a unified computing environment, offering benefits such as flexibility, resource pooling, redundancy, and avoiding vendor lock-in, distinct from multi-cloud or hybrid cloud models.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com