Sovereign cloud offers data sovereignty by ensuring that information is stored and managed within a specific country's jurisdiction, enhancing compliance and security compared to traditional colocation services. Colocation provides businesses with physical space and infrastructure to house their servers, giving more direct control over hardware but less regulatory assurance. Explore the advantages and distinctions between sovereign cloud and colocation to determine the best fit for your organization's data strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sovereign cloud and colocation is crucial for ensuring data privacy, regulatory compliance, and control over sensitive information. Sovereign cloud offers cloud services that adhere to specific national data sovereignty laws, while colocation provides physical space for servers without cloud-based management. Selecting the right option impacts data security strategies and legal obligations in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and government. Organizations must evaluate their needs for flexibility, compliance, and control to optimize their IT infrastructure.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Sovereign Cloud | Colocation |
|---|---|---|
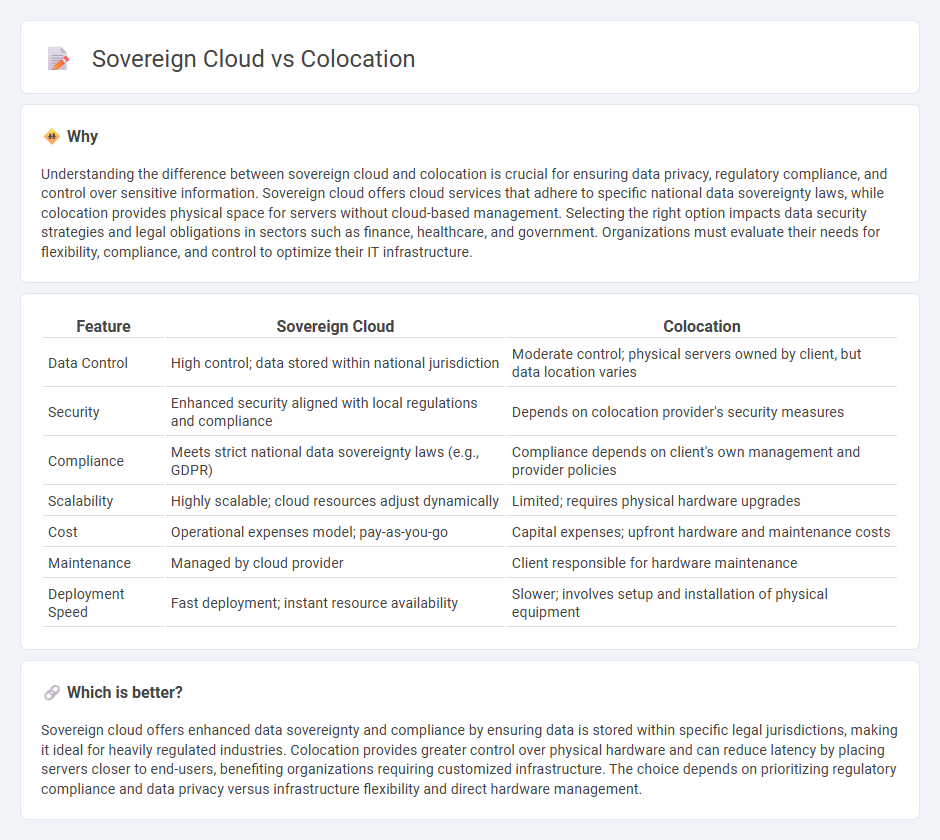
| Data Control | High control; data stored within national jurisdiction | Moderate control; physical servers owned by client, but data location varies |
| Security | Enhanced security aligned with local regulations and compliance | Depends on colocation provider's security measures |
| Compliance | Meets strict national data sovereignty laws (e.g., GDPR) | Compliance depends on client's own management and provider policies |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; cloud resources adjust dynamically | Limited; requires physical hardware upgrades |
| Cost | Operational expenses model; pay-as-you-go | Capital expenses; upfront hardware and maintenance costs |
| Maintenance | Managed by cloud provider | Client responsible for hardware maintenance |
| Deployment Speed | Fast deployment; instant resource availability | Slower; involves setup and installation of physical equipment |
Which is better?
Sovereign cloud offers enhanced data sovereignty and compliance by ensuring data is stored within specific legal jurisdictions, making it ideal for heavily regulated industries. Colocation provides greater control over physical hardware and can reduce latency by placing servers closer to end-users, benefiting organizations requiring customized infrastructure. The choice depends on prioritizing regulatory compliance and data privacy versus infrastructure flexibility and direct hardware management.
Connection
Sovereign cloud leverages colocation facilities to ensure data sovereignty by hosting infrastructure within specific geographic boundaries, complying with national regulations. Colocation offers secure, scalable physical environments where organizations can deploy sovereign cloud services while maintaining control over hardware and data residency. Combining these solutions enables businesses to enhance data privacy, regulatory compliance, and operational flexibility in cloud adoption.
Key Terms
Data Residency
Colocation facilities offer physical data residency by hosting servers within specific geographic locations, ensuring compliance with local data sovereignty laws. Sovereign cloud services provide virtualized environments designed to meet stringent national regulations, delivering enhanced control over data storage, access, and processing within a country's jurisdiction. Explore the differences in data residency solutions to determine the best fit for your compliance and security needs.
Physical Infrastructure
Colocation involves renting space in a third-party data center to house physical servers, offering robust power, cooling, and security infrastructure without ownership responsibilities. Sovereign cloud emphasizes dedicated physical infrastructure that ensures data residency and compliance by isolating hardware within specific national boundaries, often owned or tightly controlled by local entities. Explore the distinct physical infrastructure benefits of colocation and sovereign cloud to determine the best fit for your regulatory and operational needs.
Regulatory Compliance
Colocation facilities offer physical security and infrastructure control but often require extensive oversight to ensure compliance with regional data protection laws such as GDPR or HIPAA. Sovereign cloud solutions provide tailored environments designed to meet stringent regulatory requirements by localizing data storage and processing within specific jurisdictions, minimizing legal risks. Explore how choosing between colocation and sovereign cloud can impact your organization's regulatory compliance strategy.
Source and External Links
Colocation (business) - Wikipedia - Colocation involves placing multiple entities within a single location, applicable across various industries such as business, telecommunications, and retail.
What Is Colocation (Colo)? | Definition from TechTarget - Colocation facilities are data centers where businesses rent space for servers and other hardware, offering services like power, cooling, and security.
What is Colocation? Ultimate Guide to Colocation Benefits, FAQ - Colocation is the practice of renting space in a data center to host servers and IT equipment, providing a secure and efficient environment for operations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com