Generative audio employs advanced neural networks to create original soundscapes, music, or speech by learning patterns from extensive datasets, enabling innovative content production. Audio recognition utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze and identify audio signals, facilitating applications like voice commands, speech-to-text, and environmental sound detection. Explore the latest advancements in generative audio and audio recognition to understand their transformative impact on technology.
Why it is important
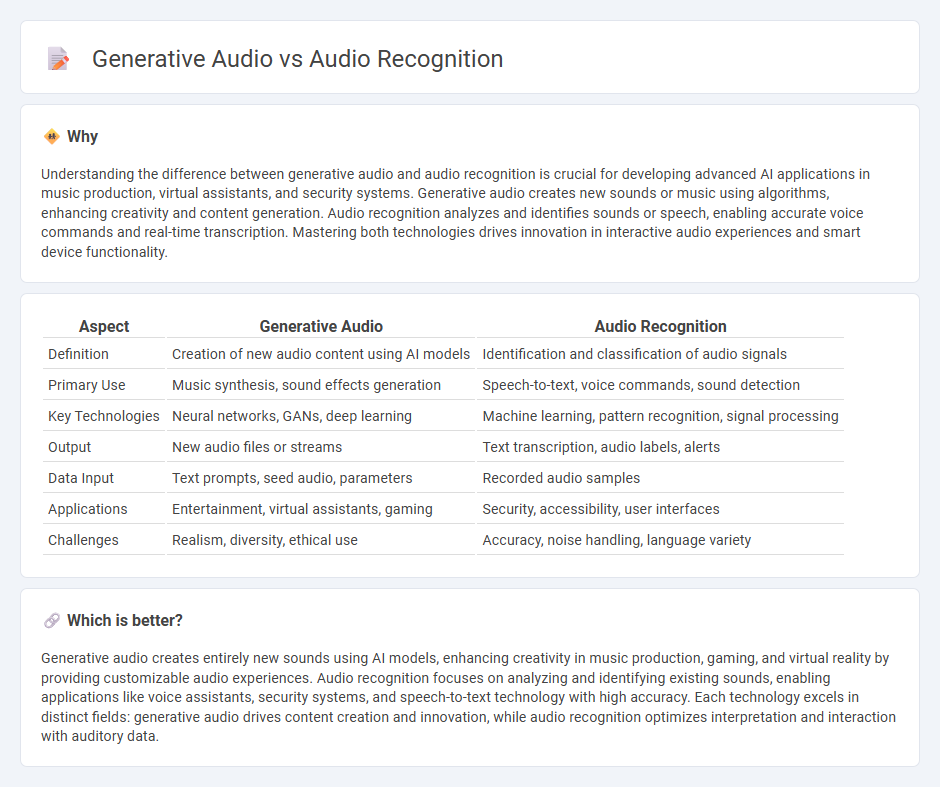
Understanding the difference between generative audio and audio recognition is crucial for developing advanced AI applications in music production, virtual assistants, and security systems. Generative audio creates new sounds or music using algorithms, enhancing creativity and content generation. Audio recognition analyzes and identifies sounds or speech, enabling accurate voice commands and real-time transcription. Mastering both technologies drives innovation in interactive audio experiences and smart device functionality.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Generative Audio | Audio Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creation of new audio content using AI models | Identification and classification of audio signals |
| Primary Use | Music synthesis, sound effects generation | Speech-to-text, voice commands, sound detection |
| Key Technologies | Neural networks, GANs, deep learning | Machine learning, pattern recognition, signal processing |
| Output | New audio files or streams | Text transcription, audio labels, alerts |
| Data Input | Text prompts, seed audio, parameters | Recorded audio samples |
| Applications | Entertainment, virtual assistants, gaming | Security, accessibility, user interfaces |
| Challenges | Realism, diversity, ethical use | Accuracy, noise handling, language variety |
Which is better?
Generative audio creates entirely new sounds using AI models, enhancing creativity in music production, gaming, and virtual reality by providing customizable audio experiences. Audio recognition focuses on analyzing and identifying existing sounds, enabling applications like voice assistants, security systems, and speech-to-text technology with high accuracy. Each technology excels in distinct fields: generative audio drives content creation and innovation, while audio recognition optimizes interpretation and interaction with auditory data.
Connection
Generative audio utilizes machine learning models to create new sounds or speech based on learned patterns, while audio recognition interprets and classifies existing audio data for identification or transcription tasks. Both technologies rely heavily on neural networks and large datasets to understand and manipulate audio signals, driving advancements in applications like voice assistants and sound synthesis. The integration of generative audio with audio recognition enhances interactive systems by enabling real-time audio generation informed by accurate audio input analysis.
Key Terms
**Audio Recognition:**
Audio recognition leverages advanced machine learning algorithms to identify and classify sounds, speech, and music by analyzing acoustic patterns and features such as frequency, amplitude, and temporal dynamics. Techniques like deep neural networks and convolutional neural networks enable high accuracy in applications ranging from voice assistants and transcription services to security systems and environmental monitoring. Discover more about how audio recognition is transforming interactive technologies and enhancing auditory data analysis.
Feature Extraction
Feature extraction in audio recognition involves analyzing and transforming raw audio signals into meaningful representations such as Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs) or spectrograms, enabling accurate speech or sound identification. In generative audio, feature extraction captures essential audio characteristics to inform models like WaveNet or GANs, which synthesize realistic soundscapes or voice outputs. Explore the technical nuances and applications of feature extraction in these two domains for a deeper understanding.
Classification
Audio recognition focuses on classifying sound inputs into predefined categories such as speech, music, or environmental noises using models like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or recurrent neural networks (RNNs). Generative audio, on the other hand, involves creating new audio content through techniques like generative adversarial networks (GANs) or variational autoencoders (VAEs), which is less about classification and more about synthesis. Explore further to understand the distinctive roles and applications of classification in audio recognition versus synthesis in generative audio.
Source and External Links
Sound recognition - Sound recognition technology uses pattern recognition and audio signal analysis to classify sounds for applications like music and speech recognition, surveillance alarms, and animal species identification.
What Is Speech Recognition? | IBM - Speech recognition, or automatic speech recognition (ASR), converts spoken language into text using AI and machine learning, involving components like speech input, feature extraction, and decoders that leverage acoustic and language models for accurate transcription.
ACRCloud - Audio Recognition Services For Doers - ACRCloud provides advanced audio recognition services including music recognition, broadcast monitoring, live channel detection, and copyright compliance, supported by APIs and patented algorithms for robust integration.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com