Soft robotics focuses on creating flexible, adaptive machines using compliant materials that mimic biological organisms, offering enhanced safety and versatility in delicate tasks. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, builds complex components layer-by-layer from digital models, enabling rapid prototyping and customization in production. Discover how these innovative manufacturing approaches are transforming industries by exploring their unique applications and benefits.
Why it is important
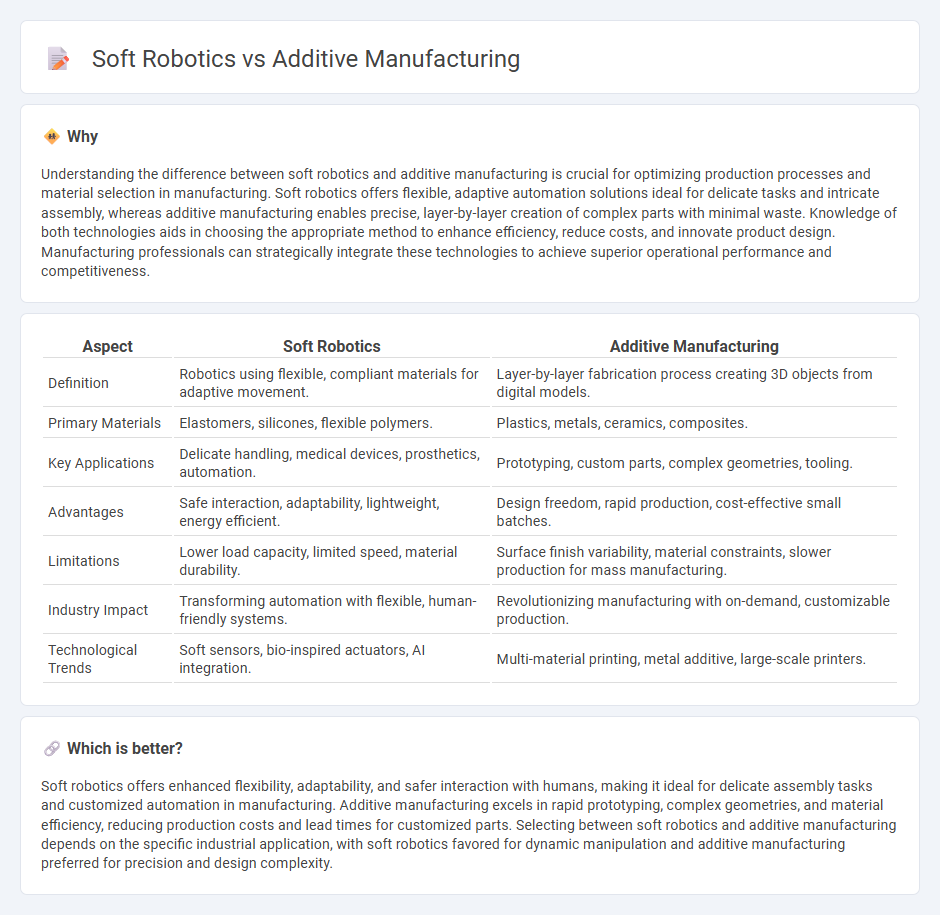
Understanding the difference between soft robotics and additive manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production processes and material selection in manufacturing. Soft robotics offers flexible, adaptive automation solutions ideal for delicate tasks and intricate assembly, whereas additive manufacturing enables precise, layer-by-layer creation of complex parts with minimal waste. Knowledge of both technologies aids in choosing the appropriate method to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and innovate product design. Manufacturing professionals can strategically integrate these technologies to achieve superior operational performance and competitiveness.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Robotics | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Robotics using flexible, compliant materials for adaptive movement. | Layer-by-layer fabrication process creating 3D objects from digital models. |
| Primary Materials | Elastomers, silicones, flexible polymers. | Plastics, metals, ceramics, composites. |
| Key Applications | Delicate handling, medical devices, prosthetics, automation. | Prototyping, custom parts, complex geometries, tooling. |
| Advantages | Safe interaction, adaptability, lightweight, energy efficient. | Design freedom, rapid production, cost-effective small batches. |
| Limitations | Lower load capacity, limited speed, material durability. | Surface finish variability, material constraints, slower production for mass manufacturing. |
| Industry Impact | Transforming automation with flexible, human-friendly systems. | Revolutionizing manufacturing with on-demand, customizable production. |
| Technological Trends | Soft sensors, bio-inspired actuators, AI integration. | Multi-material printing, metal additive, large-scale printers. |
Which is better?
Soft robotics offers enhanced flexibility, adaptability, and safer interaction with humans, making it ideal for delicate assembly tasks and customized automation in manufacturing. Additive manufacturing excels in rapid prototyping, complex geometries, and material efficiency, reducing production costs and lead times for customized parts. Selecting between soft robotics and additive manufacturing depends on the specific industrial application, with soft robotics favored for dynamic manipulation and additive manufacturing preferred for precision and design complexity.
Connection
Soft robotics and additive manufacturing are interconnected through the use of advanced 3D printing techniques that enable the fabrication of flexible, complex structures with precise control over material properties. Additive manufacturing allows for the integration of soft, compliant materials essential for creating robotic components that mimic natural movement and adaptability. This synergy drives innovations in custom-tailored soft robotic devices used in medical, industrial, and wearable applications.
Key Terms
3D Printing
Additive manufacturing revolutionizes soft robotics by enabling precise 3D printing of flexible materials and complex structures, significantly enhancing design customization and functionality. This integration facilitates the creation of lightweight, resilient soft robots with intricate geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve. Explore how advanced 3D printing technologies are transforming soft robotics innovation and design possibilities.
Flexible Actuators
Flexible actuators in soft robotics benefit significantly from additive manufacturing techniques due to their ability to create complex, custom geometries with high precision and material efficiency. Materials like silicone, TPU, and conductive polymers are frequently used, which can be precisely deposited layer by layer to achieve desired flexibility and responsiveness in actuators. Explore this synergy further to understand how advanced manufacturing drives innovation in soft robotics actuator design and performance.
Material Deposition
Additive manufacturing in material deposition relies on layer-by-layer fabrication techniques using polymers, metals, or composites to create precise, complex structures with high resolution and mechanical strength. Soft robotics emphasizes flexible, elastomeric materials deposited through techniques such as direct ink writing and pneumatic actuators to achieve adaptability, stretchability, and compliance in dynamic environments. Explore comprehensive insights into how material deposition advancements drive innovation in both additive manufacturing and soft robotics applications.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan - Additive manufacturing is the process of creating an object by building it one layer at a time from a digital design, often using 3D printing techniques that utilize materials like polymers, metals, and ceramics.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing (AM), also known as 3D printing, fabricates products layer-by-layer from digital designs, enabling complex shapes with less material waste and is increasingly used in industries like aerospace and biomedical implants.
What Is Additive Manufacturing? | 3D Printing Simulation Software - AM builds three-dimensional objects from digital CAD models by layering material using technologies such as powder bed fusion, material extrusion, and photopolymerization, with applications in prototyping, fixtures, and production parts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com