Mass customization combines the flexibility of custom-made products with the efficiency of mass production, allowing manufacturers to meet individual customer preferences while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Continuous production focuses on unbroken, high-volume manufacturing processes that maximize output and minimize downtime through automation. Explore how these approaches transform manufacturing efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Why it is important
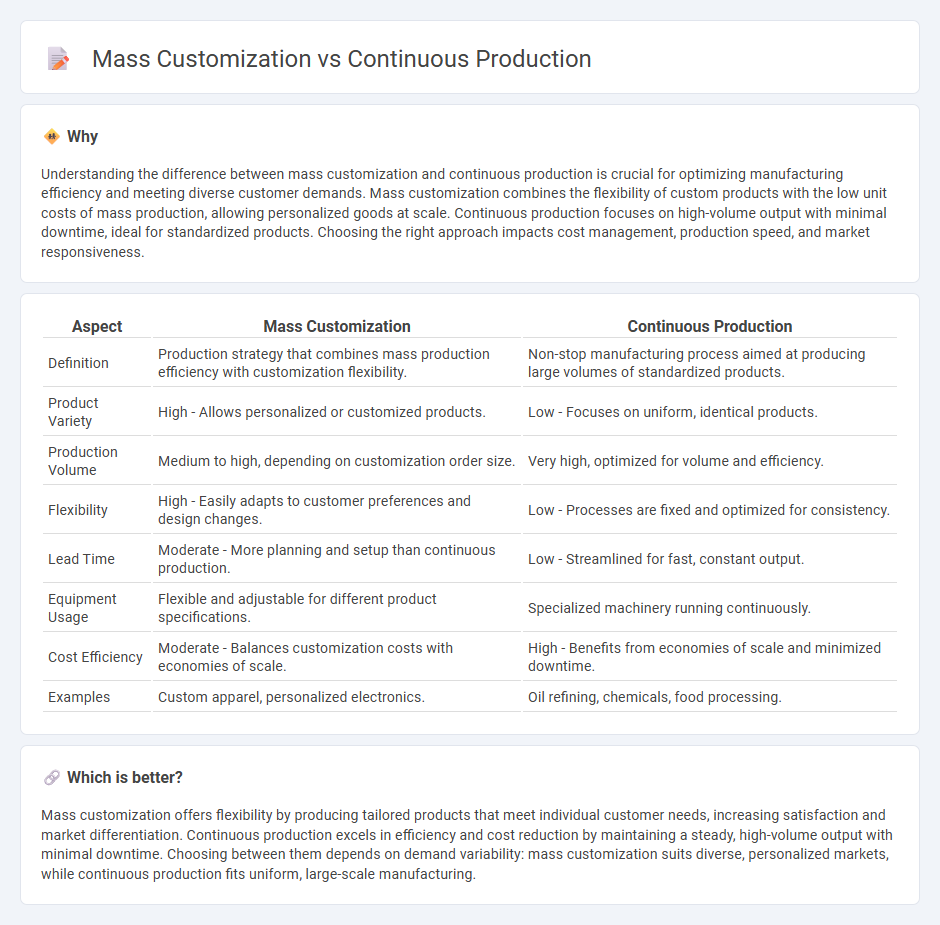
Understanding the difference between mass customization and continuous production is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and meeting diverse customer demands. Mass customization combines the flexibility of custom products with the low unit costs of mass production, allowing personalized goods at scale. Continuous production focuses on high-volume output with minimal downtime, ideal for standardized products. Choosing the right approach impacts cost management, production speed, and market responsiveness.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Mass Customization | Continuous Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production strategy that combines mass production efficiency with customization flexibility. | Non-stop manufacturing process aimed at producing large volumes of standardized products. |
| Product Variety | High - Allows personalized or customized products. | Low - Focuses on uniform, identical products. |
| Production Volume | Medium to high, depending on customization order size. | Very high, optimized for volume and efficiency. |
| Flexibility | High - Easily adapts to customer preferences and design changes. | Low - Processes are fixed and optimized for consistency. |
| Lead Time | Moderate - More planning and setup than continuous production. | Low - Streamlined for fast, constant output. |
| Equipment Usage | Flexible and adjustable for different product specifications. | Specialized machinery running continuously. |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate - Balances customization costs with economies of scale. | High - Benefits from economies of scale and minimized downtime. |
| Examples | Custom apparel, personalized electronics. | Oil refining, chemicals, food processing. |
Which is better?
Mass customization offers flexibility by producing tailored products that meet individual customer needs, increasing satisfaction and market differentiation. Continuous production excels in efficiency and cost reduction by maintaining a steady, high-volume output with minimal downtime. Choosing between them depends on demand variability: mass customization suits diverse, personalized markets, while continuous production fits uniform, large-scale manufacturing.
Connection
Mass customization integrates flexible manufacturing systems that adapt production lines to create personalized products without sacrificing efficiency, which aligns closely with continuous production processes designed for steady, uninterrupted output. Continuous production leverages automation and real-time data analytics to maintain consistent quality and speed, enabling seamless shifts between customized product variants. This synergy enhances responsiveness to customer demands while optimizing resource utilization in modern manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Standardization
Continuous production emphasizes high levels of standardization by manufacturing large volumes of uniform products, resulting in cost efficiency and consistent quality. Mass customization integrates flexibility into production processes, allowing for personalized products while maintaining some degree of standardization to optimize economies of scale. Explore how businesses balance standardization and customization to enhance competitiveness and customer satisfaction.
Flexibility
Continuous production offers high efficiency with standardized processes but lacks flexibility to accommodate varied customer demands. Mass customization combines the benefits of mass production and personalized products by adapting operations to deliver tailored solutions at scale. Explore how businesses balance these methods to optimize flexibility and competitiveness.
Production Volume
Continuous production excels in high production volumes by enabling uninterrupted manufacturing processes that maximize efficiency and minimize downtime. Mass customization balances volume and variety by producing customized products in moderate quantities using flexible manufacturing systems. Explore the advantages and applications of each approach to optimize your production strategy.
Source and External Links
Continuous Production - Continuous production is a manufacturing process running 24/7 without interruption to produce large quantities of standardized goods efficiently, heavily relying on automation and minimizing downtime.
Continuous Production System Guide - It is a flow production method where materials continuously move through processes using specialized machinery and automation to produce identical products without interruptions.
Continuous Production: Advantages & Disadvantages - This method features an uninterrupted, steady-state flow managed by automated systems and control tools, minimizing energy waste and ensuring consistent quality, though it requires high initial investment and low flexibility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com