Manufacturing is rapidly evolving with servitization focusing on adding value through services alongside products, while automation emphasizes using robotics and AI to enhance production efficiency. Servitization transforms traditional manufacturing by integrating maintenance, support, and customization services that increase customer satisfaction and revenue streams. Explore how these strategies impact operational excellence and competitive advantage in modern manufacturing.
Why it is important
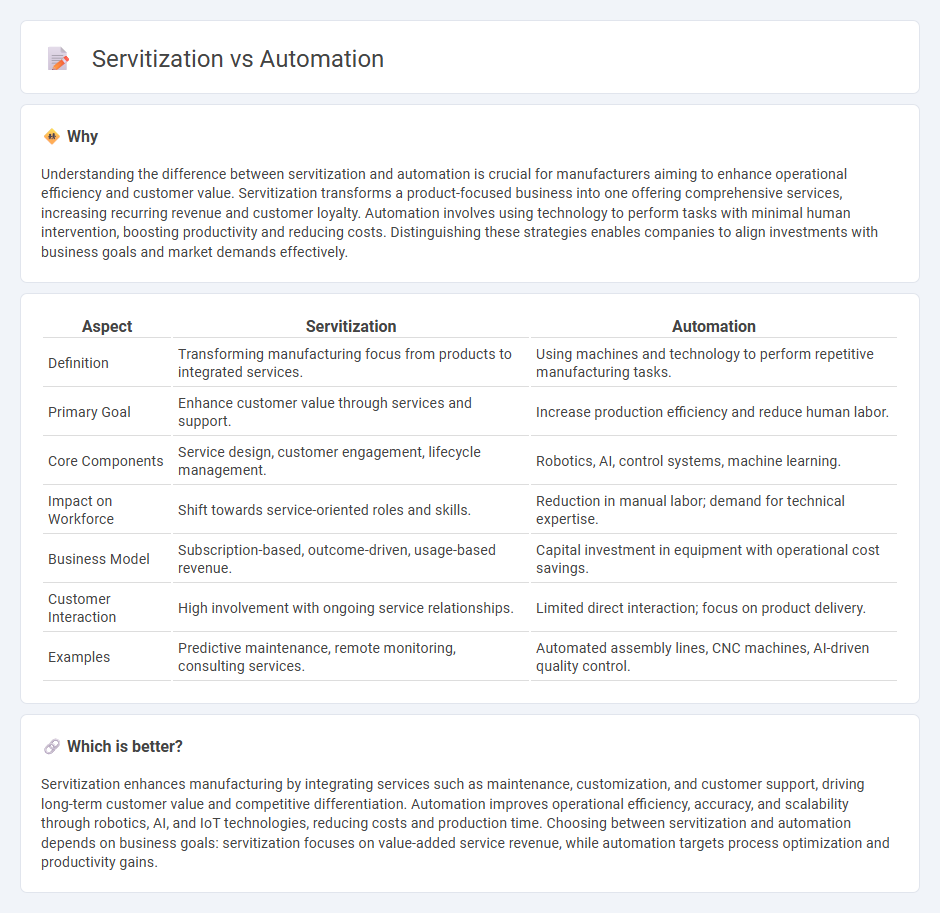
Understanding the difference between servitization and automation is crucial for manufacturers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and customer value. Servitization transforms a product-focused business into one offering comprehensive services, increasing recurring revenue and customer loyalty. Automation involves using technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention, boosting productivity and reducing costs. Distinguishing these strategies enables companies to align investments with business goals and market demands effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Servitization | Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transforming manufacturing focus from products to integrated services. | Using machines and technology to perform repetitive manufacturing tasks. |
| Primary Goal | Enhance customer value through services and support. | Increase production efficiency and reduce human labor. |
| Core Components | Service design, customer engagement, lifecycle management. | Robotics, AI, control systems, machine learning. |
| Impact on Workforce | Shift towards service-oriented roles and skills. | Reduction in manual labor; demand for technical expertise. |
| Business Model | Subscription-based, outcome-driven, usage-based revenue. | Capital investment in equipment with operational cost savings. |
| Customer Interaction | High involvement with ongoing service relationships. | Limited direct interaction; focus on product delivery. |
| Examples | Predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, consulting services. | Automated assembly lines, CNC machines, AI-driven quality control. |
Which is better?
Servitization enhances manufacturing by integrating services such as maintenance, customization, and customer support, driving long-term customer value and competitive differentiation. Automation improves operational efficiency, accuracy, and scalability through robotics, AI, and IoT technologies, reducing costs and production time. Choosing between servitization and automation depends on business goals: servitization focuses on value-added service revenue, while automation targets process optimization and productivity gains.
Connection
Servitization in manufacturing integrates service-based solutions with product offerings, enhancing customer value through continuous support and maintenance. Automation streamlines production processes, enabling real-time data collection and predictive analytics essential for delivering these advanced services effectively. Together, servitization and automation create a synergistic model that increases operational efficiency and drives innovative service opportunities.
Key Terms
Robotics
Robotics plays a pivotal role in automation by streamlining manufacturing processes and enhancing precision through programmable machines that reduce human intervention. In servitization, robotics extends beyond production to offer value-added services like predictive maintenance and remote monitoring, transforming traditional product-based models into service-oriented solutions. Explore how integrating robotics can revolutionize both automation and servitization strategies.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive Maintenance leverages automation to continuously monitor equipment health and predict failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Servitization transforms traditional product offerings into comprehensive service solutions, integrating predictive maintenance as a value-added service that enhances customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Explore the benefits and strategies behind combining automation with servitization in predictive maintenance for a competitive edge.
Product-as-a-Service
Automation enhances manufacturing efficiency by integrating advanced technologies such as robotics and AI to streamline production processes. Servitization shifts business models from selling products to offering Product-as-a-Service (PaaS), providing customers continuous access to products combined with ongoing services and maintenance. Explore how PaaS transforms traditional industries by increasing customer value and driving sustainable growth.
Source and External Links
Automation - Wikipedia - Automation is a broad range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes by predetermining decision criteria and actions, then embodying these in machines, often through mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electronic, and computer-based systems, with benefits including labor savings, improved quality, and cost reduction.
What Is Automation? - IBM - Automation is the application of technology, programs, robotics, or processes to achieve outcomes with minimal human input, enabling increased productivity, improved accuracy, reduced costs, and greater operational efficiency across industries.
Understanding automation - Red Hat - Automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks with reduced human assistance, particularly in fields like manufacturing, IT, and business processes, and includes methods such as robotic process automation, IT automation, and the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com