Farmland funds offer investors exposure to agriculture assets with steady returns and lower volatility compared to venture capital's high-risk, high-reward startup investments. Farmland benefits from land appreciation and crop yields, while venture capital targets rapid growth in innovative sectors like technology and biotech. Explore the differences in risk profiles and growth potential between these investment options to determine which aligns with your portfolio goals.
Why it is important
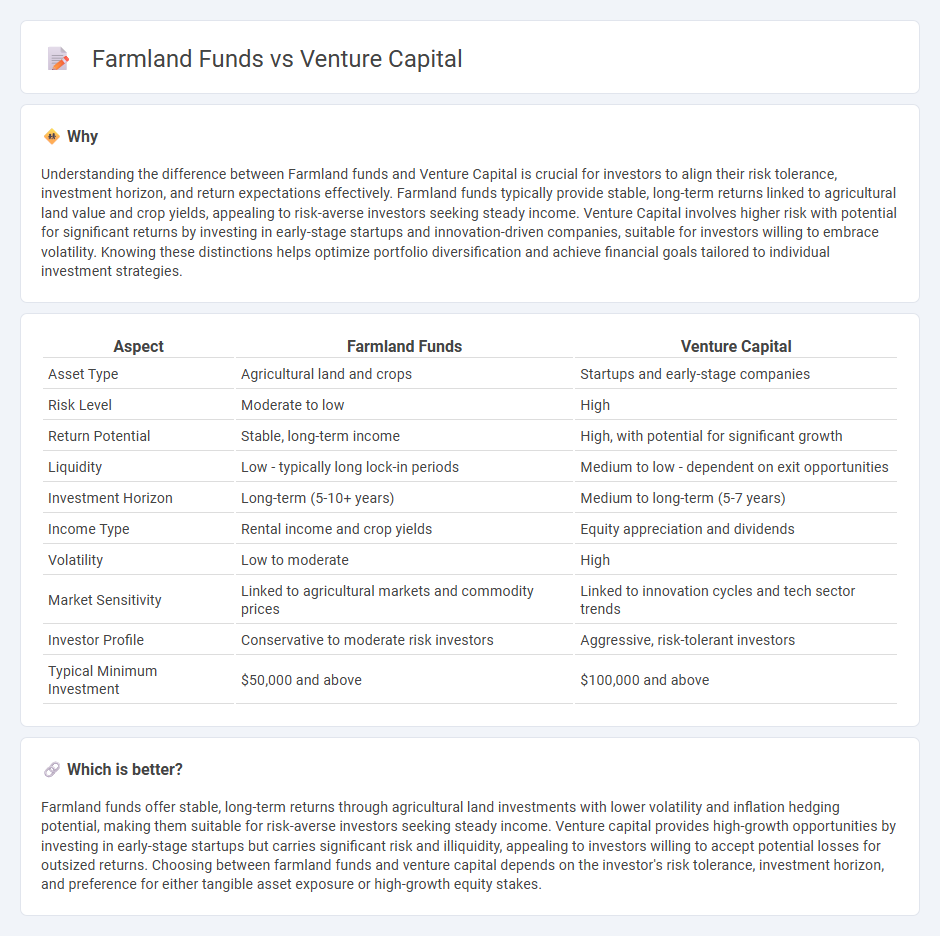
Understanding the difference between Farmland funds and Venture Capital is crucial for investors to align their risk tolerance, investment horizon, and return expectations effectively. Farmland funds typically provide stable, long-term returns linked to agricultural land value and crop yields, appealing to risk-averse investors seeking steady income. Venture Capital involves higher risk with potential for significant returns by investing in early-stage startups and innovation-driven companies, suitable for investors willing to embrace volatility. Knowing these distinctions helps optimize portfolio diversification and achieve financial goals tailored to individual investment strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Farmland Funds | Venture Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Type | Agricultural land and crops | Startups and early-stage companies |
| Risk Level | Moderate to low | High |
| Return Potential | Stable, long-term income | High, with potential for significant growth |
| Liquidity | Low - typically long lock-in periods | Medium to low - dependent on exit opportunities |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term (5-10+ years) | Medium to long-term (5-7 years) |
| Income Type | Rental income and crop yields | Equity appreciation and dividends |
| Volatility | Low to moderate | High |
| Market Sensitivity | Linked to agricultural markets and commodity prices | Linked to innovation cycles and tech sector trends |
| Investor Profile | Conservative to moderate risk investors | Aggressive, risk-tolerant investors |
| Typical Minimum Investment | $50,000 and above | $100,000 and above |
Which is better?
Farmland funds offer stable, long-term returns through agricultural land investments with lower volatility and inflation hedging potential, making them suitable for risk-averse investors seeking steady income. Venture capital provides high-growth opportunities by investing in early-stage startups but carries significant risk and illiquidity, appealing to investors willing to accept potential losses for outsized returns. Choosing between farmland funds and venture capital depends on the investor's risk tolerance, investment horizon, and preference for either tangible asset exposure or high-growth equity stakes.
Connection
Farmland funds and venture capital intersect through their shared emphasis on long-term growth and diversification within investment portfolios. Farmland funds attract venture capital by leveraging advancements in agricultural technology and sustainable practices to increase land productivity and asset value. This fusion enables venture capitalists to tap into the agritech sector, driving innovation while securing stable returns from farmland assets.
Key Terms
Equity Stake
Venture capital investments typically offer equity stakes in high-growth startups, providing potential for significant returns but with higher risk and liquidity challenges. Farmland funds invest in agricultural land, delivering more stable returns with tangible asset backing and often less volatility. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which equity stake option aligns with your investment goals.
Asset Under Management
Venture capital funds typically manage assets ranging from $100 million to over $1 billion, focusing on high-growth startups across various sectors. Farmland funds generally hold assets under management between $500 million and $2 billion, investing in stable, income-generating agricultural land. Explore more to understand which fund type aligns best with your investment goals.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Venture capital funds typically offer higher return on investment (ROI) potential, averaging 20-30% annually, driven by high-growth technology startups and innovation sectors. Farmland funds, while yielding more modest returns around 8-12% annually, provide stable cash flow and hedge against inflation due to the intrinsic value and productivity of agricultural land. Explore detailed comparisons and risk profiles to identify the optimal investment strategy for your portfolio.
Source and External Links
What is Venture Capital? - Venture capital provides high-risk, long-term equity investments to innovative startups and high-growth companies, fueling job creation and growing major tech companies like Microsoft and Apple, while offering entrepreneurs strategic guidance and capital that traditional financing cannot supply.
Fund your business | U.S. Small Business Administration - Venture capital is investment funding exchanged for equity, typically focused on startups with high growth potential; it involves investors taking active roles such as board seats, and follows a process including finding investors, due diligence, and negotiation of terms.
What is venture capital? - Silicon Valley Bank - Venture capital is a form of private equity that supports early-stage startups with substantial growth prospects by providing capital, technical support, and managerial expertise in exchange for ownership stakes, often critical for driving innovation and industry expansion.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com