Investing in sports team ownership shares offers unique opportunities for portfolio diversification through tangible assets linked to franchise valuations and fan engagement, often yielding long-term capital appreciation. Hedge funds provide access to diverse strategies including equity, fixed income, and derivatives trading, aiming for higher liquidity and risk-adjusted returns in dynamic markets. Discover the comparative benefits and risks of sports team ownership versus hedge fund investments to tailor your financial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sports team ownership shares and hedge funds is crucial for investors seeking diversified asset allocation, as sports team shares often represent long-term, passion-driven investments with low liquidity, whereas hedge funds typically offer liquid, professionally managed portfolios aiming for high returns through diverse strategies. Sports team ownership involves equity in a physical asset with brand value and fan base impact, contrasting with hedge funds that pool capital to invest in securities, derivatives, or alternative assets for financial growth. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors evaluate risk, market behavior, and potential returns aligned with their financial goals. This knowledge enhances strategic decision-making in portfolio management and capital deployment.
Comparison Table
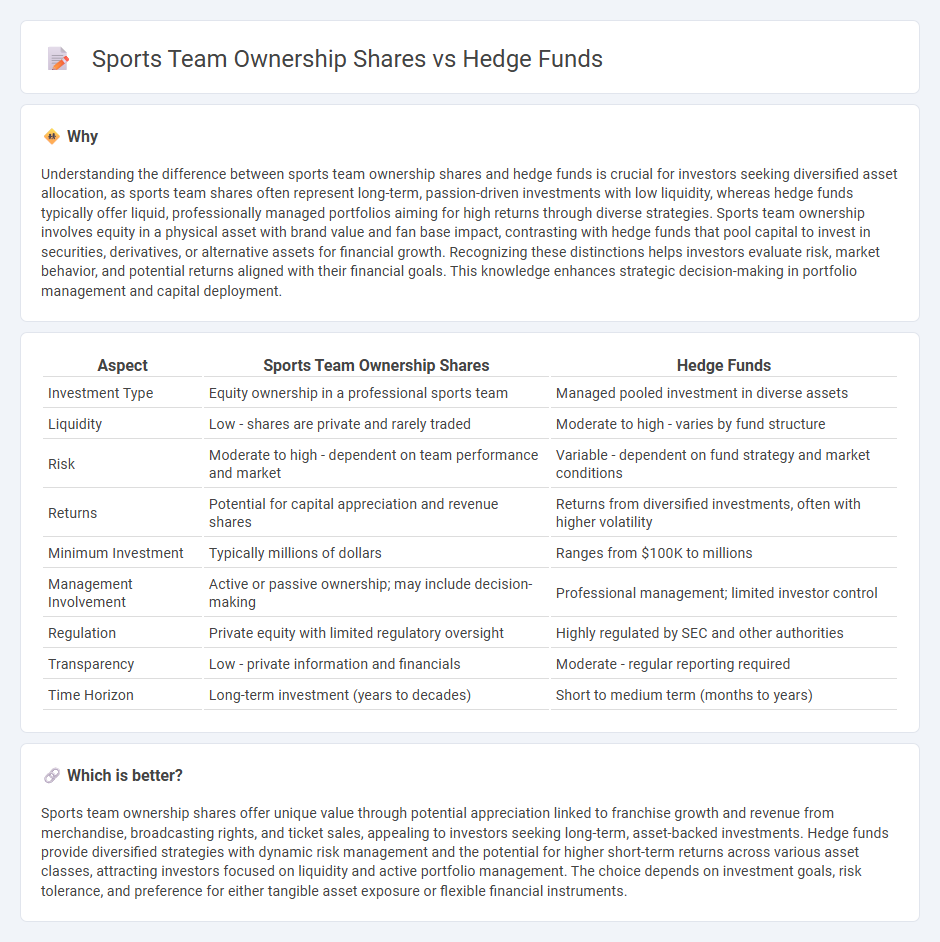
| Aspect | Sports Team Ownership Shares | Hedge Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Equity ownership in a professional sports team | Managed pooled investment in diverse assets |
| Liquidity | Low - shares are private and rarely traded | Moderate to high - varies by fund structure |
| Risk | Moderate to high - dependent on team performance and market | Variable - dependent on fund strategy and market conditions |
| Returns | Potential for capital appreciation and revenue shares | Returns from diversified investments, often with higher volatility |
| Minimum Investment | Typically millions of dollars | Ranges from $100K to millions |
| Management Involvement | Active or passive ownership; may include decision-making | Professional management; limited investor control |
| Regulation | Private equity with limited regulatory oversight | Highly regulated by SEC and other authorities |
| Transparency | Low - private information and financials | Moderate - regular reporting required |
| Time Horizon | Long-term investment (years to decades) | Short to medium term (months to years) |
Which is better?
Sports team ownership shares offer unique value through potential appreciation linked to franchise growth and revenue from merchandise, broadcasting rights, and ticket sales, appealing to investors seeking long-term, asset-backed investments. Hedge funds provide diversified strategies with dynamic risk management and the potential for higher short-term returns across various asset classes, attracting investors focused on liquidity and active portfolio management. The choice depends on investment goals, risk tolerance, and preference for either tangible asset exposure or flexible financial instruments.
Connection
Sports team ownership shares offer hedge funds a unique alternative asset class, enabling portfolio diversification beyond traditional equities and bonds. Hedge funds leverage these shares to capitalize on the growing valuation of sports franchises and associated revenue streams such as broadcasting rights, merchandising, and ticket sales. This intersection drives increased liquidity and investment returns, reflecting broader trends in alternative investments within the sports industry.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Hedge funds offer high liquidity with frequent trading opportunities, enabling quick entry and exit through daily or weekly redemptions. Sports team ownership shares are typically illiquid, with limited transfer windows and long holding periods, often requiring approval from other stakeholders. Explore more to understand the liquidity dynamics between these two investment types.
Risk profile
Hedge funds exhibit a high-risk profile due to leveraged investments, market volatility, and complex financial derivatives that can lead to substantial gains or losses. Sports team ownership shares carry risks tied to team performance, market demand, and league regulations but often provide long-term value appreciation and brand equity. Explore comprehensive analyses on risk dynamics between hedge funds and sports team ownership shares for informed investment decisions.
Regulation
Hedge funds and sports team ownership shares are both subject to rigorous regulatory frameworks but differ significantly in scope and oversight; hedge funds face stringent compliance with the SEC's Investment Advisers Act and must adhere to complex reporting and disclosure requirements. Sports team ownership shares are regulated primarily by league-specific rules and the NFL, NBA, and MLB impose strict approval processes and ownership restrictions to maintain competitive balance and financial integrity. Discover the distinct regulatory environments shaping these high-profile investment avenues.
Source and External Links
Hedge Funds: Overview, Recruitment, Careers & Salaries - Hedge funds are private investment firms that raise capital from institutional and accredited investors to invest in a broad range of alternative strategies aimed at achieving absolute returns, including short selling and derivatives, differentiating them from mutual funds that focus on relative returns.
Hedge Funds | Investor.gov - Hedge funds are private, unregistered investment funds limited to sophisticated investors, using flexible and often higher-risk strategies not available to mutual funds, and are less regulated, which can increase the risk of investment losses.
Hedge fund - Wikipedia - Hedge funds are pooled investment funds managing trillions in assets that utilize complex trading, risk management techniques, and often leverage, paying management and performance fees, with strategies that may or may not hedge risk and that have the potential to contribute to systemic financial risk.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com