Spice trading involves the buying and selling of valuable spices like cinnamon, pepper, and cardamom, often leveraging market demand and global supply chains for profit. REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) allow investors to earn returns from diversified real estate portfolios without direct property ownership, offering liquidity and steady income through dividends. Explore the unique benefits and risks of spice trading versus REIT investments to make informed financial decisions.
Why it is important
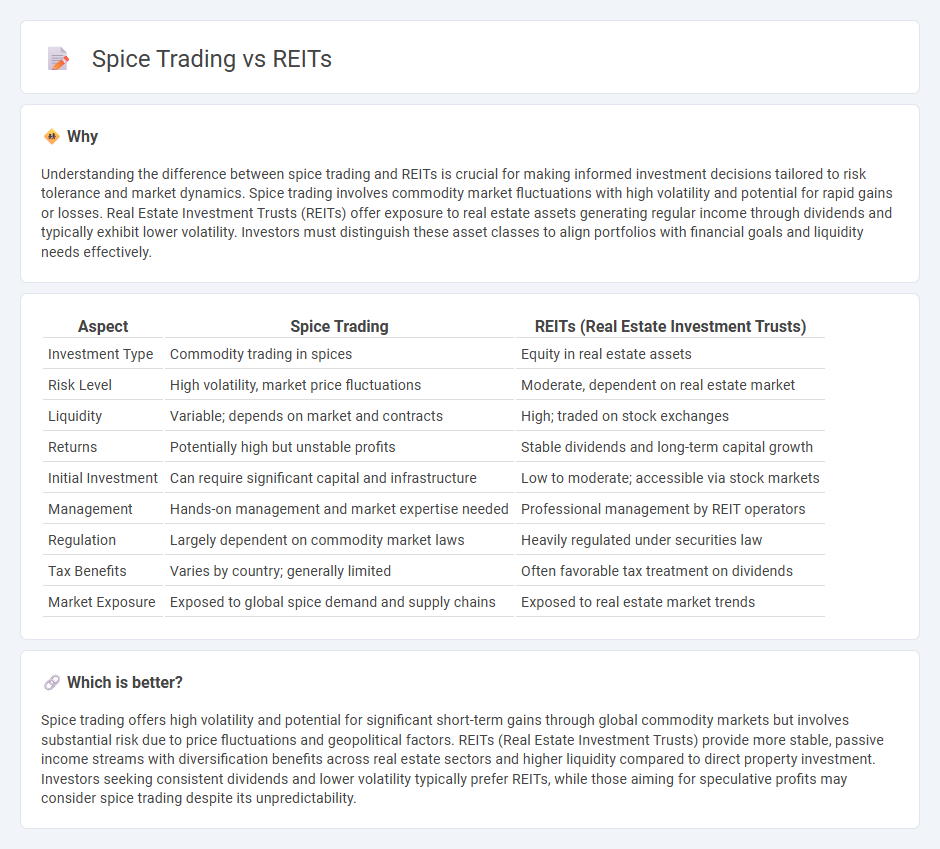
Understanding the difference between spice trading and REITs is crucial for making informed investment decisions tailored to risk tolerance and market dynamics. Spice trading involves commodity market fluctuations with high volatility and potential for rapid gains or losses. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) offer exposure to real estate assets generating regular income through dividends and typically exhibit lower volatility. Investors must distinguish these asset classes to align portfolios with financial goals and liquidity needs effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Spice Trading | REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Commodity trading in spices | Equity in real estate assets |
| Risk Level | High volatility, market price fluctuations | Moderate, dependent on real estate market |
| Liquidity | Variable; depends on market and contracts | High; traded on stock exchanges |
| Returns | Potentially high but unstable profits | Stable dividends and long-term capital growth |
| Initial Investment | Can require significant capital and infrastructure | Low to moderate; accessible via stock markets |
| Management | Hands-on management and market expertise needed | Professional management by REIT operators |
| Regulation | Largely dependent on commodity market laws | Heavily regulated under securities law |
| Tax Benefits | Varies by country; generally limited | Often favorable tax treatment on dividends |
| Market Exposure | Exposed to global spice demand and supply chains | Exposed to real estate market trends |
Which is better?
Spice trading offers high volatility and potential for significant short-term gains through global commodity markets but involves substantial risk due to price fluctuations and geopolitical factors. REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) provide more stable, passive income streams with diversification benefits across real estate sectors and higher liquidity compared to direct property investment. Investors seeking consistent dividends and lower volatility typically prefer REITs, while those aiming for speculative profits may consider spice trading despite its unpredictability.
Connection
Spice trading historically fueled wealth accumulation and global commerce, creating capital pools that investors later channeled into real estate. Modern Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) often benefit from economic infrastructures and trade hubs initially established by spice trade routes, enhancing property values in strategic locations. The legacy of spice trade underscores the transformation of commodity wealth into diversified investment vehicles like REITs, highlighting a continuum from physical goods to real estate assets.
Key Terms
Diversification
REITs provide diversification through real estate assets, generating steady income from property rentals and capital appreciation, reducing portfolio volatility. Spice trading offers diversification by leveraging commodity market fluctuations and global demand trends, though it carries higher risk and market sensitivity. Explore the strategic benefits of blending REITs and spice trading to optimize your investment diversification.
Liquidity
REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) generally offer higher liquidity compared to spice trading due to their presence on public exchanges, allowing investors to buy and sell shares quickly. Spice trading, being a physical commodity market, often involves longer transaction times and less market transparency, impacting liquidity negatively. Explore more to understand how liquidity dynamics affect investment strategies in these sectors.
Asset-backed
Asset-backed REITs and spice trading both involve tangible assets but differ significantly in structure and risk profile. REITs provide investors with liquidity and diversified exposure to real estate assets, offering regular income through dividends backed by property earnings. Explore the distinctions in asset valuation and market dynamics between these investment types to better understand their potential benefits.
Source and External Links
Wikipedia - Real estate investment trust - A REIT is a company that owns and typically operates income-producing real estate or related assets, often traded on major exchanges and offering investors a way to access real estate income without direct property ownership.
Investor.gov - Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) - REITs allow individuals to invest in large-scale, income-producing properties like offices, malls, and apartments, with shares available on public exchanges or as non-traded investments.
Nareit - What's a REIT? - Modeled after mutual funds, REITs provide regular income streams, diversification, and potential for capital appreciation by owning or financing a range of property sectors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com