Crypto staking offers investors the potential for passive income through locking digital assets, often yielding higher returns compared to traditional financial instruments. Bonds provide a more stable, lower-risk investment option by lending money to entities in exchange for fixed interest payments over time. Explore the differences between crypto staking and bonds to determine which investment strategy aligns with your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between crypto staking and bonds is crucial because staking involves locking digital assets to support blockchain operations and earn rewards, while bonds represent debt investments with fixed interest payments. Knowledge of their risk profiles is essential; staking carries higher volatility and potential rewards, whereas bonds typically offer more stability and lower returns. Investors can optimize portfolio diversification by balancing staking's growth potential with bonds' income security. Awareness of regulatory and liquidity differences further informs suitable investment choices.
Comparison Table
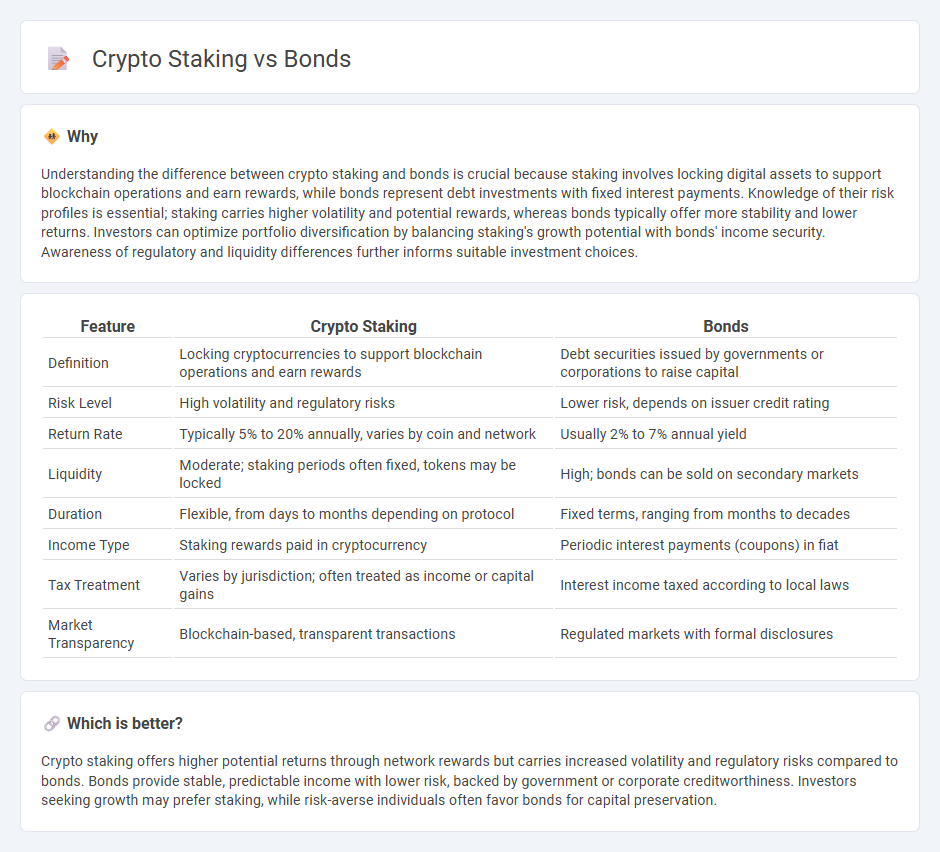
| Feature | Crypto Staking | Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Locking cryptocurrencies to support blockchain operations and earn rewards | Debt securities issued by governments or corporations to raise capital |
| Risk Level | High volatility and regulatory risks | Lower risk, depends on issuer credit rating |
| Return Rate | Typically 5% to 20% annually, varies by coin and network | Usually 2% to 7% annual yield |
| Liquidity | Moderate; staking periods often fixed, tokens may be locked | High; bonds can be sold on secondary markets |
| Duration | Flexible, from days to months depending on protocol | Fixed terms, ranging from months to decades |
| Income Type | Staking rewards paid in cryptocurrency | Periodic interest payments (coupons) in fiat |
| Tax Treatment | Varies by jurisdiction; often treated as income or capital gains | Interest income taxed according to local laws |
| Market Transparency | Blockchain-based, transparent transactions | Regulated markets with formal disclosures |
Which is better?
Crypto staking offers higher potential returns through network rewards but carries increased volatility and regulatory risks compared to bonds. Bonds provide stable, predictable income with lower risk, backed by government or corporate creditworthiness. Investors seeking growth may prefer staking, while risk-averse individuals often favor bonds for capital preservation.
Connection
Crypto staking and bonds both represent investment strategies that generate passive income through locked assets. Staking involves committing cryptocurrency to support blockchain network operations in exchange for rewards, akin to receiving periodic interest payments from bonds. Both methods provide investors with predictable returns while contributing to the financial ecosystem's stability and growth.
Key Terms
Yield
Bond yields typically range between 1% and 5%, offering steady income with lower risk and government backing. Crypto staking yields vary widely, often from 5% to 20% or more, driven by network incentives and tokenomics but accompanied by higher volatility and potential loss. Explore detailed comparisons of bond and crypto staking yields to optimize your investment strategy.
Risk
Bonds offer lower risk with predictable returns and government or corporate backing, while crypto staking involves higher volatility and potential loss due to market fluctuations and technical vulnerabilities. Bondholders benefit from fixed interest payments and principal protection, compared to the variable rewards and smart contract risks in crypto staking protocols. Explore the detailed risk profiles and decide which investment aligns with your financial goals.
Liquidity
Bonds offer relatively high liquidity through secondary markets, enabling investors to buy or sell before maturity with predictable pricing based on market interest rates. Crypto staking typically locks assets for fixed periods, reducing liquidity and creating potential risks if funds need to be accessed quickly. Explore further to understand how liquidity differences impact your investment strategy in bonds and crypto staking.
Source and External Links
Bonds | Investor.gov - Bonds are debt securities issued by borrowers to raise money, offering investors a predictable income stream and principal repayment at maturity.
Bond (finance) - Wikipedia - Bonds provide external funds for long-term investments, typically offering a lower volatility investment compared to stocks.
Treasury Bonds - TreasuryDirect - Treasury Bonds offer terms of 20 or 30 years, paying a fixed interest rate every six months until maturity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com