Forestry investment offers sustainable growth through timber asset appreciation and carbon credit opportunities, contrasting with real estate investment that focuses on property value and rental income. Timberlands provide long-term ecological benefits and diversification away from traditional markets, while real estate is often favored for liquidity and capital gains. Explore detailed comparisons to decide which investment aligns best with your financial goals.
Why it is important
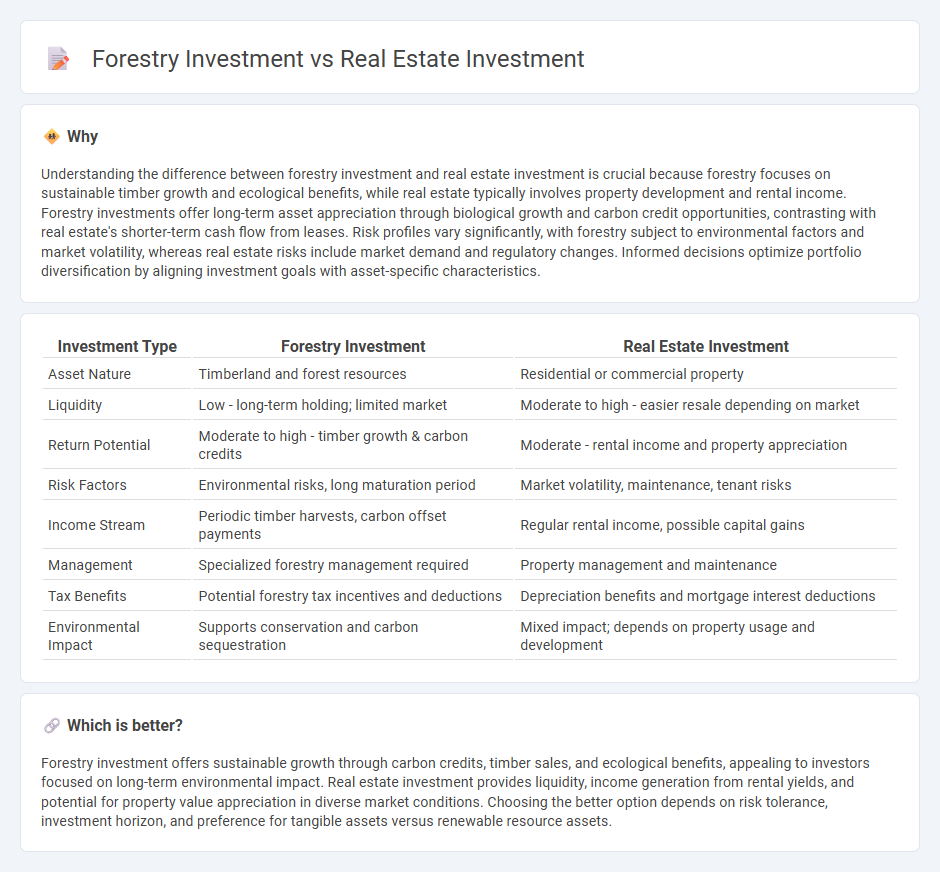
Understanding the difference between forestry investment and real estate investment is crucial because forestry focuses on sustainable timber growth and ecological benefits, while real estate typically involves property development and rental income. Forestry investments offer long-term asset appreciation through biological growth and carbon credit opportunities, contrasting with real estate's shorter-term cash flow from leases. Risk profiles vary significantly, with forestry subject to environmental factors and market volatility, whereas real estate risks include market demand and regulatory changes. Informed decisions optimize portfolio diversification by aligning investment goals with asset-specific characteristics.
Comparison Table
| Investment Type | Forestry Investment | Real Estate Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Nature | Timberland and forest resources | Residential or commercial property |
| Liquidity | Low - long-term holding; limited market | Moderate to high - easier resale depending on market |
| Return Potential | Moderate to high - timber growth & carbon credits | Moderate - rental income and property appreciation |
| Risk Factors | Environmental risks, long maturation period | Market volatility, maintenance, tenant risks |
| Income Stream | Periodic timber harvests, carbon offset payments | Regular rental income, possible capital gains |
| Management | Specialized forestry management required | Property management and maintenance |
| Tax Benefits | Potential forestry tax incentives and deductions | Depreciation benefits and mortgage interest deductions |
| Environmental Impact | Supports conservation and carbon sequestration | Mixed impact; depends on property usage and development |
Which is better?
Forestry investment offers sustainable growth through carbon credits, timber sales, and ecological benefits, appealing to investors focused on long-term environmental impact. Real estate investment provides liquidity, income generation from rental yields, and potential for property value appreciation in diverse market conditions. Choosing the better option depends on risk tolerance, investment horizon, and preference for tangible assets versus renewable resource assets.
Connection
Forestry investment and real estate investment are connected through land asset management, where both involve long-term appreciation and sustainable resource utilization. Timberland properties offer dual income streams from timber sales and potential real estate development, enhancing portfolio diversification. Integrating forestry with real estate investments aligns environmental stewardship with economic growth by maximizing land value and promoting ecological benefits.
Key Terms
Asset Appreciation
Real estate investment offers significant asset appreciation through urban development, rising property values, and rental income potential, making it a popular choice for wealth growth. Forestry investment, while often slower to appreciate, provides long-term capital gains driven by timber growth, carbon credits, and sustainable land management practices. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which investment aligns best with your financial goals.
Liquidity
Real estate investment typically offers higher liquidity through resale or rental markets, allowing investors to access funds more quickly compared to forestry investments, which often require long-term commitments due to growth cycles and harvesting periods. Forestry investments provide steady returns through timber sales and environmental credits but face challenges like market volatility and longer lock-in durations. Explore the detailed liquidity aspects of real estate and forestry investments to make informed decisions.
Yield
Real estate investment typically offers steady rental income and potential capital appreciation, with average yields ranging from 4% to 8% annually depending on location and property type. Forestry investment yields vary significantly based on tree species, growth rates, and market demand, often providing returns between 5% and 12% over longer investment horizons. Explore detailed comparisons of yield dynamics and risk factors in real estate and forestry investments to make informed decisions.
Source and External Links
Real Estate Investing: 5 Ways to Get Started - NerdWallet - Offers five main ways to invest in real estate including buying REITs, using real estate investing platforms, purchasing rental properties, and flipping investment properties, detailing pros and risks especially with REITs.
4 ways to invest in real estate - Fidelity - Describes popular approaches such as purchasing a home, investing in REITs, mutual funds or ETFs, and becoming a landlord, highlighting benefits like equity building, tax advantages, and inflation hedges.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) | Investor.gov - Explains that REITs are companies that own and operate income-producing real estate and provide individual investors access to commercial real estate income without direct property ownership, differentiating publicly traded versus non-traded REITs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com