Investment in the space economy has surged with global spending expected to reach $1.1 trillion by 2040, driven by satellite infrastructure, space tourism, and resource mining opportunities. In contrast, agriculture investment focuses on sustainable practices and technology adoption, with the sector valued at over $3 trillion globally, critical for food security and climate resilience. Explore deeper insights into how these sectors compare and complement each other for diversified investment portfolios.
Why it is important
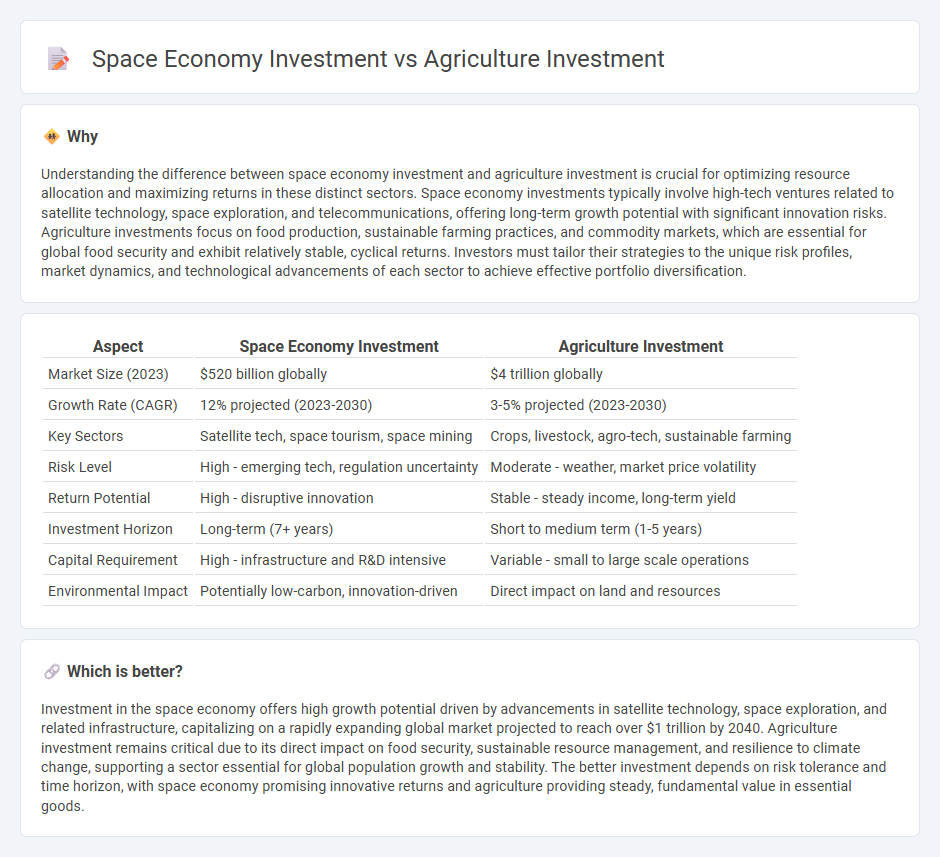
Understanding the difference between space economy investment and agriculture investment is crucial for optimizing resource allocation and maximizing returns in these distinct sectors. Space economy investments typically involve high-tech ventures related to satellite technology, space exploration, and telecommunications, offering long-term growth potential with significant innovation risks. Agriculture investments focus on food production, sustainable farming practices, and commodity markets, which are essential for global food security and exhibit relatively stable, cyclical returns. Investors must tailor their strategies to the unique risk profiles, market dynamics, and technological advancements of each sector to achieve effective portfolio diversification.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Space Economy Investment | Agriculture Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Market Size (2023) | $520 billion globally | $4 trillion globally |
| Growth Rate (CAGR) | 12% projected (2023-2030) | 3-5% projected (2023-2030) |
| Key Sectors | Satellite tech, space tourism, space mining | Crops, livestock, agro-tech, sustainable farming |
| Risk Level | High - emerging tech, regulation uncertainty | Moderate - weather, market price volatility |
| Return Potential | High - disruptive innovation | Stable - steady income, long-term yield |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term (7+ years) | Short to medium term (1-5 years) |
| Capital Requirement | High - infrastructure and R&D intensive | Variable - small to large scale operations |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially low-carbon, innovation-driven | Direct impact on land and resources |
Which is better?
Investment in the space economy offers high growth potential driven by advancements in satellite technology, space exploration, and related infrastructure, capitalizing on a rapidly expanding global market projected to reach over $1 trillion by 2040. Agriculture investment remains critical due to its direct impact on food security, sustainable resource management, and resilience to climate change, supporting a sector essential for global population growth and stability. The better investment depends on risk tolerance and time horizon, with space economy promising innovative returns and agriculture providing steady, fundamental value in essential goods.
Connection
Investment in the space economy enhances agricultural productivity through advanced satellite technologies that monitor crop health, optimize irrigation, and predict weather patterns. Funding in space-based infrastructure like Earth observation satellites directly supports precision agriculture by providing real-time data critical for sustainable farming practices. These synergistic investments drive innovation in agritech, improving food security and resource management globally.
Key Terms
**Agriculture Investment:**
Agriculture investment drives global food security by enhancing crop yields, supporting sustainable farming technologies, and boosting rural economies through job creation and infrastructure development. Investments in precision agriculture, biotechnology, and irrigation systems significantly increase productivity while reducing environmental impact. Explore how targeted agriculture funding transforms food systems and strengthens economic resilience worldwide.
Crop yield
Investing in agriculture directly enhances crop yield by funding advanced technologies such as precision farming, genetically modified seeds, and efficient irrigation systems, resulting in increased food production and sustainability. Space economy investment, while pivotal for satellite technology and climate monitoring, indirectly supports crop yield optimization through improved data on weather patterns and soil health. Explore deeper into how these investments shape the future of global food security and space innovation.
Land acquisition
Investment in agriculture heavily prioritizes land acquisition due to its critical role in crop production and livestock rearing, with arable land prices varying widely across regions but consistently impacting overall investment costs. In contrast, space economy investment rarely involves land acquisition, as it focuses more on technology development, satellite deployment, and space exploration infrastructure, where physical land is a minimal factor compared to specialized facilities. Explore further to understand the nuanced differences in resource allocation between these two vital sectors.
Source and External Links
Investing in farmland | Nuveen - Farmland offers stable returns, low correlation to other assets, and serves as a hedge against inflation as global demand for food and limited arable land rise.
Are Agricultural Investments Right for You? | Weiland Farms - Agriculture investments can diversify your portfolio through tangible assets like farmland, commodities, or AgTech, appealing to those seeking both financial returns and social impact.
Investing in Agriculture | AgAmerica - AgAmerica provides customized debt and equity solutions for agricultural land, aiming for attractive risk-adjusted returns while supporting farmers and addressing long-term food security challenges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com