Forestry investment offers a tangible asset with long-term growth potential through timber production and carbon credit opportunities, contrasting with equities that provide liquid ownership in companies with variable market-driven returns. Unlike equities, forestry assets tend to have lower volatility and can serve as a hedge against inflation due to the intrinsic value of land and natural resources. Discover how forestry investment can diversify your portfolio alongside traditional equity holdings.
Why it is important
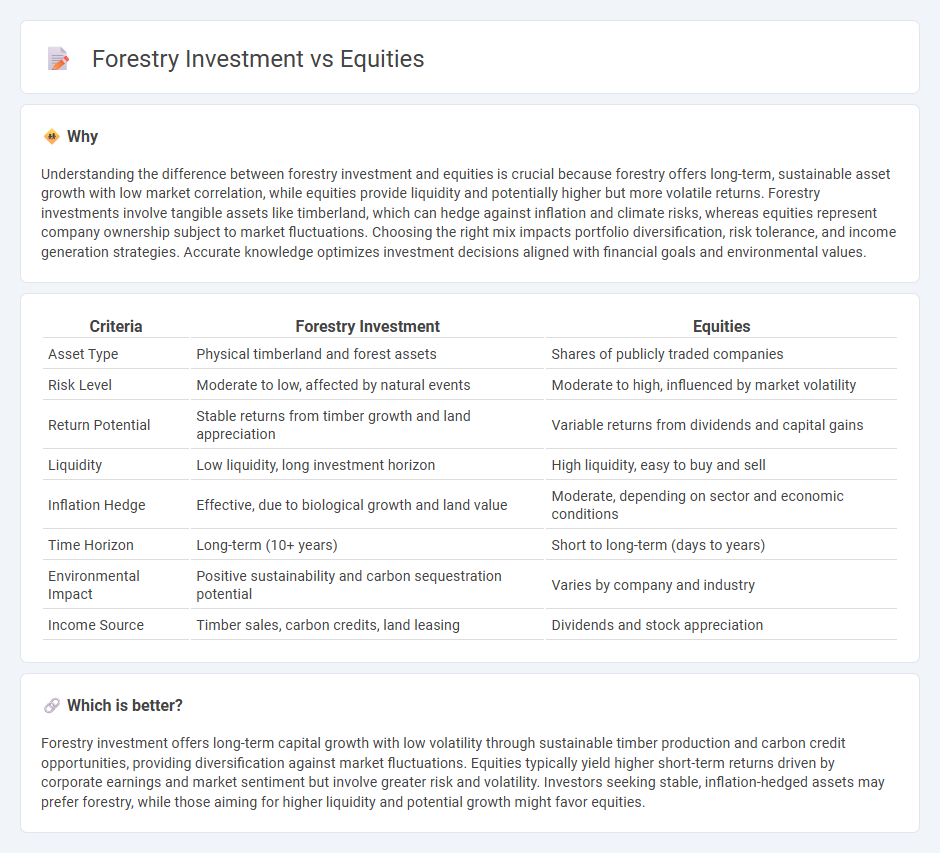
Understanding the difference between forestry investment and equities is crucial because forestry offers long-term, sustainable asset growth with low market correlation, while equities provide liquidity and potentially higher but more volatile returns. Forestry investments involve tangible assets like timberland, which can hedge against inflation and climate risks, whereas equities represent company ownership subject to market fluctuations. Choosing the right mix impacts portfolio diversification, risk tolerance, and income generation strategies. Accurate knowledge optimizes investment decisions aligned with financial goals and environmental values.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Forestry Investment | Equities |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Type | Physical timberland and forest assets | Shares of publicly traded companies |
| Risk Level | Moderate to low, affected by natural events | Moderate to high, influenced by market volatility |
| Return Potential | Stable returns from timber growth and land appreciation | Variable returns from dividends and capital gains |
| Liquidity | Low liquidity, long investment horizon | High liquidity, easy to buy and sell |
| Inflation Hedge | Effective, due to biological growth and land value | Moderate, depending on sector and economic conditions |
| Time Horizon | Long-term (10+ years) | Short to long-term (days to years) |
| Environmental Impact | Positive sustainability and carbon sequestration potential | Varies by company and industry |
| Income Source | Timber sales, carbon credits, land leasing | Dividends and stock appreciation |
Which is better?
Forestry investment offers long-term capital growth with low volatility through sustainable timber production and carbon credit opportunities, providing diversification against market fluctuations. Equities typically yield higher short-term returns driven by corporate earnings and market sentiment but involve greater risk and volatility. Investors seeking stable, inflation-hedged assets may prefer forestry, while those aiming for higher liquidity and potential growth might favor equities.
Connection
Forestry investment and equities intersect through timberland investment trusts (REITs) and publicly traded companies specializing in sustainable forestry management, offering investors access to both natural resource assets and equity markets. These investments provide diversification by combining the long-term growth potential of timber assets with the liquidity and volatility of equities. Market trends indicate that forestry equities often correlate with commodity prices and environmental policies, influencing investor strategies focused on sustainable and responsible investing.
Key Terms
Return on Investment (ROI)
Equities typically offer higher short-term Return on Investment (ROI) driven by market liquidity and dividend yields, whereas forestry investments provide steady, long-term capital appreciation through timber growth and carbon credit potential. Forestry assets present lower volatility and act as a hedge against inflation, appealing to investors seeking sustainable portfolio diversification. Explore detailed ROI comparisons and risk profiles to determine the best fit for your investment strategy.
Asset Liquidity
Equities offer higher asset liquidity due to their ability to be quickly bought and sold on public markets, allowing investors to access funds with minimal delay. Forestry investments, while providing long-term growth and environmental benefits, tend to have lower liquidity because they involve physical land assets and longer holding periods. Explore the differences in asset liquidity between equities and forestry investments to make informed financial decisions.
Diversification
Equities provide exposure to a broad range of industries, offering liquidity and potential for rapid growth, while forestry investment delivers stable, long-term returns with natural asset backing and environmental benefits. Diversification in a portfolio including equities and forestry can reduce overall risk by balancing market volatility with tangible asset stability. Explore further to understand how combining these asset classes enhances financial resilience.
Source and External Links
Introduction to Equities - Financial Education - Equities are shares representing fractional ownership in a company, providing shareholders claims on returns and assets, with types including common shares, preferred shares, and convertible preferred shares, each with distinct rights and priorities.
What Are Equities or Equity Investments? - Equities, commonly called stocks, represent ownership in a company entitling investors to a share of profits and assets, with common stocks offering voting rights and dividends, while preferred stocks usually offer fixed dividends without voting rights.
Equity (finance) - In finance, equity is an ownership interest in assets after liabilities, often represented as shareholders' equity which is the residual interest after all debts, with shareholders typically having voting rights and a residual claim on company assets upon liquidation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com