Investing in wine cask aging offers a tangible asset that appreciates through enhanced flavor profiles and rarity over time, contrasting with private equity's focus on capital growth via equity stakes in private companies. Both investment types carry unique risks and diversification benefits, with wine casks appealing to collectors and connoisseurs, while private equity targets financial returns through leveraged buyouts and growth strategies. Explore the nuances of each investment to determine which aligns best with your portfolio goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between wine cask aging and private equity investment is crucial for optimizing asset allocation and managing risk effectively. Wine cask aging represents a tangible, illiquid asset with value depending on vintage quality and market demand, while private equity involves investing in ownership stakes in private companies with potential for high returns and long-term growth. Recognizing these distinctions enables investors to diversify portfolios, balance liquidity needs, and tailor investment strategies to personal financial goals and risk tolerance. Proper knowledge can enhance decision-making in niche markets like alternative investments.
Comparison Table
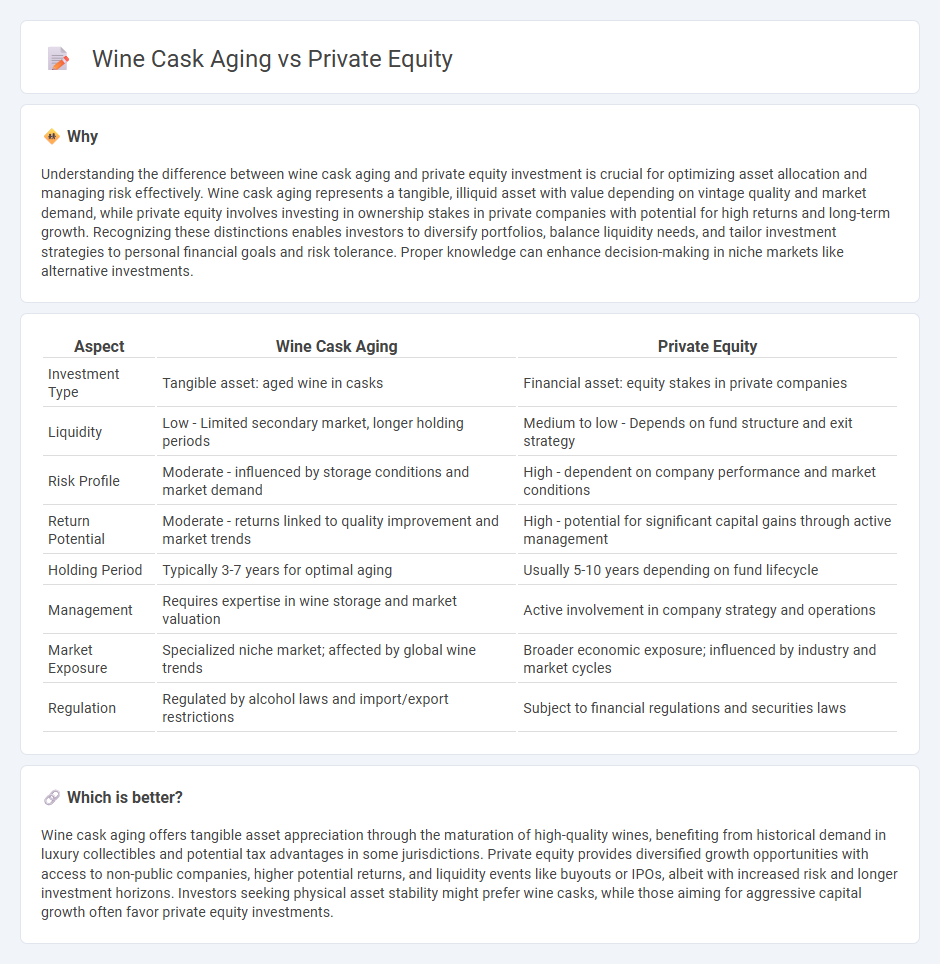
| Aspect | Wine Cask Aging | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Tangible asset: aged wine in casks | Financial asset: equity stakes in private companies |
| Liquidity | Low - Limited secondary market, longer holding periods | Medium to low - Depends on fund structure and exit strategy |
| Risk Profile | Moderate - influenced by storage conditions and market demand | High - dependent on company performance and market conditions |
| Return Potential | Moderate - returns linked to quality improvement and market trends | High - potential for significant capital gains through active management |
| Holding Period | Typically 3-7 years for optimal aging | Usually 5-10 years depending on fund lifecycle |
| Management | Requires expertise in wine storage and market valuation | Active involvement in company strategy and operations |
| Market Exposure | Specialized niche market; affected by global wine trends | Broader economic exposure; influenced by industry and market cycles |
| Regulation | Regulated by alcohol laws and import/export restrictions | Subject to financial regulations and securities laws |
Which is better?
Wine cask aging offers tangible asset appreciation through the maturation of high-quality wines, benefiting from historical demand in luxury collectibles and potential tax advantages in some jurisdictions. Private equity provides diversified growth opportunities with access to non-public companies, higher potential returns, and liquidity events like buyouts or IPOs, albeit with increased risk and longer investment horizons. Investors seeking physical asset stability might prefer wine casks, while those aiming for aggressive capital growth often favor private equity investments.
Connection
Wine cask aging and private equity share a common principle of value appreciation over time through careful management and patience. Just as wine matures and develops complexity in oak barrels, private equity investments grow in value through strategic operational improvements and market positioning. Both require long-term commitment and expertise to maximize returns and achieve superior asset performance.
Key Terms
Illiquidity
Private equity investments often involve significant illiquidity, requiring capital to be locked in for years before returns are realized, similar to the aging process of wine casks that demands patience for flavor development. Both assets emphasize long-term value creation but differ in market tradability, with private equity generally offering more structured exit options than wine casks. Explore the nuances of illiquidity in private equity and wine cask aging to understand how investors balance risk and return in these unique markets.
Due diligence
Due diligence in private equity involves comprehensive financial analysis, risk assessment, and validation of a target company's operational performance, ensuring informed investment decisions. In wine cask aging, due diligence centers on monitoring cask conditions, wood quality, and environmental factors affecting maturation to guarantee product consistency and value. Explore further to understand how meticulous due diligence enhances success in both private equity investments and wine aging processes.
Asset appreciation
Private equity investments often deliver asset appreciation through strategic company growth, operational improvements, and market expansion, leading to significant financial returns over time. In contrast, wine cask aging enhances value by naturally developing complexity and quality, with market demand and rarity influencing its price appreciation. Explore how these distinct asset classes compare in terms of risk, growth potential, and liquidity.
Source and External Links
What is Private Equity? - BVCA - Private equity is medium to long-term finance in exchange for equity in high-growth unquoted companies, focusing on operational improvements through active ownership and close management collaboration, typically holding investments for 4 to 7 years before an exit.
Private equity - Wikipedia - Private equity involves investment managers raising funds from institutions and wealthy individuals to purchase stakes in private companies using equity and debt, aiming to increase returns through revenue growth, margin expansion, cash flow improvements, or valuation multiple gains over a 4-7 year horizon.
Private Equity Funds | Investor.gov - Private equity funds pool money from investors to take controlling or minority interests in companies, actively managing these businesses over a typical 10+ year horizon to grow value, and unlike mutual funds, are not registered with the SEC or subject to regular public disclosure.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com