Fractionalized art investment offers accessible ownership in high-value artworks by dividing assets into smaller shares, allowing investors to diversify with lower capital compared to traditional private equity. Private equity typically involves large-scale investments in private companies with longer lock-in periods and higher entry thresholds. Explore how fractionalized art investment compares to private equity to enhance your portfolio diversification strategies.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between fractionalized art investment and private equity is crucial because fractionalized art allows investors to buy shares of high-value artworks with lower entry costs and increased liquidity, whereas private equity involves investing in private companies with longer lock-up periods and higher capital requirements. Fractionalized art investment offers diversification in alternative assets without the complexities of corporate governance seen in private equity. Understanding these distinctions helps investors align their portfolios with risk tolerance, liquidity needs, and investment horizons. Proper knowledge enhances decision-making efficiency in emerging markets and traditional financial instruments.
Comparison Table
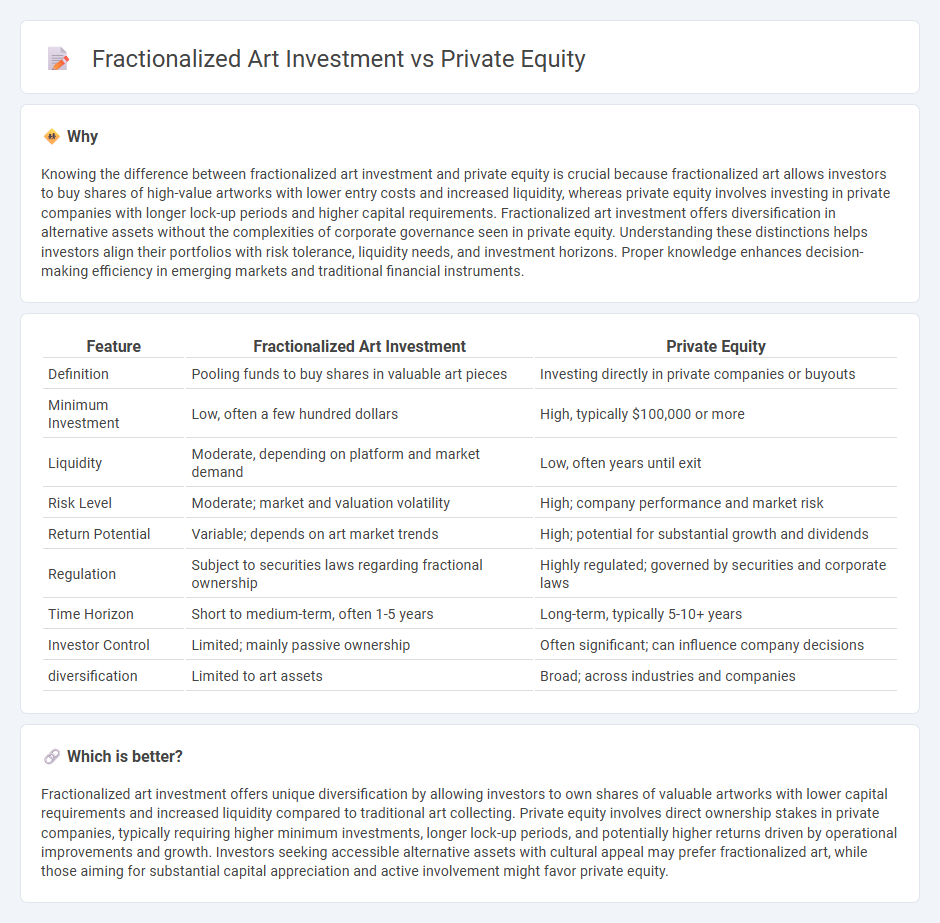
| Feature | Fractionalized Art Investment | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pooling funds to buy shares in valuable art pieces | Investing directly in private companies or buyouts |
| Minimum Investment | Low, often a few hundred dollars | High, typically $100,000 or more |
| Liquidity | Moderate, depending on platform and market demand | Low, often years until exit |
| Risk Level | Moderate; market and valuation volatility | High; company performance and market risk |
| Return Potential | Variable; depends on art market trends | High; potential for substantial growth and dividends |
| Regulation | Subject to securities laws regarding fractional ownership | Highly regulated; governed by securities and corporate laws |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium-term, often 1-5 years | Long-term, typically 5-10+ years |
| Investor Control | Limited; mainly passive ownership | Often significant; can influence company decisions |
| diversification | Limited to art assets | Broad; across industries and companies |
Which is better?
Fractionalized art investment offers unique diversification by allowing investors to own shares of valuable artworks with lower capital requirements and increased liquidity compared to traditional art collecting. Private equity involves direct ownership stakes in private companies, typically requiring higher minimum investments, longer lock-up periods, and potentially higher returns driven by operational improvements and growth. Investors seeking accessible alternative assets with cultural appeal may prefer fractionalized art, while those aiming for substantial capital appreciation and active involvement might favor private equity.
Connection
Fractionalized art investment and private equity both enable diversified ownership by pooling capital from multiple investors to acquire high-value assets. Fractionalized art investment splits expensive artworks into shares, allowing smaller investors access similar to private equity's model of holding equity in private companies. Both approaches leverage asset appreciation potential while mitigating risk through shared ownership structures.
Key Terms
Ownership structure
Private equity investments typically involve acquiring significant equity stakes or full ownership in companies, granting investors direct control and voting rights. Fractionalized art investment breaks down high-value artworks into smaller, tradeable shares, allowing multiple investors partial ownership without individual control. Explore the differences in ownership models to understand the implications for investment control and liquidity.
Liquidity
Private equity investments typically require long lock-up periods, limiting liquidity and making it challenging to exit before fund maturity. Fractionalized art investment leverages blockchain technology to enable real-time trading of shares, offering significantly higher liquidity compared to traditional private equity. Explore the advantages of liquidity in these investment models to make informed financial decisions.
Valuation
Private equity valuation typically relies on cash flow analysis, market comparables, and asset-based approaches, providing a comprehensive financial overview of company worth. Fractionalized art investment valuation is often more subjective, depending heavily on art market trends, provenance, and rarity, with fluctuating values tied to collector demand. Explore deeper insights into how valuation methods differ between these investment types to optimize portfolio strategy.
Source and External Links
Private equity - Wikipedia - Private equity is an investment in private companies offered to specialized funds, where managers raise money from institutional investors and use equity plus debt financing to buy ownership stakes aiming for returns through various growth and margin strategies over 4-7 years.
What is Private Equity? - BVCA - Private equity is medium to long-term finance in exchange for equity stakes in unquoted companies, focusing on active ownership by working closely with management to drive sustainable growth and operational improvements before exiting in 4-7 years.
What does a career in private equity look like? - CFA Institute - Private equity involves investing in private or public companies using funds raised from limited partners, with general partners actively managing and restructuring companies using strategies like venture capital, growth equity, and buyouts to improve performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com