Investing in viticulture land offers the potential for steady income through vineyard operations and the growing demand for premium wines, while residential real estate typically provides more liquidity and consistent rental income. Viticulture land acquisition requires specialized knowledge of agriculture and climate suitability, whereas residential properties benefit from broader market appeal and easier resale. Explore the advantages and challenges of each investment type to make an informed decision.
Why it is important
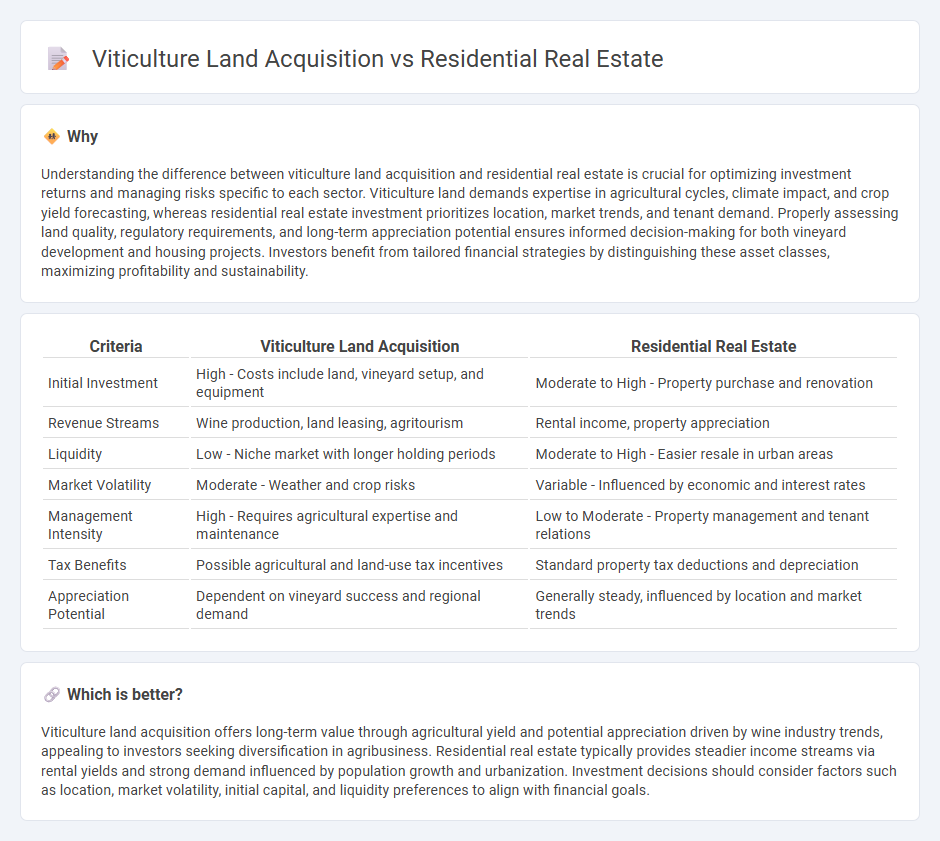
Understanding the difference between viticulture land acquisition and residential real estate is crucial for optimizing investment returns and managing risks specific to each sector. Viticulture land demands expertise in agricultural cycles, climate impact, and crop yield forecasting, whereas residential real estate investment prioritizes location, market trends, and tenant demand. Properly assessing land quality, regulatory requirements, and long-term appreciation potential ensures informed decision-making for both vineyard development and housing projects. Investors benefit from tailored financial strategies by distinguishing these asset classes, maximizing profitability and sustainability.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Viticulture Land Acquisition | Residential Real Estate |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | High - Costs include land, vineyard setup, and equipment | Moderate to High - Property purchase and renovation |
| Revenue Streams | Wine production, land leasing, agritourism | Rental income, property appreciation |
| Liquidity | Low - Niche market with longer holding periods | Moderate to High - Easier resale in urban areas |
| Market Volatility | Moderate - Weather and crop risks | Variable - Influenced by economic and interest rates |
| Management Intensity | High - Requires agricultural expertise and maintenance | Low to Moderate - Property management and tenant relations |
| Tax Benefits | Possible agricultural and land-use tax incentives | Standard property tax deductions and depreciation |
| Appreciation Potential | Dependent on vineyard success and regional demand | Generally steady, influenced by location and market trends |
Which is better?
Viticulture land acquisition offers long-term value through agricultural yield and potential appreciation driven by wine industry trends, appealing to investors seeking diversification in agribusiness. Residential real estate typically provides steadier income streams via rental yields and strong demand influenced by population growth and urbanization. Investment decisions should consider factors such as location, market volatility, initial capital, and liquidity preferences to align with financial goals.
Connection
Viticulture land acquisition often attracts investors seeking diversification in agricultural real estate, which can enhance portfolio stability by combining income-generating vineyard properties with appreciating residential real estate assets. Both asset types exhibit potential for capital growth and cash flow, leveraging location-driven value, especially in emerging wine regions with increasing residential demand. Strategic investment in these sectors capitalizes on synergies between lifestyle-driven purchases and agricultural productivity, optimizing returns in mixed-use land development markets.
Key Terms
Zoning regulations
Zoning regulations for residential real estate prioritize housing density, building codes, and land use restrictions to ensure community growth and safety, while viticulture land acquisition requires specific agricultural zoning that supports vineyard cultivation, soil protection, and water management. Residential zones often allow for infrastructure development and public utilities that cater to families and urban living, contrasting with viticulture zoning designed to preserve agricultural viability and minimize environmental impact. Explore detailed zoning considerations to make informed decisions on land acquisition tailored to your investment goals.
Market valuation
Market valuation for residential real estate typically depends on factors like location, neighborhood demand, infrastructure, and comparable property sales, whereas viticulture land is valued based on soil quality, climate suitability, grape varietals, and agricultural potential. Residential properties usually have a more stable and transparent market with frequent transaction data, while viticulture land valuation involves specialized agronomic assessments and long-term investment projections. Explore in-depth valuation methodologies and market trends to optimize acquisition strategies in these distinct sectors.
Yield potential
Residential real estate typically offers steady rental income and appreciation potential, driven by demand for housing and urban development trends. Viticulture land acquisition presents a unique yield potential through grape production, wine sales, and agritourism, influenced by factors like soil quality, climate, and vineyard management. Explore the nuances behind yield potential in these sectors to make informed investment decisions.
Source and External Links
Residential Real Estate - This webpage explains that residential real estate includes properties used for housing, contrasting it with commercial or industrial properties.
Residential Real Estate - National Association of REALTORS - This page highlights residential real estate as a primary focus for most REALTORS, emphasizing skills development for supporting clients in buying and selling homes.
Trulia - This website offers comprehensive listings of homes for sale and rent, along with neighborhood insights to help users find the right property.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com