Crowdlending platforms enable multiple investors to fund projects or businesses through small loans, offering quicker access to capital with lower entry barriers compared to traditional private equity. Private equity involves large-scale investments by institutional or accredited investors, focusing on acquiring significant ownership stakes with the goal of long-term value creation. Explore the key differences and benefits of each investment approach to determine the best fit for your financial goals.
Why it is important
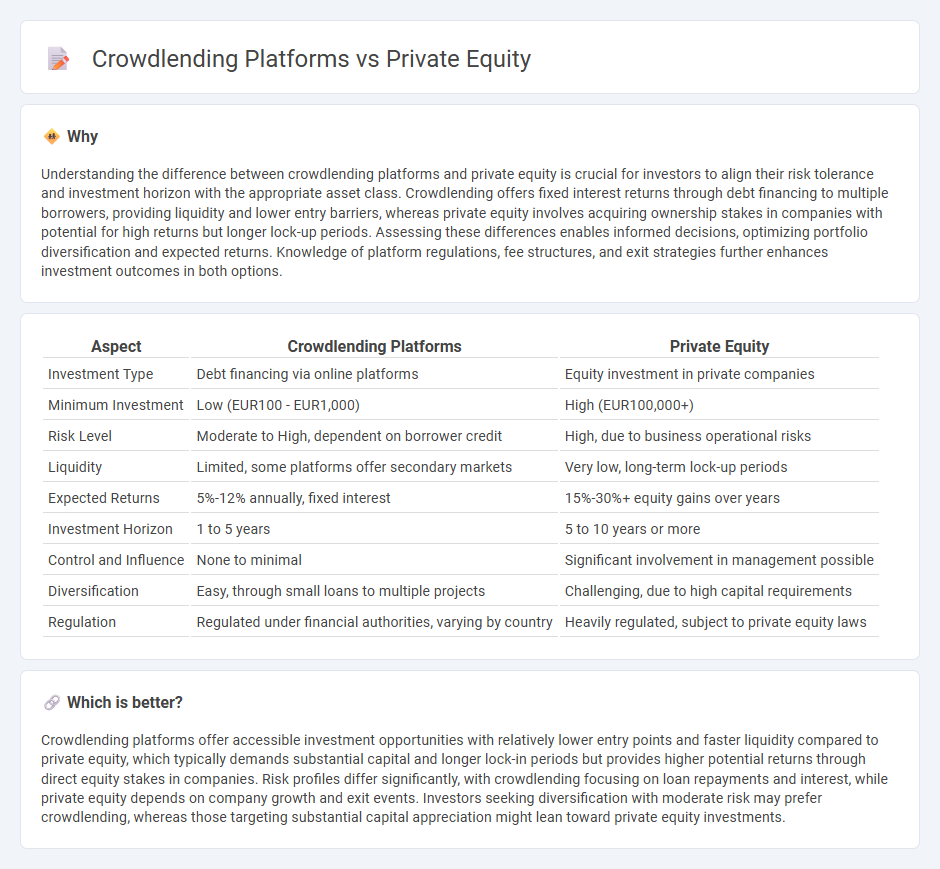
Understanding the difference between crowdlending platforms and private equity is crucial for investors to align their risk tolerance and investment horizon with the appropriate asset class. Crowdlending offers fixed interest returns through debt financing to multiple borrowers, providing liquidity and lower entry barriers, whereas private equity involves acquiring ownership stakes in companies with potential for high returns but longer lock-up periods. Assessing these differences enables informed decisions, optimizing portfolio diversification and expected returns. Knowledge of platform regulations, fee structures, and exit strategies further enhances investment outcomes in both options.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Crowdlending Platforms | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Debt financing via online platforms | Equity investment in private companies |
| Minimum Investment | Low (EUR100 - EUR1,000) | High (EUR100,000+) |
| Risk Level | Moderate to High, dependent on borrower credit | High, due to business operational risks |
| Liquidity | Limited, some platforms offer secondary markets | Very low, long-term lock-up periods |
| Expected Returns | 5%-12% annually, fixed interest | 15%-30%+ equity gains over years |
| Investment Horizon | 1 to 5 years | 5 to 10 years or more |
| Control and Influence | None to minimal | Significant involvement in management possible |
| Diversification | Easy, through small loans to multiple projects | Challenging, due to high capital requirements |
| Regulation | Regulated under financial authorities, varying by country | Heavily regulated, subject to private equity laws |
Which is better?
Crowdlending platforms offer accessible investment opportunities with relatively lower entry points and faster liquidity compared to private equity, which typically demands substantial capital and longer lock-in periods but provides higher potential returns through direct equity stakes in companies. Risk profiles differ significantly, with crowdlending focusing on loan repayments and interest, while private equity depends on company growth and exit events. Investors seeking diversification with moderate risk may prefer crowdlending, whereas those targeting substantial capital appreciation might lean toward private equity investments.
Connection
Crowdlending platforms enable individual investors to provide loans to businesses, often in early or growth stages, which aligns closely with private equity's focus on funding private companies. Both investment methods aim to support business expansion by providing capital that bypasses traditional bank financing. The convergence occurs as private equity firms increasingly leverage crowdlending to diversify funding sources and tap into a broader pool of investors.
Key Terms
Ownership stake
Private equity investments provide investors with an ownership stake in companies, granting voting rights and potential dividends linked to company performance. Crowdlending platforms, in contrast, offer debt-based financing where investors receive fixed interest payments without ownership privileges or control. Explore the differences in risk, return, and involvement to determine which investment aligns best with your financial goals.
Investor accreditation
Private equity investments typically require investor accreditation, mandating individuals to meet specific income or net worth thresholds to mitigate risk exposure. Crowdlending platforms often allow a broader range of investors, though some may impose accreditation criteria depending on regulatory frameworks. Explore the nuances of investor accreditation to determine which investment avenue aligns with your financial goals.
Risk diversification
Private equity investments often require significant capital and have lower liquidity, making risk diversification less accessible for smaller investors, whereas crowdlending platforms enable individuals to spread smaller amounts across multiple loans, enhancing portfolio diversification. Crowdlending allows for diversification across different credit risks and industries with relatively low initial investment, reducing exposure to any single borrower's default. Explore how these investment models balance risk and return to optimize your financial strategy.
Source and External Links
Private equity - Wikipedia - Private equity refers to investments in the equity of private companies not listed on public stock exchanges, typically managed by specialized funds that seek to increase value through active ownership, operational improvements, and financial engineering over a medium-term horizon.
What is Private Equity? - BVCA - Private equity provides medium- to long-term capital to unquoted, often high-growth companies, working closely with management to drive growth, efficiency, and value creation before exiting the investment, usually within four to seven years.
Private Equity Funds | Investor.gov - A private equity fund is a pooled investment vehicle that acquires significant stakes in companies, actively engages in their management to increase value, and typically holds investments for ten or more years, targeting returns primarily through operational and strategic improvements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com