Spice trading and Forex trading represent distinct investment avenues with unique market dynamics and risk profiles. Spice trading involves commodity markets influenced by factors like geopolitical events and weather conditions, while Forex trading focuses on currency exchange rates driven by economic indicators and monetary policies. Explore detailed insights to understand which investment strategy aligns best with your financial goals.
Why it is important
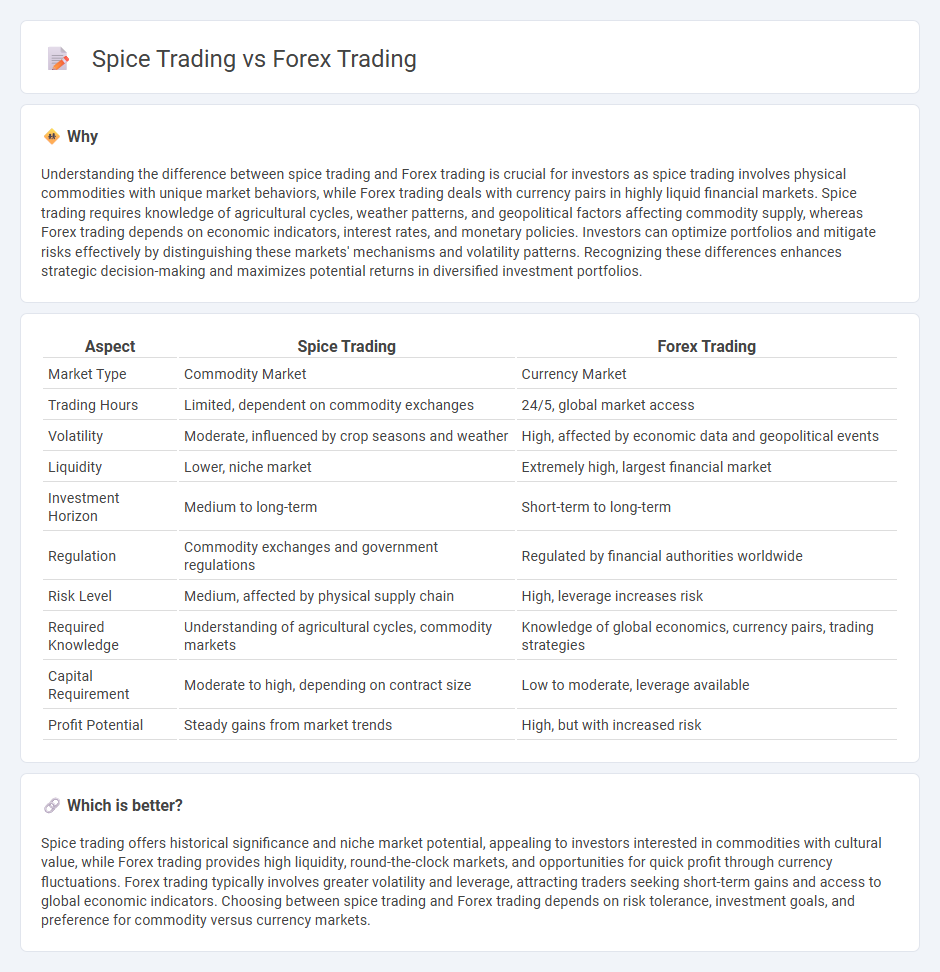
Understanding the difference between spice trading and Forex trading is crucial for investors as spice trading involves physical commodities with unique market behaviors, while Forex trading deals with currency pairs in highly liquid financial markets. Spice trading requires knowledge of agricultural cycles, weather patterns, and geopolitical factors affecting commodity supply, whereas Forex trading depends on economic indicators, interest rates, and monetary policies. Investors can optimize portfolios and mitigate risks effectively by distinguishing these markets' mechanisms and volatility patterns. Recognizing these differences enhances strategic decision-making and maximizes potential returns in diversified investment portfolios.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Spice Trading | Forex Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Market Type | Commodity Market | Currency Market |
| Trading Hours | Limited, dependent on commodity exchanges | 24/5, global market access |
| Volatility | Moderate, influenced by crop seasons and weather | High, affected by economic data and geopolitical events |
| Liquidity | Lower, niche market | Extremely high, largest financial market |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long-term | Short-term to long-term |
| Regulation | Commodity exchanges and government regulations | Regulated by financial authorities worldwide |
| Risk Level | Medium, affected by physical supply chain | High, leverage increases risk |
| Required Knowledge | Understanding of agricultural cycles, commodity markets | Knowledge of global economics, currency pairs, trading strategies |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate to high, depending on contract size | Low to moderate, leverage available |
| Profit Potential | Steady gains from market trends | High, but with increased risk |
Which is better?
Spice trading offers historical significance and niche market potential, appealing to investors interested in commodities with cultural value, while Forex trading provides high liquidity, round-the-clock markets, and opportunities for quick profit through currency fluctuations. Forex trading typically involves greater volatility and leverage, attracting traders seeking short-term gains and access to global economic indicators. Choosing between spice trading and Forex trading depends on risk tolerance, investment goals, and preference for commodity versus currency markets.
Connection
Spice trading and Forex trading are connected through the global nature of currency exchange and international markets. The spice trade historically drove demand for diverse currencies as merchants navigated various regions, influencing early forex dynamics. Today, fluctuations in currency values impact commodity prices, including spices, linking both trading activities in global economic systems.
Key Terms
Currency Pair (Forex trading)
Currency pairs in Forex trading represent the relative value of one currency against another, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY, enabling traders to speculate on price fluctuations across global financial markets. Unlike spice trading, which involves physical commodities and regional market dynamics, Forex trading thrives on high liquidity, 24-hour market accessibility, and leverage options that amplify trading potential. Explore the intricate mechanisms of currency pair analysis and market strategies to enhance your Forex trading expertise.
Exchange Rate (Forex trading)
Forex trading involves the continuous analysis of exchange rate fluctuations between currency pairs, enabling traders to profit from market volatility and economic indicators influencing global currency values. Exchange rate movements are driven by interest rates, geopolitical events, and supply-demand dynamics, which are critical for successful forex strategies. Explore the complexities of exchange rates in forex trading to enhance your market understanding and trading performance.
Commodity Price Volatility (Spice trading)
Commodity price volatility in spice trading is influenced by factors such as weather conditions, geopolitical tensions, and seasonal harvest yields, leading to significant price swings. Forex trading, while volatile, is driven by macroeconomic data, interest rate changes, and geopolitical events affecting currency values globally. Explore more insights to understand how these market dynamics impact trading strategies and risk management.
Source and External Links
What is Forex (FX) Trading and How Does it Work? - IG - Forex trading involves the buying and selling of currency pairs, where traders speculate on whether one currency will strengthen or weaken relative to another, with profits made from price movements between the buy and sell prices known as the spread.
What is Forex Trading? - Forex.com - Forex trading is the exchange of one currency for another in a decentralized global market, characterized by high liquidity and volatility, attracting traders who seek to profit from short-term price fluctuations and tight spreads on major currency pairs.
Foreign exchange market - Wikipedia - The forex market is a global decentralized or over-the-counter market for currency trading, including spot transactions which are direct currency exchanges with settlement typically within two days, and forward contracts which set exchange rates for delivery at a future date to manage currency risk.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com