Investment in space debris cleanup startups focuses on developing technologies to remove defunct satellites and debris to mitigate collision risks and maintain orbital sustainability. In-orbit servicing companies invest in extending the lifespan of active satellites through refueling, repairs, and upgrades, enhancing satellite operational efficiency and reducing replacement costs. Explore further to understand the distinct market opportunities and technological advancements driving these innovative space industry sectors.
Why it is important
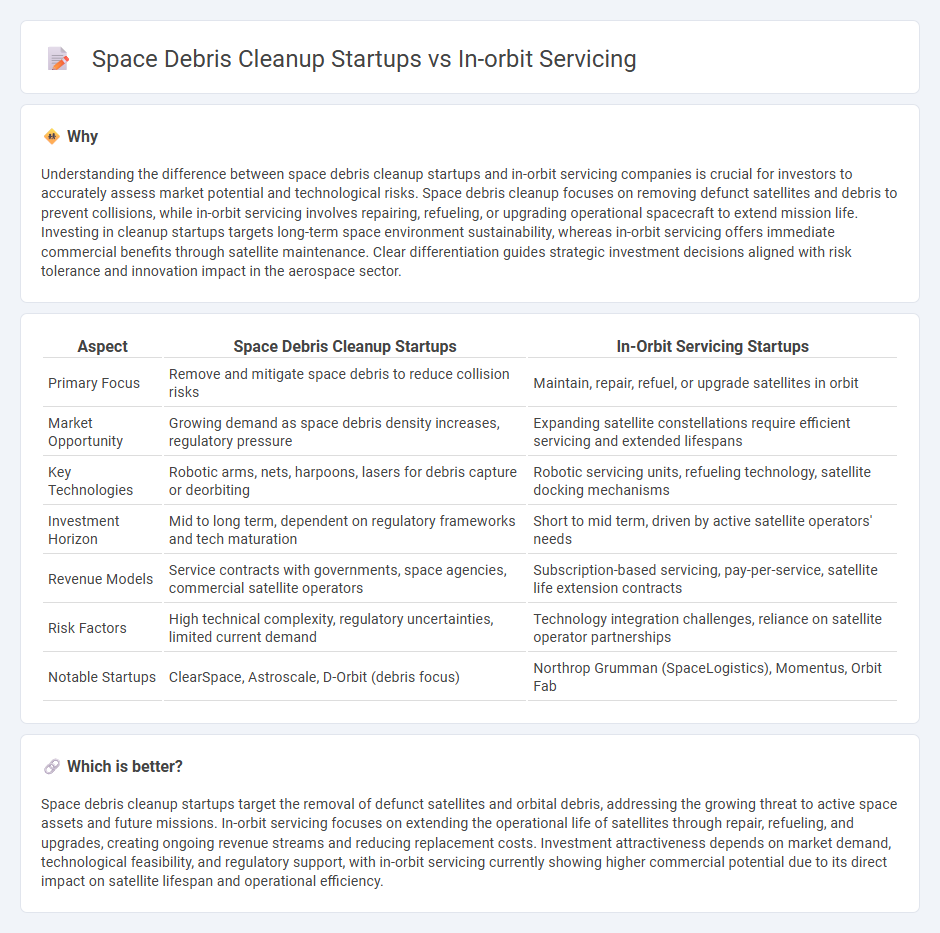
Understanding the difference between space debris cleanup startups and in-orbit servicing companies is crucial for investors to accurately assess market potential and technological risks. Space debris cleanup focuses on removing defunct satellites and debris to prevent collisions, while in-orbit servicing involves repairing, refueling, or upgrading operational spacecraft to extend mission life. Investing in cleanup startups targets long-term space environment sustainability, whereas in-orbit servicing offers immediate commercial benefits through satellite maintenance. Clear differentiation guides strategic investment decisions aligned with risk tolerance and innovation impact in the aerospace sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Space Debris Cleanup Startups | In-Orbit Servicing Startups |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Remove and mitigate space debris to reduce collision risks | Maintain, repair, refuel, or upgrade satellites in orbit |
| Market Opportunity | Growing demand as space debris density increases, regulatory pressure | Expanding satellite constellations require efficient servicing and extended lifespans |
| Key Technologies | Robotic arms, nets, harpoons, lasers for debris capture or deorbiting | Robotic servicing units, refueling technology, satellite docking mechanisms |
| Investment Horizon | Mid to long term, dependent on regulatory frameworks and tech maturation | Short to mid term, driven by active satellite operators' needs |
| Revenue Models | Service contracts with governments, space agencies, commercial satellite operators | Subscription-based servicing, pay-per-service, satellite life extension contracts |
| Risk Factors | High technical complexity, regulatory uncertainties, limited current demand | Technology integration challenges, reliance on satellite operator partnerships |
| Notable Startups | ClearSpace, Astroscale, D-Orbit (debris focus) | Northrop Grumman (SpaceLogistics), Momentus, Orbit Fab |
Which is better?
Space debris cleanup startups target the removal of defunct satellites and orbital debris, addressing the growing threat to active space assets and future missions. In-orbit servicing focuses on extending the operational life of satellites through repair, refueling, and upgrades, creating ongoing revenue streams and reducing replacement costs. Investment attractiveness depends on market demand, technological feasibility, and regulatory support, with in-orbit servicing currently showing higher commercial potential due to its direct impact on satellite lifespan and operational efficiency.
Connection
Space debris cleanup startups leverage advanced satellite technologies to remove hazardous debris, directly supporting in-orbit servicing missions by maintaining safer operational environments. In-orbit servicing relies on debris-free zones to perform satellite repairs, refueling, and upgrades effectively, highlighting a symbiotic relationship. Collaboration between these sectors accelerates sustainable space operations, reducing collision risks and extending satellite lifespans.
Key Terms
Satellite Refueling
Satellite refueling startups pioneer in-orbit servicing by extending satellite lifespans through propellant transfer, reducing the need for costly replacements and mitigating space congestion. Space debris cleanup companies concentrate on removing defunct satellites and fragments to preserve orbital safety, yet satellite refueling directly enhances satellite operability and economic value. Explore the latest innovations and market leaders revolutionizing satellite refueling technology.
Active Debris Removal
In-orbit servicing companies specialize in maintaining satellites by refueling, repairing, or upgrading them to extend operational life, whereas space debris cleanup startups primarily focus on active debris removal (ADR) to mitigate collision risks with defunct satellites and fragments. ADR techniques involve capturing or deorbiting space debris using nets, harpoons, robotic arms, or propulsion systems, effectively reducing orbital congestion in heavily trafficked low Earth orbit (LEO) regions. Explore key innovations and leading startups driving breakthroughs in active debris removal technologies to better understand this critical space industry segment.
On-orbit Servicing Contracts
On-orbit servicing startups secure contracts to extend satellite lifespans through refueling, repairs, and upgrades, leveraging advanced robotics and AI for precise operations. Space debris cleanup companies focus on removing defunct satellites and fragments to mitigate collision risks, often partnering with governments for regulatory support and funding. Explore the latest on-orbit servicing contracts and innovations shaping the space industry's sustainable future.
Source and External Links
NASA Satellite Servicing Project Report - This report discusses the potential of on-orbit satellite servicing to extend the life and capabilities of satellites, emphasizing the need for advanced autonomy and robust systems engineering.
On-Orbit Servicing - CSIS Aerospace Security - This document highlights the benefits of on-orbit servicing, such as enhancing satellite resilience through repairs and refueling, and notes the importance of autonomous robotic technologies for high orbit servicing.
ESA In-Orbit Servicing Missions - The European Space Agency (ESA) is advancing in-orbit servicing missions to extend satellite lifetimes and functionalities, aiming to launch its first such mission as early as 2028.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com