Investing in viticulture land offers tangible assets with potential for vineyard development and agricultural value appreciation, contrasting with precious metals like gold and silver that provide liquidity and hedge against inflation. Land acquisition in viticulture combines agricultural income with capital growth, whereas precious metals serve primarily as a store of value and portfolio diversification tool. Explore the benefits and risks of each investment type to determine the optimal strategy for your financial goals.
Why it is important
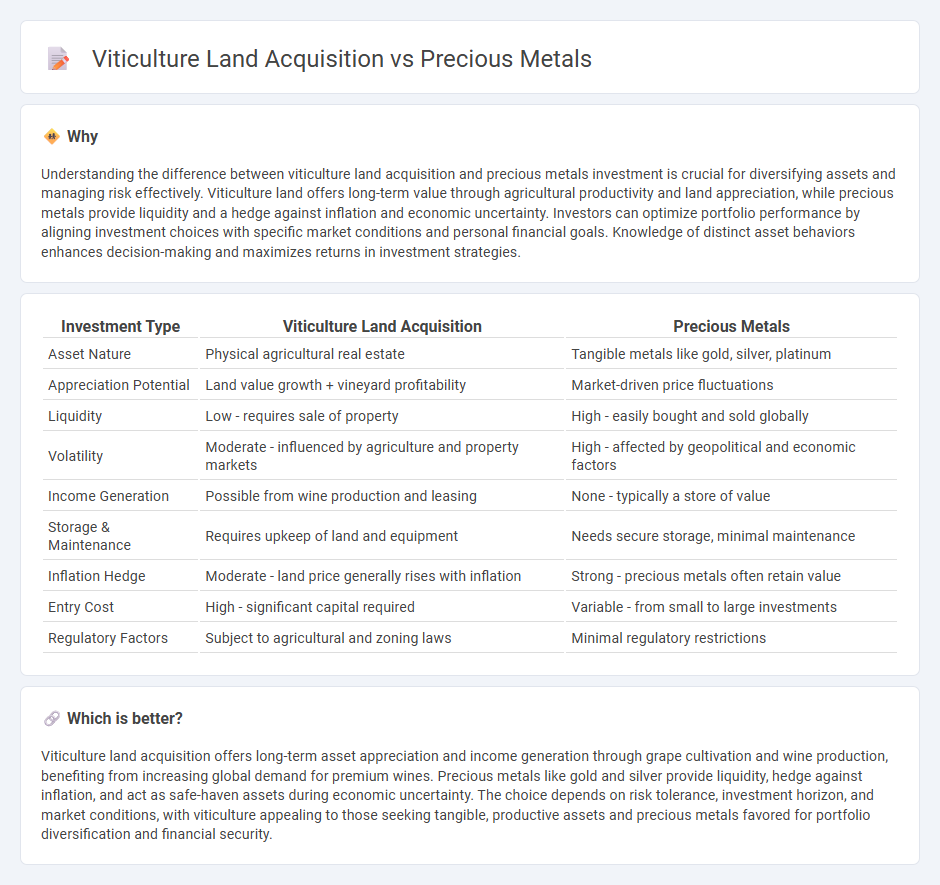
Understanding the difference between viticulture land acquisition and precious metals investment is crucial for diversifying assets and managing risk effectively. Viticulture land offers long-term value through agricultural productivity and land appreciation, while precious metals provide liquidity and a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty. Investors can optimize portfolio performance by aligning investment choices with specific market conditions and personal financial goals. Knowledge of distinct asset behaviors enhances decision-making and maximizes returns in investment strategies.
Comparison Table
| Investment Type | Viticulture Land Acquisition | Precious Metals |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Nature | Physical agricultural real estate | Tangible metals like gold, silver, platinum |
| Appreciation Potential | Land value growth + vineyard profitability | Market-driven price fluctuations |
| Liquidity | Low - requires sale of property | High - easily bought and sold globally |
| Volatility | Moderate - influenced by agriculture and property markets | High - affected by geopolitical and economic factors |
| Income Generation | Possible from wine production and leasing | None - typically a store of value |
| Storage & Maintenance | Requires upkeep of land and equipment | Needs secure storage, minimal maintenance |
| Inflation Hedge | Moderate - land price generally rises with inflation | Strong - precious metals often retain value |
| Entry Cost | High - significant capital required | Variable - from small to large investments |
| Regulatory Factors | Subject to agricultural and zoning laws | Minimal regulatory restrictions |
Which is better?
Viticulture land acquisition offers long-term asset appreciation and income generation through grape cultivation and wine production, benefiting from increasing global demand for premium wines. Precious metals like gold and silver provide liquidity, hedge against inflation, and act as safe-haven assets during economic uncertainty. The choice depends on risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market conditions, with viticulture appealing to those seeking tangible, productive assets and precious metals favored for portfolio diversification and financial security.
Connection
Acquiring viticulture land often correlates with investment in precious metals due to their shared role as tangible assets that hedge against inflation and economic volatility. Both sectors attract investors seeking portfolio diversification through real estate in wine-producing regions and physical commodities like gold and silver. The stability and intrinsic value of these assets provide a strategic balance in long-term investment planning.
Key Terms
Asset Liquidity
Precious metals like gold and silver offer high asset liquidity due to their global demand and ease of conversion into cash, making them ideal for investors seeking quick asset turnover. Viticulture land acquisition, while potentially lucrative through wine production, involves lower liquidity as selling agrarian property requires longer transaction times and market-specific expertise. Explore further insights on balancing asset liquidity with investment diversification to optimize your portfolio.
Market Volatility
Precious metals such as gold and silver serve as traditional hedges against market volatility due to their intrinsic value and liquidity, often appreciating during economic downturns or financial crises. Viticulture land acquisition offers long-term investment stability by generating consistent income through grape production and wine sales, with land values less susceptible to short-term market fluctuations. Explore more about how these asset classes perform under varying economic conditions to make informed investment decisions.
Tangible Value
Precious metals such as gold and silver offer liquidity and global demand, serving as a hedge against inflation and economic downturns, while viticulture land provides tangible value through agricultural productivity, long-term appreciation, and unique terroir advantages. The intrinsic worth of precious metals is rooted in rarity and industrial applications, whereas viticulture land combines physical asset appreciation with the potential for consistent revenue generation via high-quality wine production. Discover the strategic benefits and investment potential of each asset to optimize your portfolio's tangible value.
Source and External Links
Precious metal - Wikipedia - Precious metals are rare, naturally occurring metallic chemical elements with high economic value, known for corrosion resistance and use historically as currency and currently in investment and industry, including gold, silver, platinum, and palladium as the most recognized types.
Buy Precious Metals Online from Money Metals Exchange - Gold, silver, platinum, and palladium are precious metals prized for their rarity and industrial uses, as well as their role as investment assets for wealth protection and portfolio diversification.
A List of Precious Metals - ThoughtCo - The primary precious metals are gold, silver, platinum, and palladium, valued for rarity, industrial application, and investment purposes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com