Forestry investment offers long-term asset growth through sustainable timber production and carbon credit opportunities, contrasting with venture capital's focus on high-risk, high-reward funding of early-stage startups in innovative sectors. Forestry investments provide tangible, renewable resources with steady cash flow, while venture capital targets disruptive technologies and rapid scalability for exponential returns. Explore the unique benefits and risks of forestry investment versus venture capital to determine the optimal strategy for your portfolio.
Why it is important
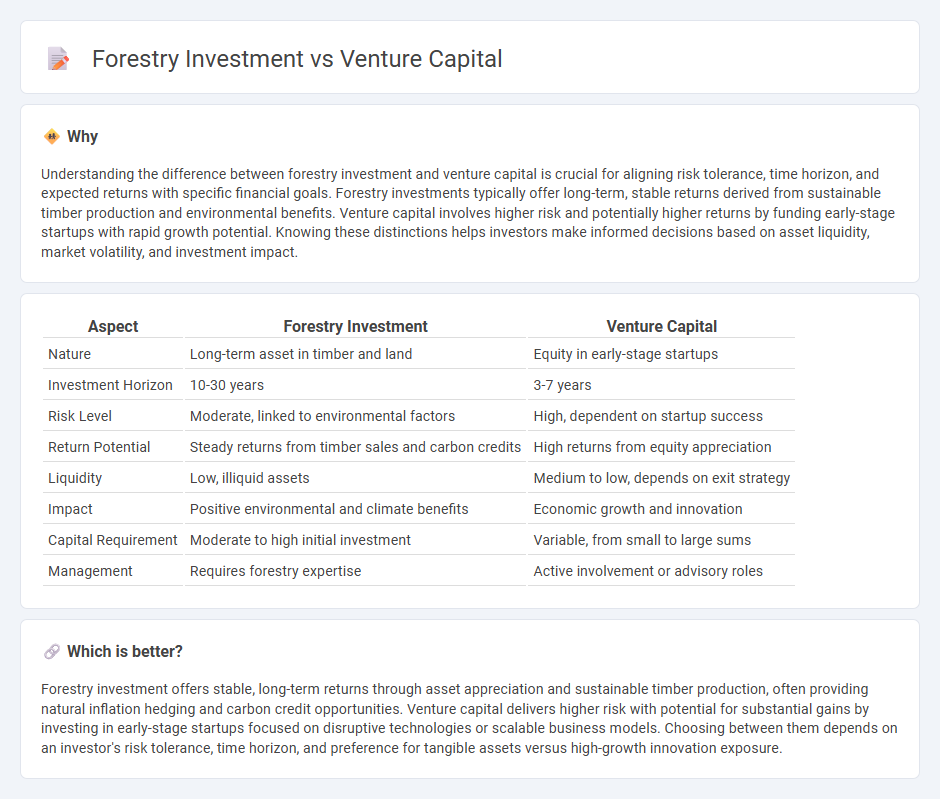
Understanding the difference between forestry investment and venture capital is crucial for aligning risk tolerance, time horizon, and expected returns with specific financial goals. Forestry investments typically offer long-term, stable returns derived from sustainable timber production and environmental benefits. Venture capital involves higher risk and potentially higher returns by funding early-stage startups with rapid growth potential. Knowing these distinctions helps investors make informed decisions based on asset liquidity, market volatility, and investment impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Forestry Investment | Venture Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Long-term asset in timber and land | Equity in early-stage startups |
| Investment Horizon | 10-30 years | 3-7 years |
| Risk Level | Moderate, linked to environmental factors | High, dependent on startup success |
| Return Potential | Steady returns from timber sales and carbon credits | High returns from equity appreciation |
| Liquidity | Low, illiquid assets | Medium to low, depends on exit strategy |
| Impact | Positive environmental and climate benefits | Economic growth and innovation |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate to high initial investment | Variable, from small to large sums |
| Management | Requires forestry expertise | Active involvement or advisory roles |
Which is better?
Forestry investment offers stable, long-term returns through asset appreciation and sustainable timber production, often providing natural inflation hedging and carbon credit opportunities. Venture capital delivers higher risk with potential for substantial gains by investing in early-stage startups focused on disruptive technologies or scalable business models. Choosing between them depends on an investor's risk tolerance, time horizon, and preference for tangible assets versus high-growth innovation exposure.
Connection
Forestry investment and venture capital intersect through the funding of innovative sustainable forestry technologies and businesses that enhance carbon capture, resource management, and ecological restoration. Venture capital accelerates growth in forestry startups focusing on eco-friendly solutions, precision harvesting, and supply chain optimization, driving higher returns and environmental impact. This synergy promotes scalable investments that address climate change while generating diversified financial portfolios.
Key Terms
Risk profile
Venture capital investments typically exhibit high risk profiles due to market volatility and startup failure rates, while forestry investments offer lower risk with stable, long-term returns driven by biological growth and timber demand. Forestry assets benefit from natural capital appreciation and carbon sequestration value, providing a hedge against inflation and market downturns. Explore more about the comparative risk profiles of these investment types to optimize your portfolio strategy.
Return horizon
Venture capital investments typically seek high returns within a 5 to 10-year horizon, driven by innovation and rapid business growth. Forestry investments offer long-term returns over 20 to 30 years, benefiting from timber growth and sustainable land appreciation. Explore detailed comparisons to align your investment strategy with your desired return timelines.
Asset liquidity
Venture capital investments typically offer lower asset liquidity due to long lock-in periods and exit strategies reliant on IPOs or acquisitions, while forestry investments provide moderate liquidity through timber sales and land value appreciation. Forestry assets tend to have tangible value and can generate steady cash flow from sustainable harvests, in contrast to volatile and high-risk venture capital portfolios. Explore deeper insights into liquidity profiles and risk management strategies between these investment types to make informed financial decisions.
Source and External Links
What is Venture Capital? - Venture capital is a form of financing that turns innovative ideas and research into high-growth companies, providing strategic partnership, risk capital, and long-term investment for startups that often cannot be funded through traditional means.
Fund your business | U.S. Small Business Administration - Venture capital is funding provided to high-growth startups in exchange for equity and often a board seat, involving a multi-step process including finding investors, due diligence, agreeing on terms, and investment rounds.
What is venture capital? - Venture capital is a type of private equity that supports startups and early-stage companies with fast growth potential by investing funds raised from limited partners and often providing technical and managerial support in return for ownership stakes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com