Song catalog purchases generate steady royalties by leveraging the enduring popularity of music rights, offering investors consistent cash flow and potential appreciation. Patents present high-risk, high-reward opportunities tied to innovations with market exclusivity and licensing possibilities, often requiring strategic management. Explore further to understand which investment aligns best with your financial goals and risk appetite.
Why it is important
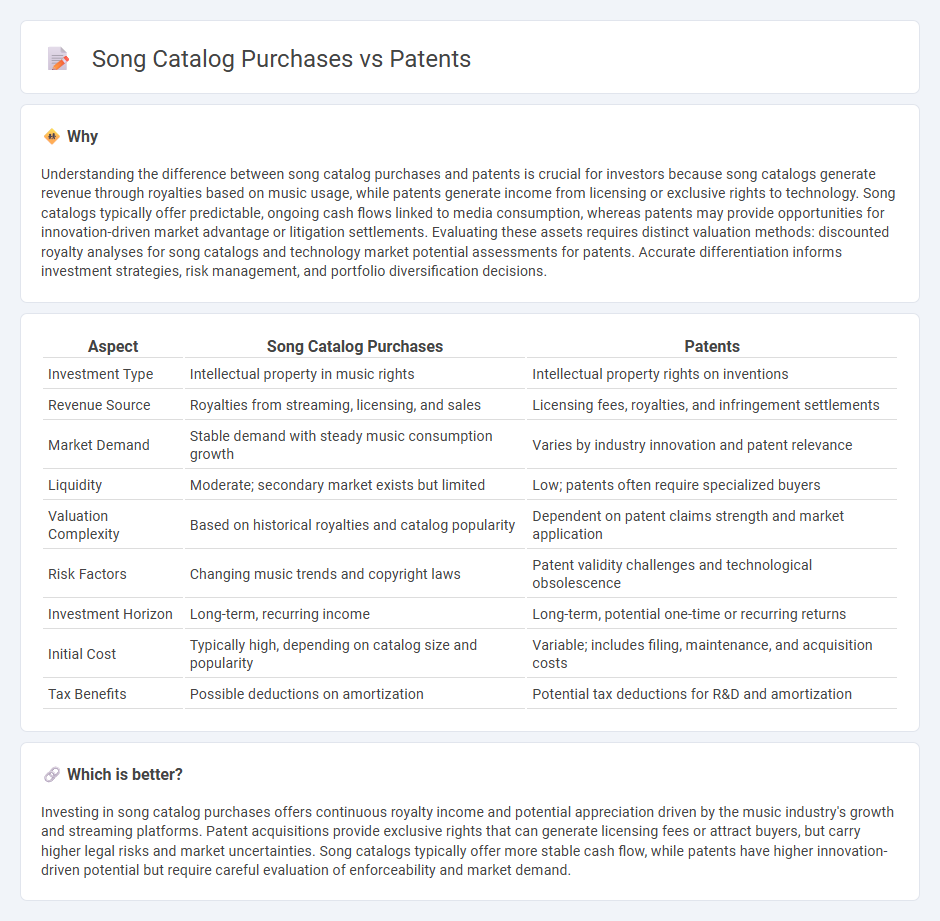
Understanding the difference between song catalog purchases and patents is crucial for investors because song catalogs generate revenue through royalties based on music usage, while patents generate income from licensing or exclusive rights to technology. Song catalogs typically offer predictable, ongoing cash flows linked to media consumption, whereas patents may provide opportunities for innovation-driven market advantage or litigation settlements. Evaluating these assets requires distinct valuation methods: discounted royalty analyses for song catalogs and technology market potential assessments for patents. Accurate differentiation informs investment strategies, risk management, and portfolio diversification decisions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Song Catalog Purchases | Patents |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Intellectual property in music rights | Intellectual property rights on inventions |
| Revenue Source | Royalties from streaming, licensing, and sales | Licensing fees, royalties, and infringement settlements |
| Market Demand | Stable demand with steady music consumption growth | Varies by industry innovation and patent relevance |
| Liquidity | Moderate; secondary market exists but limited | Low; patents often require specialized buyers |
| Valuation Complexity | Based on historical royalties and catalog popularity | Dependent on patent claims strength and market application |
| Risk Factors | Changing music trends and copyright laws | Patent validity challenges and technological obsolescence |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term, recurring income | Long-term, potential one-time or recurring returns |
| Initial Cost | Typically high, depending on catalog size and popularity | Variable; includes filing, maintenance, and acquisition costs |
| Tax Benefits | Possible deductions on amortization | Potential tax deductions for R&D and amortization |
Which is better?
Investing in song catalog purchases offers continuous royalty income and potential appreciation driven by the music industry's growth and streaming platforms. Patent acquisitions provide exclusive rights that can generate licensing fees or attract buyers, but carry higher legal risks and market uncertainties. Song catalogs typically offer more stable cash flow, while patents have higher innovation-driven potential but require careful evaluation of enforceability and market demand.
Connection
Song catalog purchases and patents both represent valuable intangible assets that generate ongoing revenue streams through licensing and royalties. Investors leverage these assets to diversify portfolios with intellectual property that has predictable cash flows and potential for appreciation. The strategic acquisition of song catalogs and patents enhances investment value by capitalizing on exclusive rights and market demand.
Key Terms
Intellectual Property
Patents and song catalog purchases represent two distinct facets of intellectual property, each with unique valuation models and revenue streams; patents primarily generate income through licensing and litigation, whereas song catalogs earn royalties from public performance, mechanical, and synchronization rights. Understanding the nuances of intellectual property law, market demand, and asset liquidity is crucial for investors seeking to maximize returns in either domain. Explore our detailed analysis to uncover strategic insights and investment opportunities in the evolving IP marketplace.
Royalties
Patents generate royalties through licensing agreements related to the use of patented technology, often involving upfront fees and recurring payments based on product sales or usage. Song catalog purchases result in royalty income from performance rights, mechanical royalties, and sync licensing, driven by streaming, radio play, and media placements. Explore how each asset class delivers unique royalty revenue streams and investment potential.
Asset Valuation
Patents and song catalogs represent distinct asset classes with unique valuation methodologies driven by their revenue generation and market demand. Patents are valued based on their technological potential, exclusivity period, and licensing income, while song catalogs rely on streaming data, royalties, and synch opportunities to determine worth. Explore our detailed insights to better understand optimizing asset valuation strategies across these intellectual properties.
Source and External Links
Patent - A patent is a type of intellectual property that grants its owner the exclusive legal right to prevent others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period.
What are patents? - Patents protect new, useful, and inventive inventions such as devices, substances, methods, and processes, providing exclusive commercial rights for up to 20 years (25 years for pharmaceuticals) in the country where granted.
Patent Basics - The U.S. patent process covers applying for, maintaining, enforcing, and transferring patent rights, with resources available for inventors and guidance through every stage of the process.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com