Farmland funds provide investors with exposure to agricultural land assets, offering potential for long-term capital appreciation and inflation protection through crop yield revenues. Fixed income funds focus on debt securities, delivering regular interest income and lower volatility, suitable for conservative income-focused portfolios. Explore more about how these investment options align with your financial goals.
Why it is important
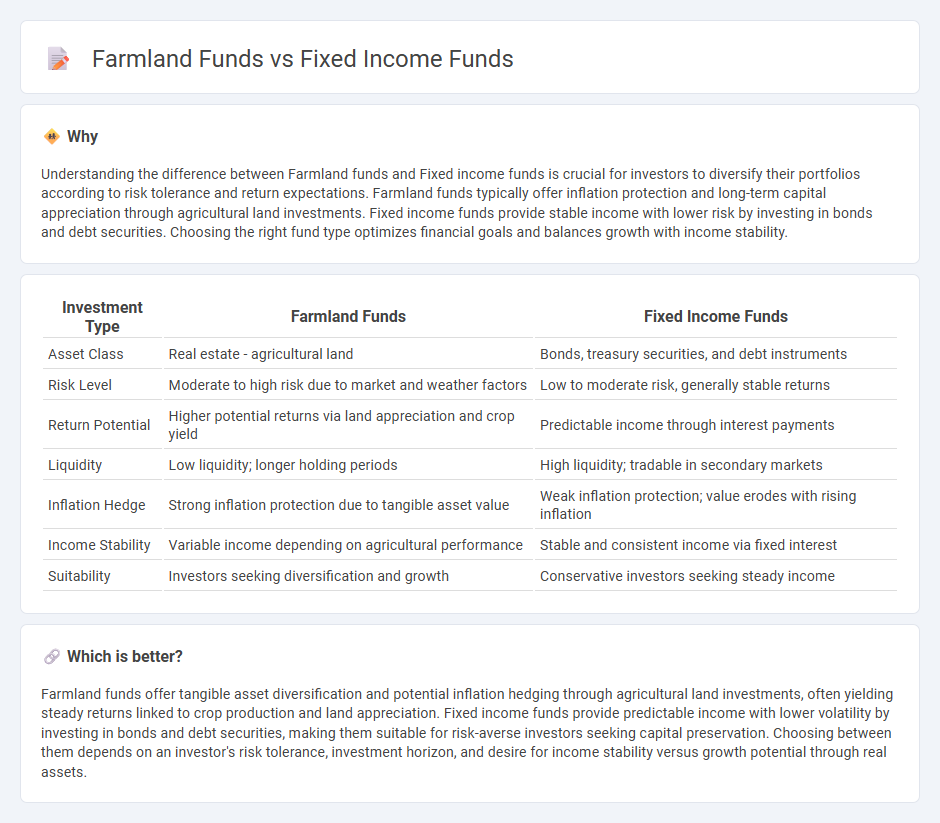
Understanding the difference between Farmland funds and Fixed income funds is crucial for investors to diversify their portfolios according to risk tolerance and return expectations. Farmland funds typically offer inflation protection and long-term capital appreciation through agricultural land investments. Fixed income funds provide stable income with lower risk by investing in bonds and debt securities. Choosing the right fund type optimizes financial goals and balances growth with income stability.
Comparison Table
| Investment Type | Farmland Funds | Fixed Income Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Class | Real estate - agricultural land | Bonds, treasury securities, and debt instruments |
| Risk Level | Moderate to high risk due to market and weather factors | Low to moderate risk, generally stable returns |
| Return Potential | Higher potential returns via land appreciation and crop yield | Predictable income through interest payments |
| Liquidity | Low liquidity; longer holding periods | High liquidity; tradable in secondary markets |
| Inflation Hedge | Strong inflation protection due to tangible asset value | Weak inflation protection; value erodes with rising inflation |
| Income Stability | Variable income depending on agricultural performance | Stable and consistent income via fixed interest |
| Suitability | Investors seeking diversification and growth | Conservative investors seeking steady income |
Which is better?
Farmland funds offer tangible asset diversification and potential inflation hedging through agricultural land investments, often yielding steady returns linked to crop production and land appreciation. Fixed income funds provide predictable income with lower volatility by investing in bonds and debt securities, making them suitable for risk-averse investors seeking capital preservation. Choosing between them depends on an investor's risk tolerance, investment horizon, and desire for income stability versus growth potential through real assets.
Connection
Farmland funds and fixed income funds are connected through their roles as alternative investments offering diversification and consistent income streams. Farmland funds generate returns via agricultural land leases and crop sales, providing inflation-hedged income akin to fixed income funds that deliver regular interest payments from bonds. Both fund types appeal to investors seeking stable cash flow with lower correlation to traditional equity markets.
Key Terms
Yield
Fixed income funds typically offer lower but stable yields by investing in government and corporate bonds, making them suitable for risk-averse investors seeking predictable income streams. Farmland funds, on the other hand, can provide higher yields through agricultural lease payments and capital appreciation tied to land value, but they carry risks linked to commodity prices and weather conditions. Explore the distinct yield potentials and risk profiles of these investment options to make an informed choice.
Liquidity
Fixed income funds typically offer higher liquidity due to their investment in bonds and debt instruments traded on established markets, allowing investors to buy or sell shares with relative ease. Farmland funds, on the other hand, involve investing in agricultural land, which is less liquid because of the longer holding periods and complexities in buying or selling physical assets. Explore more to understand how liquidity impacts your investment strategy in fixed income and farmland funds.
Diversification
Fixed income funds primarily invest in bonds and debt securities, offering steady income with lower volatility, while farmland funds allocate capital to agricultural land, providing diversification through exposure to real assets linked to food production and land value appreciation. Diversification benefits arise as fixed income funds tend to perform differently under economic cycles compared to farmland funds, which are influenced by agricultural productivity, commodity prices, and land market trends. Explore how combining fixed income and farmland funds can enhance portfolio resilience and yield stability under varying market conditions.
Source and External Links
What Are Fixed-Income Investments - Provides information on fixed-income investments, including options like municipal bonds, corporate bonds, and treasury bonds that offer regular interest payments.
Fixed Income Investments - Offers insights into fixed-income investments, highlighting benefits such as lower risk and consistent income, along with options like bond mutual funds and CDs.
Fixed Income Funds - Features mutual funds designed to generate income while maintaining stability, with options focusing on government bonds, municipal bonds, and corporate bonds.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com