Investing in wine offers a tangible asset with potential for long-term capital appreciation, driven by rarity, vintage quality, and global demand from collectors. Hedge funds provide diversified portfolios managed by professionals, utilizing strategies like long-short equity, market neutral, and arbitrage to optimize returns and mitigate risks. Explore the advantages and risks of wine investing versus hedge funds to determine the best fit for your portfolio goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between wine investing and hedge funds is crucial because wine investing involves tangible assets with long-term illiquidity and value appreciation based on rarity and provenance, whereas hedge funds manage diverse portfolios with liquid assets aimed at maximizing short-term returns through sophisticated financial strategies. Wine investments require expertise in vintages and storage conditions, while hedge funds demand knowledge of market trends and risk management techniques. Investors must evaluate their risk tolerance, investment horizon, and liquidity needs to choose the appropriate vehicle. Misunderstanding these differences can lead to suboptimal portfolio diversification and financial outcomes.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Wine Investing | Hedge Funds |
|---|---|---|
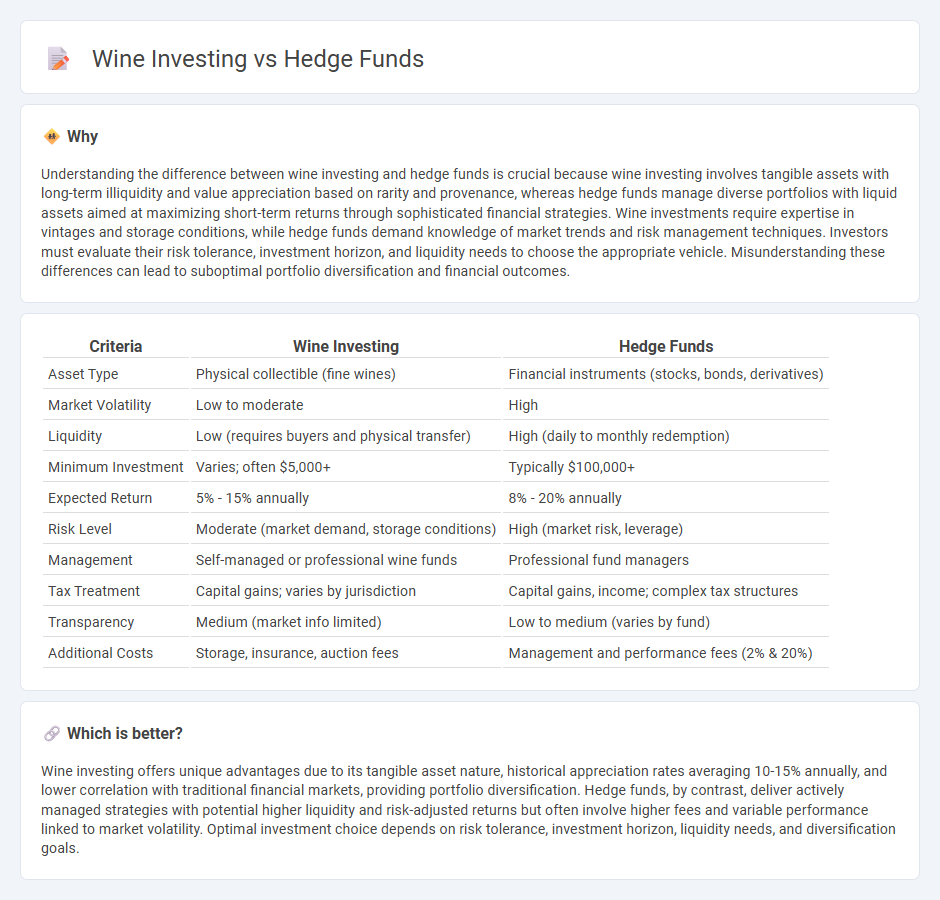
| Asset Type | Physical collectible (fine wines) | Financial instruments (stocks, bonds, derivatives) |
| Market Volatility | Low to moderate | High |
| Liquidity | Low (requires buyers and physical transfer) | High (daily to monthly redemption) |
| Minimum Investment | Varies; often $5,000+ | Typically $100,000+ |
| Expected Return | 5% - 15% annually | 8% - 20% annually |
| Risk Level | Moderate (market demand, storage conditions) | High (market risk, leverage) |
| Management | Self-managed or professional wine funds | Professional fund managers |
| Tax Treatment | Capital gains; varies by jurisdiction | Capital gains, income; complex tax structures |
| Transparency | Medium (market info limited) | Low to medium (varies by fund) |
| Additional Costs | Storage, insurance, auction fees | Management and performance fees (2% & 20%) |
Which is better?
Wine investing offers unique advantages due to its tangible asset nature, historical appreciation rates averaging 10-15% annually, and lower correlation with traditional financial markets, providing portfolio diversification. Hedge funds, by contrast, deliver actively managed strategies with potential higher liquidity and risk-adjusted returns but often involve higher fees and variable performance linked to market volatility. Optimal investment choice depends on risk tolerance, investment horizon, liquidity needs, and diversification goals.
Connection
Wine investing offers an alternative asset class that hedge funds sometimes include for portfolio diversification and risk management. Both wine investing and hedge funds aim to capitalize on market inefficiencies and long-term value appreciation, with wine's historical scarcity complementing hedge funds' dynamic strategies. Hedge funds leverage wine's relatively low correlation with traditional financial markets to enhance returns and reduce overall portfolio volatility.
Key Terms
Leverage
Hedge funds often employ leverage to amplify returns, using borrowed capital to increase exposure to various asset classes and hedge risks effectively. Wine investing, in contrast, typically involves little to no leverage, relying instead on the intrinsic value appreciation of rare and collectible wines over time. Explore the nuances of leverage in both hedge fund strategies and wine asset management to make informed investment decisions.
Liquidity
Hedge funds offer high liquidity with the ability to quickly buy or sell assets, while wine investing tends to have lower liquidity due to the niche market and longer holding periods required for optimal value appreciation. The wine market's limited daily transactions and dependency on auctions or private sales result in slower asset turnover compared to the rapid trading capabilities seen in hedge funds. Explore deeper insights on how liquidity impacts these investment strategies and their suitability for different portfolios.
Asset Valuation
Hedge funds rely on complex financial models and market data to assess asset valuation, focusing on liquidity, volatility, and intrinsic value to maximize returns. Wine investing values rare vintages and provenance, with prices driven by scarcity, auction results, and expert appraisals rather than traditional financial metrics. Discover how these distinct approaches shape investment strategies and risk management in asset valuation.
Source and External Links
Hedge Funds: Overview, Recruitment, Careers & Salaries - Provides an overview of hedge funds, including their definition, strategies, and career opportunities in the industry.
Hedge Funds | Investor.gov - Explains the basic concept of hedge funds, their investment strategies, and the regulatory environment surrounding them.
Hedge Funds - Institutional - BlackRock - Details BlackRock's approach to hedge funds, including their investment strategies and management solutions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com