Investment in the space economy targets innovative sectors like satellite technology, space exploration, and orbital infrastructure, driving exponential growth and long-term returns. Renewable resources investment focuses on sustainable energy solutions such as solar, wind, and bioenergy, addressing climate change and reducing carbon emissions. Explore the distinct advantages and future potential of both investment avenues to make informed financial decisions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between space economy investment and renewable resources investment is crucial for optimizing portfolio diversification and risk management. Space economy investments focus on satellite technologies, space exploration, and infrastructure, driving innovation in communication and defense. Renewable resources investments prioritize sustainable energy sources like solar, wind, and bioenergy, promoting environmental resilience and reducing carbon footprints. Differentiating these sectors enables targeted capital allocation aligned with distinct growth potentials and regulatory frameworks.
Comparison Table
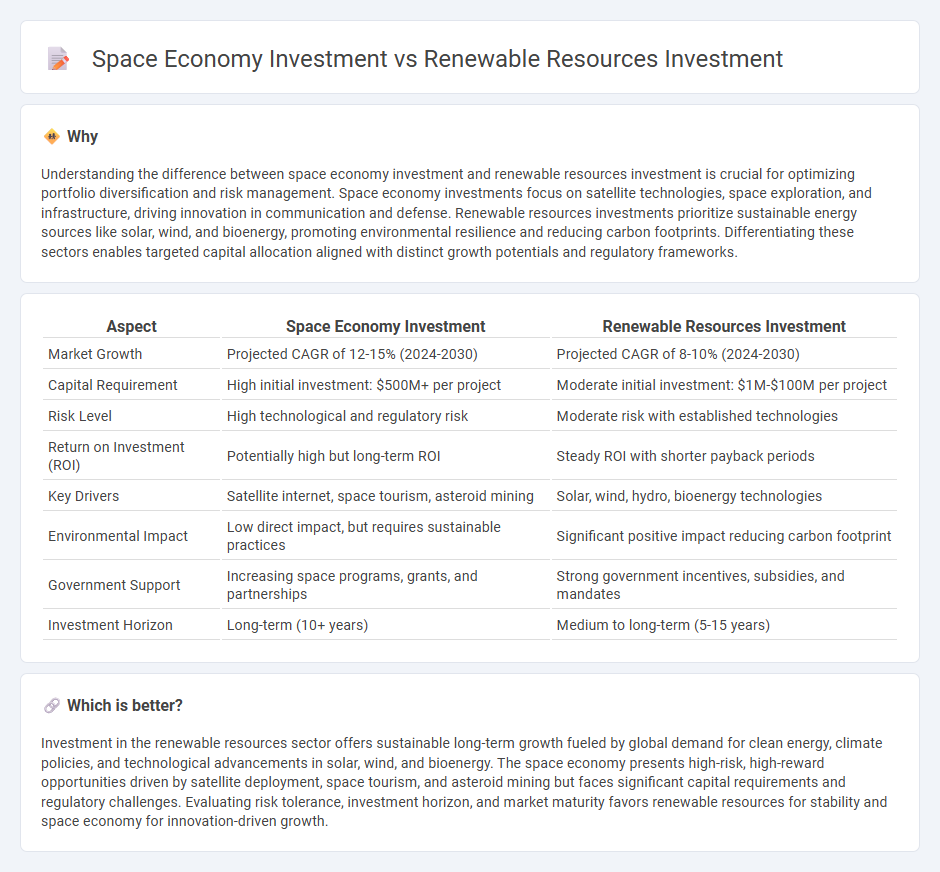
| Aspect | Space Economy Investment | Renewable Resources Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Market Growth | Projected CAGR of 12-15% (2024-2030) | Projected CAGR of 8-10% (2024-2030) |
| Capital Requirement | High initial investment: $500M+ per project | Moderate initial investment: $1M-$100M per project |
| Risk Level | High technological and regulatory risk | Moderate risk with established technologies |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Potentially high but long-term ROI | Steady ROI with shorter payback periods |
| Key Drivers | Satellite internet, space tourism, asteroid mining | Solar, wind, hydro, bioenergy technologies |
| Environmental Impact | Low direct impact, but requires sustainable practices | Significant positive impact reducing carbon footprint |
| Government Support | Increasing space programs, grants, and partnerships | Strong government incentives, subsidies, and mandates |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term (10+ years) | Medium to long-term (5-15 years) |
Which is better?
Investment in the renewable resources sector offers sustainable long-term growth fueled by global demand for clean energy, climate policies, and technological advancements in solar, wind, and bioenergy. The space economy presents high-risk, high-reward opportunities driven by satellite deployment, space tourism, and asteroid mining but faces significant capital requirements and regulatory challenges. Evaluating risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market maturity favors renewable resources for stability and space economy for innovation-driven growth.
Connection
Investment in the space economy drives advancements in technologies such as solar power satellites, which harness renewable energy in innovative ways. Capital allocated to renewable resources supports the development of sustainable materials and energy solutions critical for long-duration space missions. The synergy between these investments accelerates progress toward clean energy adoption both on Earth and beyond.
Key Terms
**Renewable resources investment:**
Renewable resources investment encompasses funding in solar, wind, hydro, and bioenergy projects aimed at reducing carbon emissions and enhancing sustainable energy security globally. This sector attracted over $500 billion in global investments in 2023, driven by government incentives and technological advancements in energy storage and grid integration. Explore more about the impact and growth potential of renewable energy investments.
Green Bonds
Green Bonds channel significant capital towards renewable resources investment, driving projects in solar, wind, and bioenergy sectors that reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable development. In contrast, space economy investment, though growing rapidly, often centers on satellite technology and exploration with longer-term environmental impacts. Explore how Green Bonds shape the future of clean energy finance and their comparative role in funding the emerging space economy.
Feed-in Tariffs
Investment in renewable resources, particularly through Feed-in Tariffs (FiTs), guarantees fixed payments for producers of renewable electricity, fostering market stability and accelerating clean energy adoption. In contrast, space economy investment emphasizes innovative technologies and infrastructure with high capital risk but potential for exponential growth in sectors like satellite communications and space exploration. Discover more about the comparative advantages and economic impacts of these investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Overview and key findings - World Energy Investment 2024 - IEA - Global energy investment is set to exceed USD 3 trillion in 2024, with USD 2 trillion focused on clean energy technologies and infrastructure, showing strong growth in renewable energy investment worldwide.
Renewable Energy Investments | Definition, Types, Pros & Cons - Renewable resource investments include solar (PV and CSP), wind (onshore and offshore), and hydropower projects, each with varying costs, benefits, and investment horizons attracting diverse investor profiles.
Renewable energy investing | Robeco USA - Investment in renewables can be done by acquiring equities or bonds in utility companies or equipment suppliers, covering sources such as hydroelectric, wind, solar, biomass, and geothermal energy, with emerging interest in technologies like tidal power and green hydrogen.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com