The secondaries market offers investors liquidity by allowing the purchase and sale of pre-existing private equity and hedge fund stakes, providing access to mature assets with potentially lower risk compared to primary investments. Hedge funds actively manage diversified portfolios using strategies like long-short equity, event-driven, and global macro to generate alpha and hedge against market volatility. Explore further to understand the unique benefits and strategic roles of secondaries markets and hedge funds in a diversified investment portfolio.
Why it is important
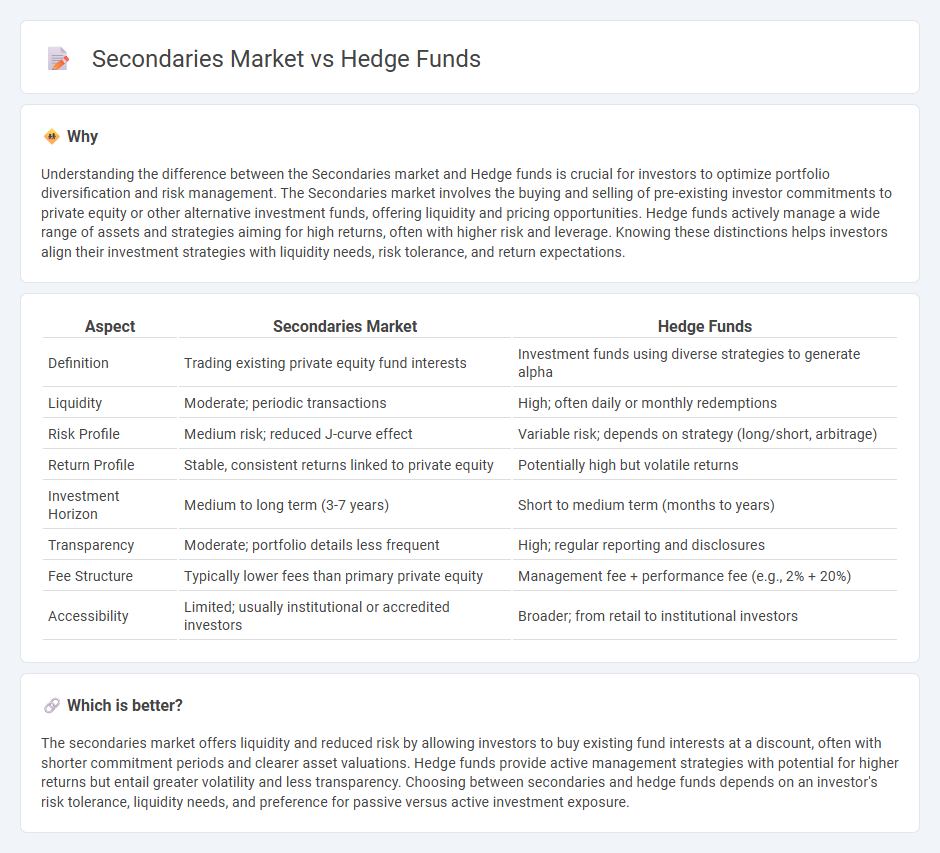
Understanding the difference between the Secondaries market and Hedge funds is crucial for investors to optimize portfolio diversification and risk management. The Secondaries market involves the buying and selling of pre-existing investor commitments to private equity or other alternative investment funds, offering liquidity and pricing opportunities. Hedge funds actively manage a wide range of assets and strategies aiming for high returns, often with higher risk and leverage. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align their investment strategies with liquidity needs, risk tolerance, and return expectations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Secondaries Market | Hedge Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading existing private equity fund interests | Investment funds using diverse strategies to generate alpha |
| Liquidity | Moderate; periodic transactions | High; often daily or monthly redemptions |
| Risk Profile | Medium risk; reduced J-curve effect | Variable risk; depends on strategy (long/short, arbitrage) |
| Return Profile | Stable, consistent returns linked to private equity | Potentially high but volatile returns |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long term (3-7 years) | Short to medium term (months to years) |
| Transparency | Moderate; portfolio details less frequent | High; regular reporting and disclosures |
| Fee Structure | Typically lower fees than primary private equity | Management fee + performance fee (e.g., 2% + 20%) |
| Accessibility | Limited; usually institutional or accredited investors | Broader; from retail to institutional investors |
Which is better?
The secondaries market offers liquidity and reduced risk by allowing investors to buy existing fund interests at a discount, often with shorter commitment periods and clearer asset valuations. Hedge funds provide active management strategies with potential for higher returns but entail greater volatility and less transparency. Choosing between secondaries and hedge funds depends on an investor's risk tolerance, liquidity needs, and preference for passive versus active investment exposure.
Connection
The secondaries market enables investors to buy and sell pre-existing stakes in hedge funds, providing liquidity and flexibility that are typically limited in primary hedge fund investments. Hedge funds benefit from the secondaries market by attracting a broader range of investors who seek opportunities to enter or exit positions without waiting for traditional lock-up periods. This dynamic enhances price discovery and portfolio management efficiency within the hedge fund ecosystem.
Key Terms
Leverage
Hedge funds often utilize leverage to amplify returns, employing borrowed capital to increase their market exposure and enhance profit potential. In contrast, the secondaries market, which involves the buying and selling of pre-existing investor commitments in private equity funds, typically features lower leverage levels due to the defensive nature of these assets and the aim to mitigate risk. Explore more about how leverage strategies differ fundamentally between hedge funds and the secondaries market.
Liquidity
Hedge funds typically offer lower liquidity due to lock-up periods and redemption restrictions, while the secondaries market provides greater flexibility by enabling investors to buy and sell existing fund positions. The secondaries market enhances portfolio liquidity by allowing investors to access capital before fund maturity, often at negotiated discounts or premiums. Explore more about liquidity dynamics in hedge funds and secondaries to optimize investment strategies.
Valuation
Hedge funds often face complex valuation challenges due to their diverse and illiquid asset portfolios, whereas the secondaries market provides a more transparent pricing mechanism through the trading of pre-existing private equity interests. Valuations in the secondaries market benefit from observable transaction prices, enabling more accurate assessment of underlying asset worth compared to the mark-to-model approaches common in hedge fund valuations. Explore deeper insights into how valuation methodologies differ between hedge funds and the secondaries market to enhance investment decision-making.
Source and External Links
Hedge Funds: Overview, Recruitment, Careers & Salaries - This webpage provides an overview of hedge funds, including their definition, strategies, recruitment, careers, and salaries.
Hedge Funds - This Investor.gov page explains what hedge funds are, how they operate, and considerations for potential investors.
Hedge Fund - This Wikipedia article provides detailed information on the definition, history, strategies, and structure of hedge funds.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com