Regenerative agriculture investing focuses on funding farming practices that restore soil health and increase biodiversity while generating economic returns, contrasting with conservation finance which aims to protect natural resources through sustainable projects and ecosystem preservation. Both approaches leverage financial tools to address environmental challenges but differ in their impact mechanisms and targeted outcomes. Explore how these investment strategies uniquely contribute to sustainable development and environmental resilience.
Why it is important
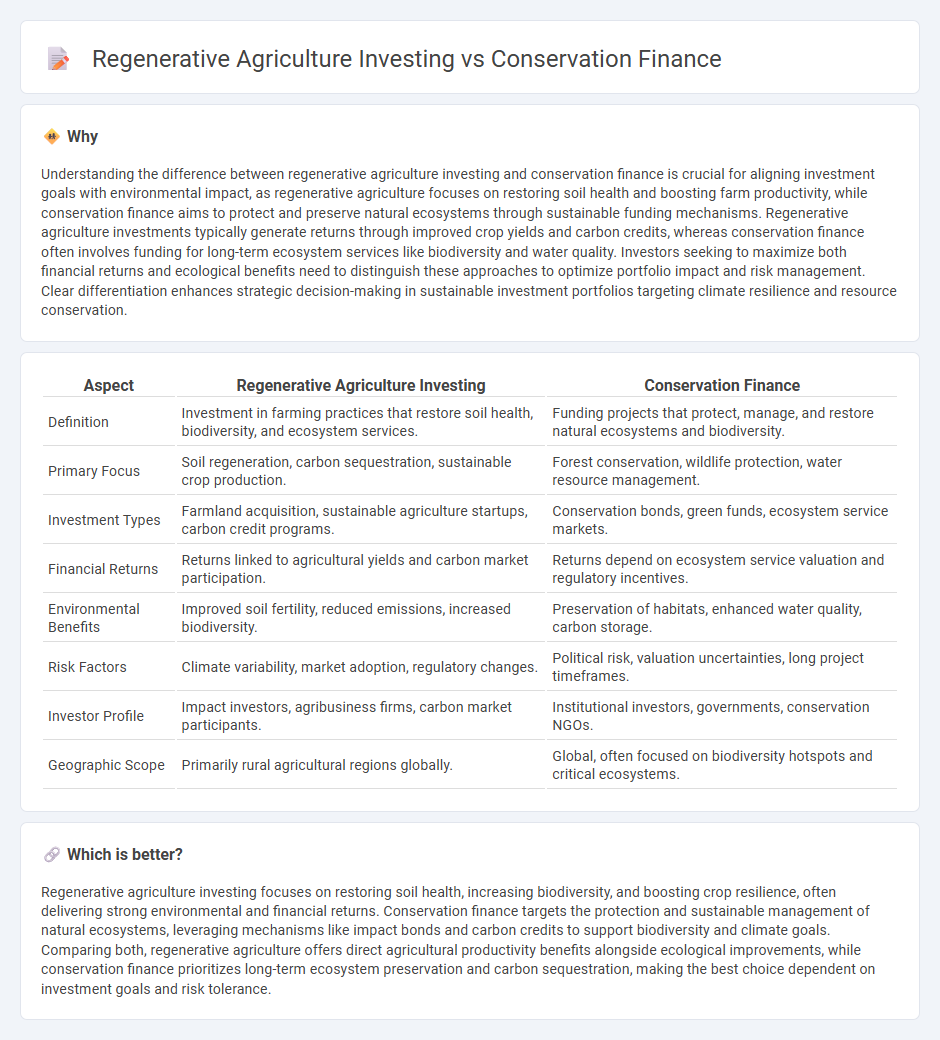
Understanding the difference between regenerative agriculture investing and conservation finance is crucial for aligning investment goals with environmental impact, as regenerative agriculture focuses on restoring soil health and boosting farm productivity, while conservation finance aims to protect and preserve natural ecosystems through sustainable funding mechanisms. Regenerative agriculture investments typically generate returns through improved crop yields and carbon credits, whereas conservation finance often involves funding for long-term ecosystem services like biodiversity and water quality. Investors seeking to maximize both financial returns and ecological benefits need to distinguish these approaches to optimize portfolio impact and risk management. Clear differentiation enhances strategic decision-making in sustainable investment portfolios targeting climate resilience and resource conservation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Regenerative Agriculture Investing | Conservation Finance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in farming practices that restore soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. | Funding projects that protect, manage, and restore natural ecosystems and biodiversity. |
| Primary Focus | Soil regeneration, carbon sequestration, sustainable crop production. | Forest conservation, wildlife protection, water resource management. |
| Investment Types | Farmland acquisition, sustainable agriculture startups, carbon credit programs. | Conservation bonds, green funds, ecosystem service markets. |
| Financial Returns | Returns linked to agricultural yields and carbon market participation. | Returns depend on ecosystem service valuation and regulatory incentives. |
| Environmental Benefits | Improved soil fertility, reduced emissions, increased biodiversity. | Preservation of habitats, enhanced water quality, carbon storage. |
| Risk Factors | Climate variability, market adoption, regulatory changes. | Political risk, valuation uncertainties, long project timeframes. |
| Investor Profile | Impact investors, agribusiness firms, carbon market participants. | Institutional investors, governments, conservation NGOs. |
| Geographic Scope | Primarily rural agricultural regions globally. | Global, often focused on biodiversity hotspots and critical ecosystems. |
Which is better?
Regenerative agriculture investing focuses on restoring soil health, increasing biodiversity, and boosting crop resilience, often delivering strong environmental and financial returns. Conservation finance targets the protection and sustainable management of natural ecosystems, leveraging mechanisms like impact bonds and carbon credits to support biodiversity and climate goals. Comparing both, regenerative agriculture offers direct agricultural productivity benefits alongside ecological improvements, while conservation finance prioritizes long-term ecosystem preservation and carbon sequestration, making the best choice dependent on investment goals and risk tolerance.
Connection
Regenerative agriculture investing and conservation finance intersect by channeling capital into projects that restore ecosystems and enhance biodiversity while delivering financial returns. Both approaches prioritize sustainable land management practices, reducing carbon footprints and promoting soil health, thereby aligning environmental impact with investment goals. Their synergy amplifies funding opportunities for innovative agricultural solutions that support climate resilience and long-term ecological balance.
Key Terms
Conservation Finance:
Conservation finance mobilizes private and public capital to fund projects that protect biodiversity, restore ecosystems, and mitigate climate change impacts, often through innovative financial instruments such as green bonds, impact investing, and payment for ecosystem services. It targets scalable, biodiversity-positive outcomes by aligning investor returns with environmental sustainability goals, promoting the preservation of natural habitats and carbon sequestration. Explore how conservation finance is transforming environmental impact through market-driven strategies for deeper insights.
Ecosystem Services
Conservation finance prioritizes funding projects that preserve and protect natural ecosystems, emphasizing carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and water quality improvements as key ecosystem services. Regenerative agriculture investing focuses on enhancing soil health, increasing carbon capture, and restoring biodiversity through sustainable farming practices that improve ecosystem services and long-term productivity. Explore how both investment strategies contribute uniquely to ecosystem service enhancement and environmental sustainability.
Green Bonds
Green Bonds have emerged as a pivotal financing tool in both conservation finance and regenerative agriculture investing, channeling capital toward sustainable projects that restore ecosystems and promote biodiversity. The distinct advantage of Green Bonds lies in their ability to fund large-scale initiatives that deliver measurable environmental impact while providing financial returns. Explore how Green Bonds are transforming investment strategies and accelerating sustainable development goals.
Source and External Links
Conservation Finance 101 - Conservation finance refers to the diverse tools and strategies for raising and managing funds--such as government grants, charitable donations, and for-profit investments--to support land conservation, restoration, and sustainable resource management.
Conservation Finance Program | US Forest Service - USDA - The USDA Forest Service's Conservation Finance Program develops innovative models to attract private capital, accelerating conservation projects through investment opportunities that align environmental, social, and financial outcomes.
Conservation Finance | Initiatives - WWF - WWF partners with governments, private industries, and communities to create long-term financing solutions--such as debt-for-nature swaps and conservation trust funds--that ensure sustainable funding for global biodiversity conservation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com