Carbon credit trading allows companies to buy and sell allowances to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide, incentivizing emission reductions through market mechanisms. ESG investing evaluates companies based on environmental, social, and governance criteria, promoting sustainable and ethical business practices. Explore how carbon credit trading and ESG investing shape the future of responsible investment strategies.
Why it is important
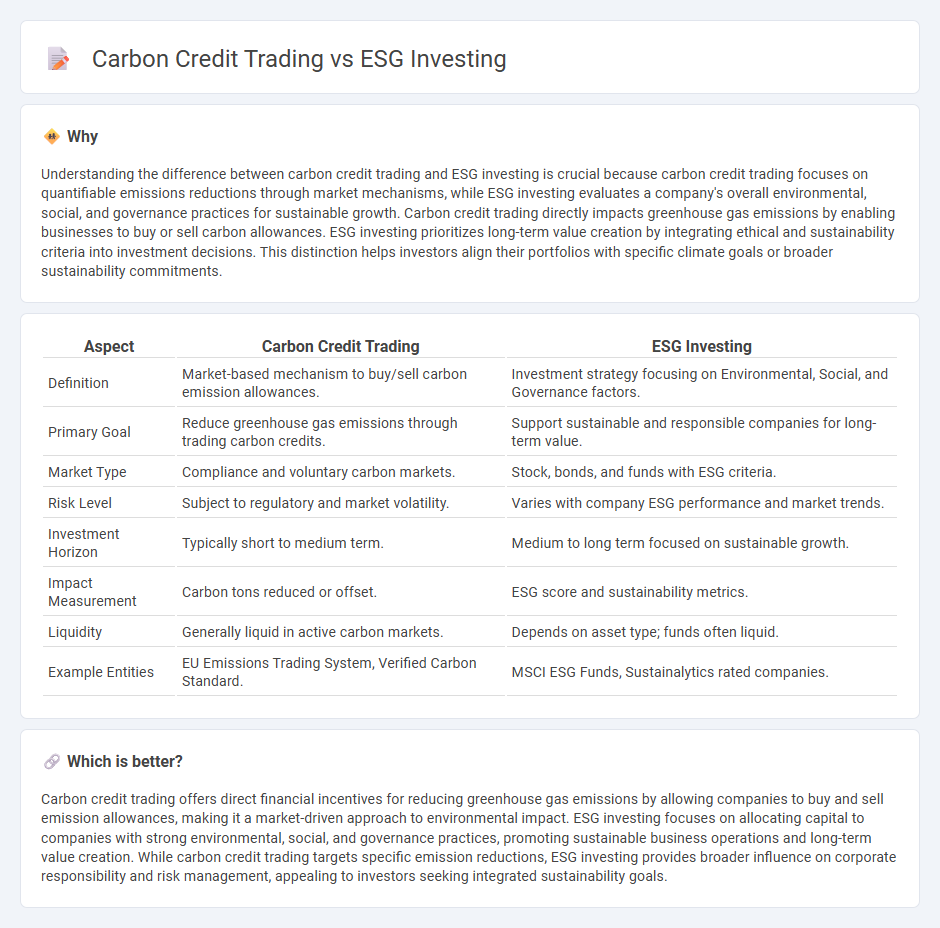
Understanding the difference between carbon credit trading and ESG investing is crucial because carbon credit trading focuses on quantifiable emissions reductions through market mechanisms, while ESG investing evaluates a company's overall environmental, social, and governance practices for sustainable growth. Carbon credit trading directly impacts greenhouse gas emissions by enabling businesses to buy or sell carbon allowances. ESG investing prioritizes long-term value creation by integrating ethical and sustainability criteria into investment decisions. This distinction helps investors align their portfolios with specific climate goals or broader sustainability commitments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Credit Trading | ESG Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market-based mechanism to buy/sell carbon emission allowances. | Investment strategy focusing on Environmental, Social, and Governance factors. |
| Primary Goal | Reduce greenhouse gas emissions through trading carbon credits. | Support sustainable and responsible companies for long-term value. |
| Market Type | Compliance and voluntary carbon markets. | Stock, bonds, and funds with ESG criteria. |
| Risk Level | Subject to regulatory and market volatility. | Varies with company ESG performance and market trends. |
| Investment Horizon | Typically short to medium term. | Medium to long term focused on sustainable growth. |
| Impact Measurement | Carbon tons reduced or offset. | ESG score and sustainability metrics. |
| Liquidity | Generally liquid in active carbon markets. | Depends on asset type; funds often liquid. |
| Example Entities | EU Emissions Trading System, Verified Carbon Standard. | MSCI ESG Funds, Sustainalytics rated companies. |
Which is better?
Carbon credit trading offers direct financial incentives for reducing greenhouse gas emissions by allowing companies to buy and sell emission allowances, making it a market-driven approach to environmental impact. ESG investing focuses on allocating capital to companies with strong environmental, social, and governance practices, promoting sustainable business operations and long-term value creation. While carbon credit trading targets specific emission reductions, ESG investing provides broader influence on corporate responsibility and risk management, appealing to investors seeking integrated sustainability goals.
Connection
Carbon credit trading incentivizes companies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by allowing the buying and selling of emission allowances, directly supporting Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investing goals focused on sustainability. ESG investing evaluates corporate practices including environmental impact, where carbon credit participation signals strong climate responsibility and risk management. Integrating carbon credit trading into ESG portfolios enhances investment strategies by aligning financial returns with measurable environmental benefits.
Key Terms
**ESG Investing:**
ESG investing integrates environmental, social, and governance criteria to evaluate companies' long-term sustainability and ethical impact, focusing on responsible investment strategies that align with stakeholders' values. This approach targets companies with strong governance, reduced carbon footprints, social responsibility, and transparent operations, supporting systemic change towards sustainability. Explore how ESG investing drives value creation and mitigates risks across sectors by learning more about its principles and market trends.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Criteria
ESG investing integrates Environmental, Social, and Governance criteria to evaluate companies' sustainability and ethical impact, guiding investors toward responsible financial decisions that support long-term value creation. Carbon credit trading specifically targets environmental goals by allowing companies to buy and sell permits that limit their carbon emissions, promoting reduction in greenhouse gases. Explore the nuances of ESG investing and carbon credit trading to understand their distinct roles in sustainable finance.
Sustainability Reporting
ESG investing integrates environmental, social, and governance criteria to evaluate a company's long-term sustainability and ethical impact, influencing capital allocation decisions. Carbon credit trading enables organizations to offset greenhouse gas emissions by buying and selling permits, directly targeting carbon reduction goals. Explore more to understand how sustainability reporting bridges ESG investing and carbon credit trading to drive transparent environmental accountability.
Source and External Links
Embracing Sustainable Investment Practices with ESG Investing - ESG investing is an investment strategy that considers a company's environmental, social, and governance risks and has grown to represent about $4 trillion of assets globally, offering better long-term growth and lower risks.
What is ESG Investing? - ESG investing focuses on environmental, social, and governance factors and is rooted in the tradition of ethical investing, gaining mainstream attention since the UN Principles for Responsible Investment in 2006.
What is ESG investing? - Deutsche Bank Wealth Management - ESG investing integrates environmental, social, and governance criteria with financial factors and had $35.3 trillion of assets invested under ESG principles by 2020 across major global markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com