Carbon offset investing focuses on funding projects that reduce or capture greenhouse gas emissions, directly mitigating environmental impact. ESG funds invest in companies based on environmental, social, and governance criteria, promoting sustainable business practices across multiple dimensions. Explore the differences and benefits of each approach to make informed investment decisions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between carbon offset investing and ESG funds is crucial for aligning investments with specific sustainability goals and risk tolerance. Carbon offset investing targets direct emission reductions by funding projects that compensate for carbon footprints, while ESG funds integrate environmental, social, and governance criteria into broader financial analysis. This knowledge empowers investors to choose strategies that either directly mitigate climate impact or promote comprehensive corporate responsibility. Accurate differentiation ensures optimized portfolio impact and supports informed decision-making in responsible investing.
Comparison Table
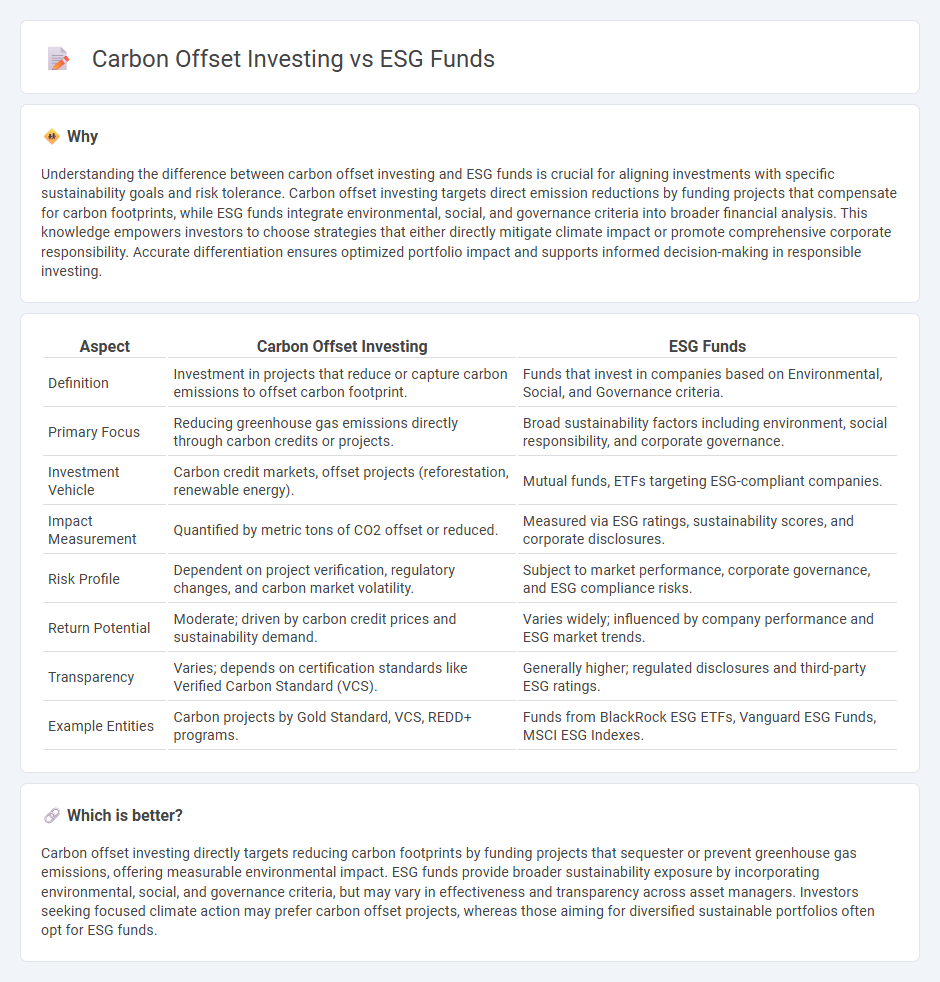
| Aspect | Carbon Offset Investing | ESG Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in projects that reduce or capture carbon emissions to offset carbon footprint. | Funds that invest in companies based on Environmental, Social, and Governance criteria. |
| Primary Focus | Reducing greenhouse gas emissions directly through carbon credits or projects. | Broad sustainability factors including environment, social responsibility, and corporate governance. |
| Investment Vehicle | Carbon credit markets, offset projects (reforestation, renewable energy). | Mutual funds, ETFs targeting ESG-compliant companies. |
| Impact Measurement | Quantified by metric tons of CO2 offset or reduced. | Measured via ESG ratings, sustainability scores, and corporate disclosures. |
| Risk Profile | Dependent on project verification, regulatory changes, and carbon market volatility. | Subject to market performance, corporate governance, and ESG compliance risks. |
| Return Potential | Moderate; driven by carbon credit prices and sustainability demand. | Varies widely; influenced by company performance and ESG market trends. |
| Transparency | Varies; depends on certification standards like Verified Carbon Standard (VCS). | Generally higher; regulated disclosures and third-party ESG ratings. |
| Example Entities | Carbon projects by Gold Standard, VCS, REDD+ programs. | Funds from BlackRock ESG ETFs, Vanguard ESG Funds, MSCI ESG Indexes. |
Which is better?
Carbon offset investing directly targets reducing carbon footprints by funding projects that sequester or prevent greenhouse gas emissions, offering measurable environmental impact. ESG funds provide broader sustainability exposure by incorporating environmental, social, and governance criteria, but may vary in effectiveness and transparency across asset managers. Investors seeking focused climate action may prefer carbon offset projects, whereas those aiming for diversified sustainable portfolios often opt for ESG funds.
Connection
Carbon offset investing and ESG funds are intrinsically linked through their shared goal of promoting sustainable and responsible investment practices. ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) funds prioritize companies with strong environmental performance, often including investments in carbon offset projects to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. By integrating carbon offset strategies, ESG funds enhance their impact on climate change while appealing to socially conscious investors seeking to align portfolios with global sustainability goals.
Key Terms
Sustainability Criteria
ESG funds prioritize environmental, social, and governance criteria by investing in companies with sustainable practices, ensuring long-term risk management and ethical impact. Carbon offset investing targets the reduction of carbon footprints by funding projects that capture or prevent carbon emissions, directly addressing climate change mitigation. Explore more to understand which strategy aligns best with your sustainability goals.
Carbon Credits
ESG funds integrate environmental, social, and governance criteria into diversified portfolios aiming for sustainable impact, while carbon offset investing specifically targets reducing emissions through carbon credits that finance projects like reforestation and renewable energy. Carbon credits represent a quantifiable reduction of one metric ton of CO2 or equivalent greenhouse gases, providing a direct mechanism for companies and individuals to neutralize their carbon footprint. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how carbon credits can complement ESG strategies and enhance your sustainable investment approach.
Impact Measurement
ESG funds integrate environmental, social, and governance criteria to evaluate company performance, emphasizing sustainable business practices and risk management. Carbon offset investing specifically targets the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by funding projects such as reforestation or renewable energy initiatives, with measurable climate impact outcomes. Explore further to understand the distinct methodologies and effectiveness of impact measurement in each investment strategy.
Source and External Links
7 Best-Performing ESG ETFs and 7 Cheapest ... - ESG funds invest in companies focused on environmental, social, and governance principles, offering diversified risk by investing in groups of stocks through ETFs, with some top-performing ESG ETFs achieving returns over 70% annually as of mid-2025.
Investing in ESG Funds: Reflect What Matters Most | Vanguard - Vanguard offers a lineup of ESG-indexed and actively managed funds and ETFs that cover U.S. and international markets, designed to align investments with personal values around sustainability while maintaining diversification and low costs.
ESG Fund Ratings - MSCI ESG Fund Ratings evaluate the environmental, social, and governance characteristics of a fund's holdings on a scale from AAA to CCC, helping investors assess and compare the sustainability profile and impact of mutual funds and ETFs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com