Private credit funds pool capital from multiple investors to provide debt financing, offering diversification and professional management. Direct lending involves non-bank lenders extending loans directly to companies, often yielding higher returns with potentially greater risk. Discover how these investment strategies compare and which aligns best with your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between private credit funds and direct lending is crucial for investors to accurately assess risk, liquidity, and return profiles. Private credit funds pool capital from multiple investors to diversify exposure across various loans, while direct lending involves a direct loan from a single lender to a borrower, offering more control but potentially higher risk. Knowing these differences helps in optimizing portfolio allocation according to individual investment goals and risk tolerance. In 2023, private credit assets under management reached over $1 trillion, highlighting the growing relevance of these investment vehicles.
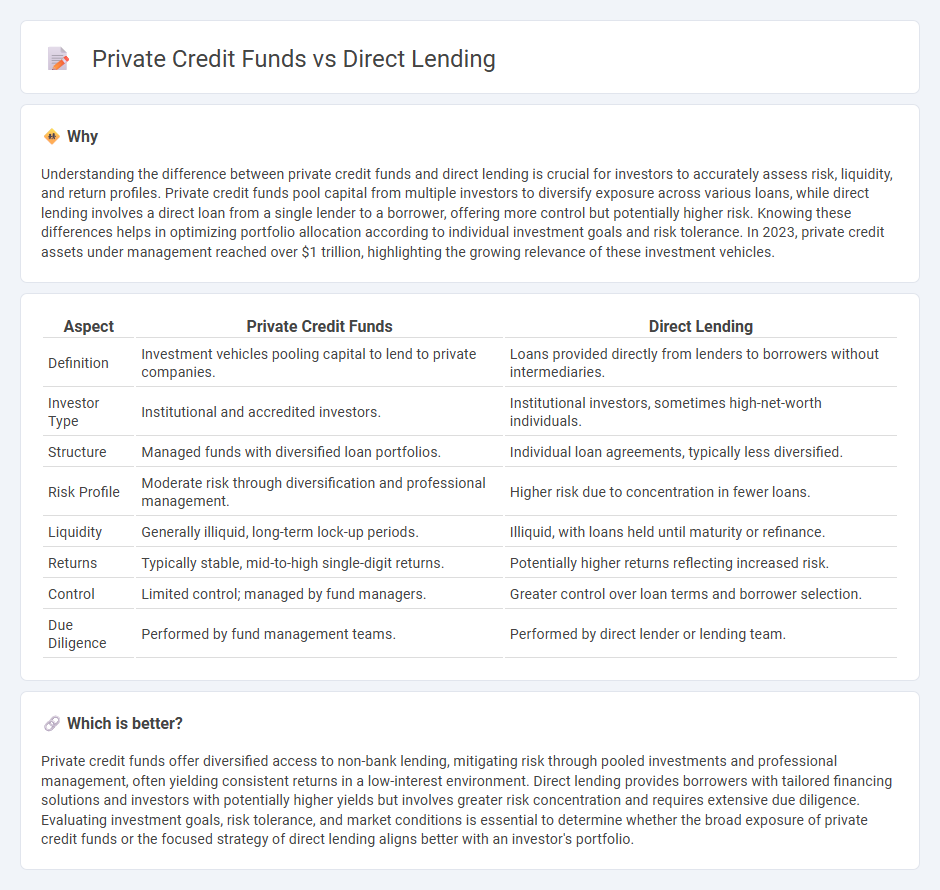
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Private Credit Funds | Direct Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment vehicles pooling capital to lend to private companies. | Loans provided directly from lenders to borrowers without intermediaries. |
| Investor Type | Institutional and accredited investors. | Institutional investors, sometimes high-net-worth individuals. |
| Structure | Managed funds with diversified loan portfolios. | Individual loan agreements, typically less diversified. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk through diversification and professional management. | Higher risk due to concentration in fewer loans. |
| Liquidity | Generally illiquid, long-term lock-up periods. | Illiquid, with loans held until maturity or refinance. |
| Returns | Typically stable, mid-to-high single-digit returns. | Potentially higher returns reflecting increased risk. |
| Control | Limited control; managed by fund managers. | Greater control over loan terms and borrower selection. |
| Due Diligence | Performed by fund management teams. | Performed by direct lender or lending team. |
Which is better?
Private credit funds offer diversified access to non-bank lending, mitigating risk through pooled investments and professional management, often yielding consistent returns in a low-interest environment. Direct lending provides borrowers with tailored financing solutions and investors with potentially higher yields but involves greater risk concentration and requires extensive due diligence. Evaluating investment goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions is essential to determine whether the broad exposure of private credit funds or the focused strategy of direct lending aligns better with an investor's portfolio.
Connection
Private credit funds specialize in providing capital through direct lending, bypassing traditional banks to offer tailored financing solutions for middle-market companies. These funds pool capital from institutional investors and deploy loans directly to borrowers, enabling faster access to funds with flexible terms. Direct lending serves as the primary mechanism through which private credit funds generate returns by earning interest and fees on these privately negotiated loans.
Key Terms
Origination
Direct lending involves non-bank lenders providing loans directly to borrowers, often small and medium-sized enterprises, bypassing traditional financial intermediaries. Private credit funds aggregate capital from institutional investors to offer tailored debt solutions, emphasizing diversified risk through multiple originations. Explore the nuances of origination strategies in both models to understand their distinct approaches and benefits.
Fund Structure
Direct lending typically involves a single lender providing loans directly to borrowers, resulting in a simpler fund structure with more control over loan terms and portfolio management. Private credit funds pool capital from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of loans, often structured as limited partnerships or closed-end funds with defined investment horizons and liquidity constraints. Explore the nuances of fund structures in direct lending and private credit funds to optimize investment strategies and risk management.
Risk Profile
Direct lending typically involves non-bank lenders providing loans directly to borrowers, often resulting in higher risk exposure due to less diversification and concentrated credit risk. Private credit funds, on the other hand, pool capital from multiple investors to diversify risk across various loans and sectors, offering a more balanced risk profile. Explore the nuances of risk management strategies in direct lending and private credit funds to understand their impact on your investment portfolio.
Source and External Links
Direct lending - Wikipedia - Direct lending is corporate debt provision where lenders other than banks make loans directly to smaller or mid-sized companies without intermediaries, often involving senior or unitranche debt and generating steady cash flows through quarterly interest payments.
Direct Lending Evolution: Driving Force of Private Credit Market - Direct lending is a private credit strategy providing illiquid loans to middle market companies outside the banking system, growing due to bank pullback and strong investor demand with loans often used for leveraged buyouts and refinancing.
direct lending: benefits, risks and opportunities (Oaktree Capital) - Direct lenders, typically non-bank creditors, make loans directly to middle-market firms for purposes like leveraged buyouts and acquisitions, including debt forms from first lien to mezzanine and unitranche, addressing a large market vital to the economy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com