Carbon credits trading involves buying and selling permits that allow companies to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide, providing a market-driven mechanism to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Responsible investing focuses on incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions to support sustainable and ethical business practices. Explore how both strategies impact financial performance and environmental sustainability to make informed investment choices.
Why it is important
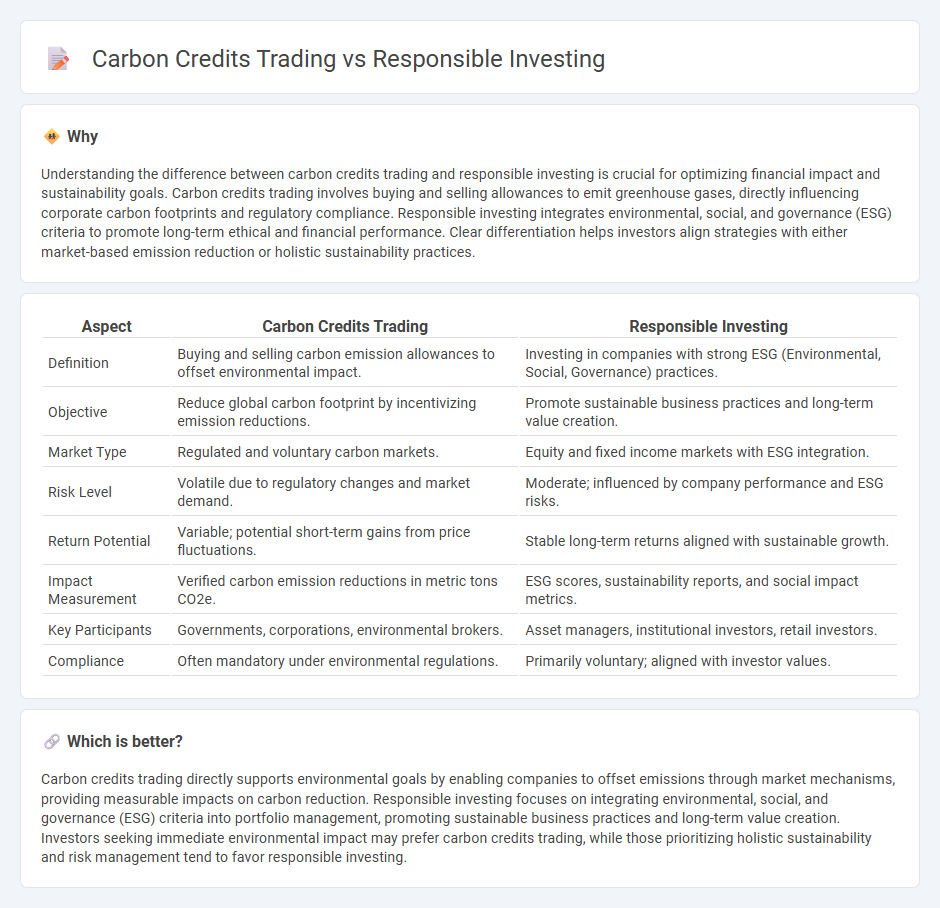
Understanding the difference between carbon credits trading and responsible investing is crucial for optimizing financial impact and sustainability goals. Carbon credits trading involves buying and selling allowances to emit greenhouse gases, directly influencing corporate carbon footprints and regulatory compliance. Responsible investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term ethical and financial performance. Clear differentiation helps investors align strategies with either market-based emission reduction or holistic sustainability practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Credits Trading | Responsible Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying and selling carbon emission allowances to offset environmental impact. | Investing in companies with strong ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) practices. |
| Objective | Reduce global carbon footprint by incentivizing emission reductions. | Promote sustainable business practices and long-term value creation. |
| Market Type | Regulated and voluntary carbon markets. | Equity and fixed income markets with ESG integration. |
| Risk Level | Volatile due to regulatory changes and market demand. | Moderate; influenced by company performance and ESG risks. |
| Return Potential | Variable; potential short-term gains from price fluctuations. | Stable long-term returns aligned with sustainable growth. |
| Impact Measurement | Verified carbon emission reductions in metric tons CO2e. | ESG scores, sustainability reports, and social impact metrics. |
| Key Participants | Governments, corporations, environmental brokers. | Asset managers, institutional investors, retail investors. |
| Compliance | Often mandatory under environmental regulations. | Primarily voluntary; aligned with investor values. |
Which is better?
Carbon credits trading directly supports environmental goals by enabling companies to offset emissions through market mechanisms, providing measurable impacts on carbon reduction. Responsible investing focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into portfolio management, promoting sustainable business practices and long-term value creation. Investors seeking immediate environmental impact may prefer carbon credits trading, while those prioritizing holistic sustainability and risk management tend to favor responsible investing.
Connection
Carbon credits trading incentivizes companies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by assigning economic value to carbon reductions, aligning with the principles of responsible investing that prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. Responsible investors integrate carbon credit markets into portfolio strategies to support sustainable business practices and mitigate climate risks, enhancing long-term financial performance. This synergy drives capital towards low-carbon technologies and fosters corporate accountability in addressing climate change.
Key Terms
Responsible Investing:
Responsible investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to guide investment decisions that promote sustainable business practices and long-term value creation. This approach reduces risks associated with climate change and social inequality by supporting companies with strong ethical standards and transparent reporting. Discover how responsible investing can drive positive impact while delivering competitive financial returns.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Responsible investing integrates Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria to evaluate companies for sustainable long-term value, emphasizing ethical practices, social responsibility, and environmental stewardship. Carbon credits trading, a market-based mechanism, allows businesses to buy and sell allowances to emit a certain amount of greenhouse gases, supporting carbon reduction goals but often lacking the comprehensive ESG oversight of responsible investing. Explore deeper insights into how ESG-focused strategies shape sustainable finance and impact global environmental policies.
Impact Investing
Responsible investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate sustainable, long-term impact alongside financial returns, whereas carbon credits trading primarily targets emission reductions through market-based mechanisms. Impact investing emphasizes measurable social and environmental outcomes by directing capital to companies and projects actively contributing to positive change. Explore more to understand how these strategies drive global sustainability goals.
Source and External Links
Responsible investing | TIAA - Responsible investing integrates environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors with traditional financial criteria to aim for long-term resilient returns while addressing climate impact, diversity, governance, and stewardship for sustainable value and risk mitigation.
What is responsible investment? - Responsible investment acknowledges environmental, social, and governance factors as crucial for generating long-term sustainable returns by combining financial and non-financial value creation and properly pricing social and environmental risks.
Socially responsible investing - Wikipedia - Socially responsible investing (SRI) seeks to align financial returns with ethical, social, and environmental goals using practices such as screening companies for ESG risks, impact investing, shareholder advocacy, and community investing for sustainable and ethical outcomes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com